(六) 区块链数据结构 – 密钥对(公钥和私钥)
密钥是构建比特币信任网络的核心要素。密钥通常包括私钥和公钥两部分。其中私钥用于生成签名、公钥用于生成地址。
密钥生成曲线
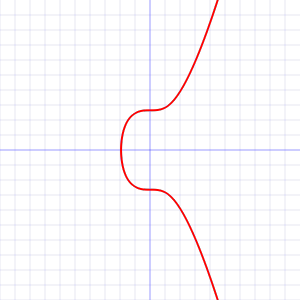
比特币的密钥采用椭圆曲线算法 SECP256k1来生成。SECP256K1曲线的大致形状如下:
该曲线的数学表达是为:y^2 \ \% \ p=(x^3+7) \ \%\ py2 % p=(x3+7) % p,其中
p=2^{256} - 2^{32} - 2^9 - 2^8 - 2^7 - 2^6 - 2^4 - 1p=2256−232−29−28−27−26−24−1
在生成秘钥时,回先选取一个基点G。然后生成一个256位的随机数k,该随机数即为私钥。然后通过椭圆随机曲线乘法,得出曲线上的一个点K,K即为公钥。其中K=k*GK=k∗G,注意该公式,以目前的算力几乎是不可逆的。因此可以通过私钥计算公钥,但是目前无法通过公钥反推出私钥。具体的秘钥生成过程,参见[1] 椭圆曲线算法
因为公钥为椭圆曲线的上的点,因此可以用其坐标
公钥的数据格式如下:
其中标志位如果为04,代表公钥采用未压缩的格式存储,如果标志位为02或03,则代表公钥采用压缩格式存储,02代表y的为正数,03代表y为负数。
核心代码
核心变量定义
//比特币使用的secp256k1椭圆曲线参数
private static final X9ECParameters CURVE_PARAMS = CustomNamedCurves.getByName("secp256k1");
/** The parameters of the secp256k1 curve that Bitcoin uses. */
public static final ECDomainParameters CURVE;
/**
* Equal to CURVE.getN().shiftRight(1), used for canonicalising the S value of a signature. If you aren't
* sure what this is about, you can ignore it.
* 等于曲线最大值域右移一位,作为签名S值的基数
*/
public static final BigInteger HALF_CURVE_ORDER;
private static final SecureRandom secureRandom;
static {
// Init proper random number generator, as some old Android installations have bugs that make it unsecure.
if (Utils.isAndroidRuntime())
new LinuxSecureRandom();
// Tell Bouncy Castle to precompute data that's needed during secp256k1 calculations. Increasing the width
// number makes calculations faster, but at a cost of extra memory usage and with decreasing returns. 12 was
// picked after consulting with the BC team.
FixedPointUtil.precompute(CURVE_PARAMS.getG(), 12);
//设置密钥生成使用的椭圆曲线参数
CURVE = new ECDomainParameters(CURVE_PARAMS.getCurve(), CURVE_PARAMS.getG(), CURVE_PARAMS.getN(),
CURVE_PARAMS.getH());
//设置签名S值生成的基数标准
HALF_CURVE_ORDER = CURVE_PARAMS.getN().shiftRight(1);
//实例化随机数生成对象
secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
}
// The two parts of the key. If "priv" is set, "pub" can always be calculated. If "pub" is set but not "priv", we
// can only verify signatures not make them.
// 密钥的两部分:公钥和私钥。通过私钥可以计算公钥,通过公钥无法反退出私钥。
// 当只设置了公钥而未设置私钥时,该密钥智能用于签名验证,不能用于签名生成
protected final BigInteger priv; // A field element.
protected final LazyECPoint pub;
生成秘钥对象
/**
* Generates an entirely new keypair with the given {@link SecureRandom} object. Point compression is used so the
* resulting public key will be 33 bytes (32 for the co-ordinate and 1 byte to represent the y bit).
* 通过提供的随机数生成器,生成完整的密钥对。
* 生成的公钥包含33个字节,其中x坐标占用32额字节,y坐标占用1个字节(因为y值可以通过x只计算出来,因此这个字节用于标识正负)
*/
public ECKey(SecureRandom secureRandom) {
//实例化密钥对生成器
ECKeyPairGenerator generator = new ECKeyPairGenerator();
//设置密钥对生成器的相关参数,包括曲线类型和随机数生成器
ECKeyGenerationParameters keygenParams = new ECKeyGenerationParameters(CURVE, secureRandom);
//初始化密钥生成器相关参数
generator.init(keygenParams);
//生成密钥对
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair keypair = generator.generateKeyPair();
//获取公钥和私钥参数对象
ECPrivateKeyParameters privParams = (ECPrivateKeyParameters) keypair.getPrivate();
ECPublicKeyParameters pubParams = (ECPublicKeyParameters) keypair.getPublic();
//获取私钥和公钥值
priv = privParams.getD();
pub = new LazyECPoint(CURVE.getCurve(), pubParams.getQ().getEncoded(true));
//设置密钥对生成时间
creationTimeSeconds = Utils.currentTimeSeconds();
}
生成公钥和私钥
/**
* Given the domain parameters this routine generates an EC key
* pair in accordance with X9.62 section 5.2.1 pages 26, 27.
*/
public AsymmetricCipherKeyPair generateKeyPair()
{
BigInteger n = params.getN();
int nBitLength = n.bitLength();
int minWeight = nBitLength >>> 2;
BigInteger d;
for (;;)
{
d = new BigInteger(nBitLength, random);
if (d.compareTo(TWO) < 0 || (d.compareTo(n) >= 0))
{
continue;
}
if (WNafUtil.getNafWeight(d) < minWeight)
{
continue;
}
break;
}
ECPoint Q = createBasePointMultiplier().multiply(params.getG(), d);
return new AsymmetricCipherKeyPair(
new ECPublicKeyParameters(Q, params),
new ECPrivateKeyParameters(d, params));
}
上一篇:(五) 区块链数据结构 – 输入脚本和输出脚本