数据结构之图的创建以及深度和广度优先遍历
图的存储结构
图这种结构想想就复杂,图中既有顶点还有两顶点构成的边,依靠简单的顺序存储结构是无法来表达的。
因此就有了
- 邻接矩阵存储
- 邻接表存储
邻接矩阵
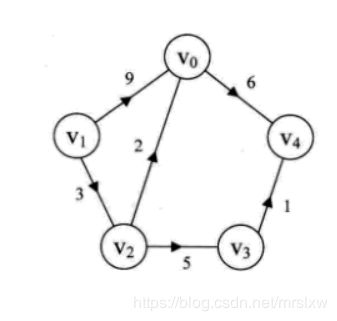
用矩阵来存储图,想想就是二维数组啦;不过只用二维数组来存储元素来说,如果这些元素是字符,那岂不是很麻烦,如果是将其转换为数字关系来存储会非常方便;于是就另需要一个一维数组来存储这些元素,用这些元素对应的数组的索引来表示图的关系.先来看下一个简单的图
接下来就用矩阵来建立图的各个顶点之间的关系了
其中的 ∞ 表示两顶点之间不构成边
这张图是有向图,而无向图的矩阵中存在对称关系
代码
typedef char VertexType; //顶点类型 vertex type
typedef int EdgeType; //边上的权值类型 weight type on edge
#define MAXVEX 100 //最大顶点数 Maximum vertex
#define INFINITY 65535 //用65535来代表 ∞ The 65535 represents ∞
typedef struct
{
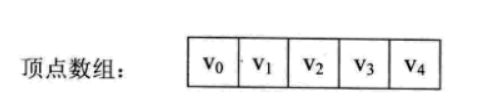
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; //vertex table 顶点表
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; //Edge table 边表 邻接矩阵
int numVertexes; //图中顶点数 Number of vertices in the figure
int numEdges; //图中边数
}MGraph;
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
printf("Please enter the number of vertexes and edges : ");
scanf("%d %d", &G->numVertexes, &G->numEdges);
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
getchar();
scanf("%c", &G->vexs[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
G->arc[i][j] = INFINITY;
int i, j, w;
for (int k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++)
{
printf("输入边(vi,vj)上的两个下标以及权值:"); //赋权值为 1 ,代表两顶点能形成边
scanf("%d %d %d", &i, &j, &w);
G->arc[i][j] = w;
G->arc[j][i] = G->arc[i][j]; //此处是无向图的步骤,若是有向图可省略该行
}
}
邻接表
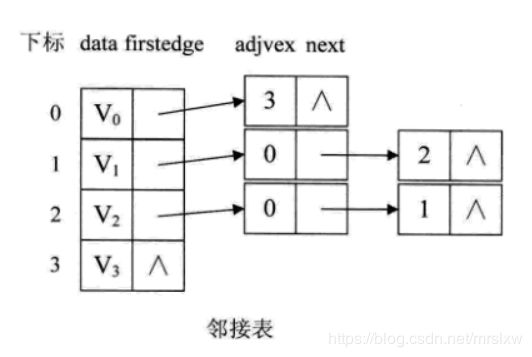
图的邻接表存储结构和树的孩子表示法的存储结构非常相似,相对于邻接矩阵来说某个角度上是控制了内存空间的消耗
邻接表是利用了一位数组和链表来完成的,直接看图吧
邻接表表示
此图是有向图,对于无向图,在存储中也存在这对称关系;上图的右边链表部分,存储顶点是用的索引来存储的。
代码
typedef char VertexType; //顶点类型 vertex type
typedef int EdgeType; //边上的权值类型 weight type on edge
#define MAXVEX 100 //最大顶点数 Maximum vertex
typedef struct EdgeNode //edge table node 边表结点
{
int agjvex; //邻接表域,存储下标 Adjacent table domains are used to store subscripts
EdgeType weight; //用于存储权值 storage weight
struct EdgeNode *next;
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode //顶点表结点 vertex table node
{
VertexType data; //存储顶点信息 storage vertex information
EdgeNode *firstedge; //边表头节点 edge table header node
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList;
int numVertexes; //图中顶点数 Number of vertices in the figure
int numEdges; //图中边数
}GraphAdjList;
void create_Graph(GraphAdjList *G)
{
int i, j;
EdgeNode *e;
printf("Please enter the number of vertexes and edges : ");
scanf("%d %d", &G->numVertexes, &G->numEdges);
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
getchar();
//输入顶点信息
scanf("%c", &G->adjList[i].data);
//将边表置空 Place the edge table as an empty table
G->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL;
}
for (int k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++) //Build edge table
{
printf("Please enter vertex serial number on the edge like (vi, vj) :");
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->agjvex = j;
e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge;
G->adjList[i].firstedge = e;
//由于无向图存在对称性
e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->agjvex = i;
e->next = G->adjList[j].firstedge;
G->adjList[j].firstedge = e;
}
}
邻接矩阵和邻接表的优点和缺点
邻接矩阵
- 优点:对于稠密图来说,邻接矩阵存起来很合理,而且邻接矩阵存储结构可以直接查找图的权值,顶点的度,顶点的邻接顶点等
- 缺点:由于矩阵是 n×n 的所以存储稀疏图是非常浪费空间的
邻接表
- 优点:空间利用率高,容易找到某个顶点的邻接顶点
- 缺点:判断两顶点之间是否构成边不方便
邻接矩阵的空间复杂度为O(n^2),而邻接表的空间复杂度为O(n+e)。
图的遍历
图的遍历分为深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
深度优先遍历
对于该遍历,是以图的一个顶点出发,再随便深入一个邻接顶点,重复此步骤,其中对每个访问过的顶点做一下标记,就这样不断的访问,直到所有的顶点都访问完。
代码
void DFS(MGraph G, int i)
{
//先打印顶点
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);
//标记访问过
visited[i] = true;
//开始深度遍历
for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++)
{
//寻找未访问过的邻接顶点
if (!visited[j] && G.arc[i][j] == 1)
{
DFS(G, j);
}
}
}
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
//将顶点全部标记为未访问
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i]) //对于连通图来说一遍就可以
{
DFS(G, i);
}
}
}
广度优先遍历
图的广度优先遍历,其中涉及到了队列;广度遍历是以图的某个顶点出发,然后将该顶点存入队列,接着将队列的一个元素拿出来,并且访问它的所有邻接顶点存入队列,如此循环,直到队列为空。
代码
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
LinkQueue Q;
//初始化标记顶点
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
init_Queue(&Q);
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
visited[i] = true;
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);
EnQueue(&Q, i);
while(!isEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q, &i); //若该顶点未访问过,取出给i
for (j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++)
{
//找出顶点i的所有未访问过的邻接点
if (!visited[j] && G.arc[i][j] == 1)
{
visited[j] = true;
printf("%c ", G.vexs[j]);
EnQueue(&Q, j);
}
}
}
}
}
}
图的邻接矩阵的两种遍历
#include
#include
typedef char VertexType; //顶点类型 vertex type
typedef int EdgeType; //边上的权值类型 weight type on edge
#define MAXVEX 100 //最大顶点数 Maximum vertex
#define INFINITY 65535 //用65535来代表 ∞ The 65535 represents ∞
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; //vertex table 顶点表
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; //Edge table 边表 邻接矩阵
int numVertexes; //图中顶点数 Number of vertices in the figure
int numEdges; //图中边数
}MGraph;
typedef int QElemType;
typedef struct QNode
{
QElemType data;
struct QNode *next;
}QNode, *Queue;
typedef struct
{
Queue Front;
Queue Rear;
}LinkQueue;
bool visited[MAXVEX];
void init_Queue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
Q->Front = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!Q->Front)
{
printf("The memory allocation failed ! Queue initialization falied! \n");
exit(0);
}
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
Q->Front->next = NULL;
}
void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, int value)
{
Queue qNew = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!qNew)
{
printf("The memory allocation failed!Element can not enter queue!\n");
exit(0);
}
qNew->data = value;
qNew->next = NULL;
Q->Rear->next = qNew;
Q->Rear = qNew;
}
void DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, int *value)
{
Queue q;
if (Q->Front == Q->Rear)
{
printf("The queue is empty!\n");
exit(0);
}
q = Q->Front->next;
*value = q->data;
Q->Front->next = q->next;
if (Q->Rear == q)
{
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
}
free(q);
q = NULL;
}
bool isEmpty(LinkQueue Q)
{
if (Q.Front == Q.Rear)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
printf("Please enter the number of vertexes and edges : ");
scanf("%d %d", &G->numVertexes, &G->numEdges);
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
getchar();
scanf("%c", &G->vexs[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
G->arc[i][j] = INFINITY;
int i, j, w;
for (int k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++)
{
printf("输入边(vi,vj)上的两个下标以及权值:"); //赋权值为 1 ,代表两顶点能形成边
scanf("%d %d %d", &i, &j, &w);
G->arc[i][j] = w;
G->arc[j][i] = G->arc[i][j]; //此处是无向图的步骤,若是有向图可省略该行
}
}
void DFS(MGraph G, int i)
{
//先打印顶点
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);
//标记访问过
visited[i] = true;
//开始深度遍历
for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++)
{
//寻找未访问过的邻接顶点
if (!visited[j] && G.arc[i][j] == 1)
{
DFS(G, j);
}
}
}
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
//将顶点全部标记为未访问
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i]) //对于连通图来说一遍就可以
{
DFS(G, i);
}
}
}
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
LinkQueue Q;
//初始化标记顶点
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
init_Queue(&Q);
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
visited[i] = true;
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);
EnQueue(&Q, i);
while(!isEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q, &i); //若该顶点未访问过,取出给i
for (j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++)
{
//找出顶点i的所有未访问过的邻接点
if (!visited[j] && G.arc[i][j] == 1)
{
visited[j] = true;
printf("%c ", G.vexs[j]);
EnQueue(&Q, j);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
MGraph G;
CreateMGraph(&G);
//深度遍历
DFSTraverse(G);
//广度遍历
BFSTraverse(G);
return 0;
}
图的邻接表的两种遍历
#include
#include
typedef char VertexType; //顶点类型 vertex type
typedef int EdgeType; //边上的权值类型 weight type on edge
#define MAXVEX 100 //最大顶点数 Maximum vertex
typedef struct EdgeNode //edge table node 边表结点
{
int agjvex; //邻接表域,存储下标 Adjacent table domains are used to store subscripts
EdgeType weight; //用于存储权值 storage weight
struct EdgeNode *next;
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode //顶点表结点 vertex table node
{
VertexType data; //存储顶点信息 storage vertex information
EdgeNode *firstedge; //边表头节点 edge table header node
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList;
int numVertexes; //图中顶点数 Number of vertices in the figure
int numEdges; //图中边数
}GraphAdjList;
typedef int QElemType;
typedef struct QNode
{
QElemType data;
struct QNode *next;
}QNode, *Queue;
typedef struct
{
Queue Front;
Queue Rear;
}LinkQueue;
bool visited[MAXVEX];
void init_Queue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
Q->Front = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!Q->Front)
{
printf("The memory allocation failed ! Queue initialization falied! \n");
exit(0);
}
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
Q->Front->next = NULL;
}
void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, int value)
{
Queue qNew = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!qNew)
{
printf("The memory allocation failed!Element can not enter queue!\n");
exit(0);
}
qNew->data = value;
qNew->next = NULL;
Q->Rear->next = qNew;
Q->Rear = qNew;
}
void DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, int *value)
{
Queue q;
if (Q->Front == Q->Rear)
{
printf("The queue is empty!\n");
exit(0);
}
q = Q->Front->next;
*value = q->data;
Q->Front->next = q->next;
if (Q->Rear == q)
{
Q->Rear = Q->Front;
}
free(q);
q = NULL;
}
bool isEmpty(LinkQueue Q)
{
if (Q.Front == Q.Rear)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void create_Graph(GraphAdjList *G)
{
int i, j;
EdgeNode *e;
printf("Please enter the number of vertexes and edges : ");
scanf("%d %d", &G->numVertexes, &G->numEdges);
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
getchar();
//输入顶点信息
scanf("%c", &G->adjList[i].data);
//将边表置空 Place the edge table as an empty table
G->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL;
}
for (int k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++) //Build edge table
{
printf("Please enter vertex serial number on the edge like (vi, vj) :");
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->agjvex = j;
e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge;
G->adjList[i].firstedge = e;
//由于无向图存在对称性
e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->agjvex = i;
e->next = G->adjList[j].firstedge;
G->adjList[j].firstedge = e;
}
}
void DFS(GraphAdjList G, int i)
{
visited[i] = true;
printf("%c ", G.adjList[i].data);
EdgeNode *p;
p = G.adjList[i].firstedge;
//此时访问邻接顶点 Accessing adjacent vertices
while(p)
{
if (!visited[p->agjvex])
{
//进行深度遍历
DFS(G, p->agjvex);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void DFSTraverse(GraphAdjList G)
{
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
//false 表示顶点未访问过 False indicates that the vertex has not been accessed
visited[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
//For connectivity diagram, DFS be used only one. Non-connected diagrams are used more than one.
//连通图只调用一次。非连通图不止一次
if (!visited[i])
{
DFS(G, i);
}
}
}
void BFSTraverse(GraphAdjList G)
{
int i;
EdgeNode *p;
LinkQueue Q;
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
init_Queue(&Q);
for (i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
visited[i] = true;
printf("%c ", G.adjList[i].data);
EnQueue(&Q, i);
while(!isEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q, &i);
p = G.adjList[i].firstedge;
while(p)
{
if (!visited[p->agjvex])
{
visited[p->agjvex] = true;
printf("%c ", G.adjList[p->agjvex].data);
EnQueue(&Q, p->agjvex);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
GraphAdjList G;
create_Graph(&G);
//深度遍历
DFSTraverse(G);
//广度遍历
BFSTraverse(G);
return 0;
}