Android SVG矢量动画机制
导语
黑科技来了,Google在Android5.X中增加了对SVG矢量图形的支持,这对于创造新的高效率动画具有很深远的意义。
主要内容
- < path >标签
- SVG常见指令
- SVG编辑器
- Android中使用SVG
- SVG动画实例
具体内容
首先,我们来了解一下什么是SVG:
- 可伸缩矢量图形
- 定义用于网络的基于矢量的图形
- 使用xml格式定义图形
- 图片在放大或者改变尺寸的情况下其图形质量不会有所损失
- 万维网联盟的标准
- 与诸多DOM和XSL之类的W3C标准是一个整体
SVG在web上应用非常广泛,在Android5.X之前的Android版本上,大家可以通过一些第三方库在Android中使用SVG,而在Android5.X后,Android中添加了对< path >标签的支持,从而让开发者可以使用SVG来创建更加丰富的动画效果,那么SVG对传统的Bitmap,究竟有什么好处呢?bitmap通过每个像素点上存储色彩信息来表达图像,而SVG是一个绘图标准,与之相对,最大的优势是SVG放大不会失真,而且bitmap需要不同分辨率适配,SVG不需要。
< path >标签
使用< path >标签来创建SVG,就是用指令的方式来控制一支画笔,列入,移动画笔来到某一个坐标位置,画一条线,画一条曲线,结束,< path >标签所支持的指令大致有一下几种:
- M = moveto(M X,Y):将画笔移动到指定的坐标位置,但未发生绘制。
- L = lineto(L X,Y):画直线到指定的位置。
- H = horizontal lineto( H X):画水平线到指定的X坐标位置。
- V = vertical lineto(V Y ):画垂直线到指定的Y坐标。
- C = curveto(C ,X1,Y1,X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝塞尔曲线。
- S = smooth curveto(S X2,Y2,ENDX,ENDY):三次贝塞尔曲线。
- Q = quadratic Belzier curve(Q X Y,ENDX,ENDY):二次贝塞尔曲线。
- T = smooth quadratic Belzier curvrto(T,ENDX,ENDY):映射前面路径的重点。
- A = elliptical Are(A RX,RY,XROTATION,FLAG1,FLAG2,X,Y):弧线。
- Z = closepath():关闭路径。
使用上面的指令时,需要注意的几点:
- 坐标轴以(0,0)位中心,X轴水平向右,Y轴水平向下。
- 所有指令大小写均可,大写绝对定位,参照全局坐标系,小写相对定位,参照父容器坐标系。
- 指令和数据间的空格可以无视。
- 同一指令出现多次可以用一个。
SVG常见指令
- L
绘制直线的指令是“L”,代表从当前点绘制直线到给定点,“L”之后的参数是一个点坐标,如“L 200 400”绘制直线,同时,还可以使用“H”和“V”指令来绘制水平竖直线,后面的参数是x坐标个y坐标。
- M
M指令类似Android绘图中的path类moveto方法,即代表画笔移动到某一点,但并不发生绘图动作。
- A
A指令是用来绘制一条弧线,且允许弧线不闭合,可以把A指令绘制的弧度想象成椭圆的某一段A指令一下有七个指令。
- RX,RY指所有的椭圆的半轴大小。
- XROTATION 指椭圆的X轴和水平方向顺时针方向的夹角,可以想象成。一个水平的椭圆饶中心点顺时针旋转XROTATION 的角度。
- FLAG1 只有两个值,1表示大角度弧度,0为小角度弧度。
- FLAG2 只有两个值,确定从起点到终点的方向1顺时针,0逆时针。
- X,Y为终点坐标。
SVG的指令参数非常的复杂,但是再Android中,不需要绘制太多的SVG图像,后面会有几个小案例。
SVG编辑器
SVG参数的写法固定而且复杂,因此完全可以使用程序来实现,所以一般通过SVG编辑器来编辑SVG图像,网上有很多在线的编辑器,通过可视化编辑图像之后,点击view→source可以转换成SVG代码。
地址:http://editor.method.ac/
下载离线的SVG编辑器,由很多强大的功能,这里就不一一赘述了。
Android中使用SVG
Google在Android5.X后给我们提供了两个新的API来支持SVG:
- VectorDrawable
- AnimatedVectorDrawable
其中,VectorDrawable可以让你创建基于XML的SVG图像,并且结合AnimatedVectorDrawable来实现动画效果。
VectorDrawable
在XML中创建一个静态的SVG,通常是如下结构。
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="200dp"
android:height="200dp"
android:viewportHeight="100"
android:viewportWidth="100">
vector>这个代码之中包含了两组高宽,width和height是表示SVG图像的具体大小,后面的是表示SVG图像划分的比例,后面再绘制path时所使用的参数,就是根据这两个值来进行转换的,比如上面的代码,将200dp划分100份,如果在绘图中使用坐标(50,50),则意味着该坐标为正中间,现在我们加上path标签。
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="200dp"
android:height="200dp"
android:viewportHeight="100"
android:viewportWidth="100">
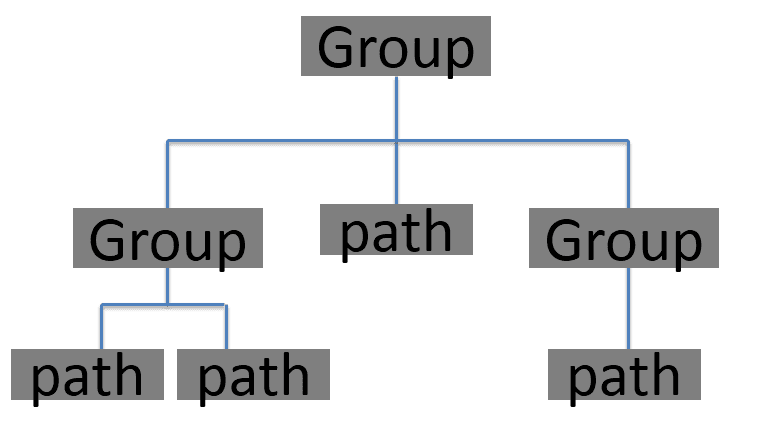
<group
android:name="svg1"
android:rotation="0">
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:pathData="M 25 50 a 25,25 0 1,0 50,0" />
group>
vector>通过添加< path>标签绘制一个SVG图形,pathData就是图形所用到的指令了,先用M指令,将画笔移动到(25 , 50)的位置,再通过A指令来绘制一个圆弧并且填充他,通过以上代码,就可以绘制一个SVG图形了。
上面使用android:fillColor属性来绘制填充图形,如果要绘制非填充的图形可以使用以下属性。
android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:strokeWidth="2"AnimatedVectorDrawable
AnimatedVectorDrawable的作用是给VectorDrawable提供动画效果,Google的工程师将AnimatedVectorDrawable比喻一个胶水,通过AnimatedVectorDrawable来连接静态的VectorDrawable和动态的objectAnimator。
下面我们来看看具体是怎么样来做的,首先我们在xml中定义一个< animated-vector>,来申明对AnimatedVectorDrawable的使用,并且指明是作用在path或者group上。
- anim_vector.xml
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@drawable/verctor">
<target
android:name="test"
android:animation="@animator/anim_rotate" >
target>
animated-vector>对应的vector即为静态的VectorDrawable。
- vector.xml
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:height="200dp"
android:width="200dp"
android:viewportWidth="100"
android:viewportHeight="100">
<group
android:name="test"
android:rotation="0"
>
<path
android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:strokeWidth="2"
android:pathData="
M 25 50
a 25 , 25 0 1 , 0 50 ,0"
>
path>
group>
vector>需要注意的是,AnimatedVectorDrawable中指明的target和name属性,必须与VectorDrawable中需要的name保持一致,这样系统能找到找到要实现的动画元素,最后,通过AnimatedVectorDrawable中的target和animation属性,将一个动画作用在对应的name上,objectAnimator代码如下。
- anim_rotat.xml:
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="4000"
android:propertyName="rotation"
android:valueFrom="0"
android:valueTo="360">
objectAnimator>最后,我们看到的,对动画效果的实现,还是通过属性动画来完成的,只是属性稍有不同。
在< group>标签和< path>标签中添加rotation,fillColor,pathData属性,那么在objecyAnimator中,就可以通过指定,android:valueFrom=XXX,和android:property=”XXX”属性,控制动画的起始值,唯一需要注意的是,如果指定属性为pathData,那么需要添加一个属性android:valueType-“pathType”来告诉系统进行pathData变换,类似的情况,可以使用rotation来进行旋转变换,使用fileColor实现变换颜色,使用pathData进行形状,位置的变换。
当所有的XML准备好之后,我们就可以直接给一个imageview设置背景了。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/status_view"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@drawable/anim_vector"
/>
LinearLayout>到这里就有些不同了,书上写的是,程序中使用如下代码就可以开始SVG动画。
Drawable drawable = imageView.getDrawable();
if(drawable instanceof Animatable) {
((Animatable) drawable).start();
}上面的方法只能是一个动画,可能不太好控制,如下代码也可以使用SVG动画。
public class SvgActivity extends Activity {
private ImageView imageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_svg);
imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
imageView.setResource(R.drawable.anim_vector); // 设置Resource为动画资源
imageView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
anim.start(); // 开始动画
}
});
}
}效果如下:
SVG动画实例
线图动画
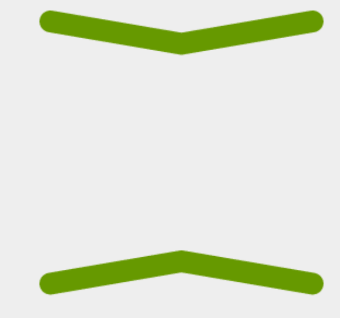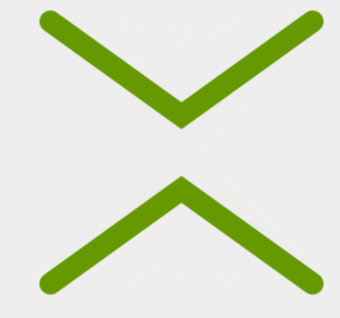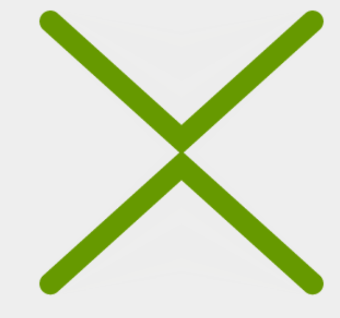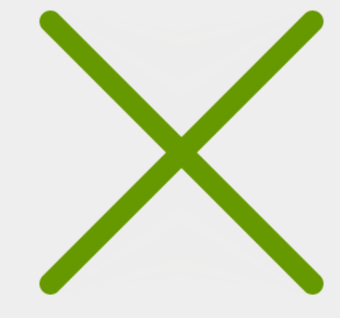
在android5.X之后,Google大量引入了线图动画,当页面发生改变的时候,页面的icon不再是生硬的切换,而是通过非常生动的动画,转换成另一种形态。
我们要实现的效果就是上下两根线,然后他们形成一个X的效果。
- 定义我们的VectorDrawable
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="200dp"
android:height="200dp"
android:viewportHeight="100"
android:viewportWidth="100">
<group>
<path
android:name="path1"
android:pathData="
M 20,80
L 50,80 80,80"
android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:strokeLineCap="round"
android:strokeWidth="5" />
<path
android:name="path2"
android:pathData="
M 20,20
L 50,20 80,20"
android:strokeColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:strokeLineCap="round"
android:strokeWidth="5" />
group>
vector>path1和path2分别绘制了一条直线,每条线都有三个点控制,接下来就是变换的动画了。
- 定义两个Path的objectAnimator,从path1到path2
<objectAnimator
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="5000"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/bounce_interpolator"
android:propertyName="pathData"
android:valueFrom="
M 20,80
L 50,80 80,80"
android:valueTo="
M 20,80
L 50,50 80,80"
android:valueType="pathType" /><objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="5000"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/bounce_interpolator"
android:propertyName="pathData"
android:valueFrom="
M 20,20
L 50,20 80,20"
android:valueTo="
M 20,20
L 50,50 80,20"
android:valueType="pathType" />这两个值是对应的起始点,不过需要注意的是,SVG的路径变换属性动画中,变换前后阶段属必须相同,这也是前面需要使用的三个点看来绘制一条直线的原因,有了VectorDrawable和objectAnimator,现在只需要AnimatedVectorDrawable将他们黏合在一起即可。
- 定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@drawable/trick">
<target
android:name="path1"
android:animation="@anim/anim_path1" />
<target
android:name="path2"
android:animation="@anim/anim_path2" />
animated-vector>针对trick这样的一个VectorDrawable中的path1和path2的路径,分别使用了objectAnimator,最后只需要去启动动画就可以了。
- 在代码中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable();
if (drawable instanceof Animatable) {
((Animatable) drawable).start();
}代码就完成了,接下来看一下效果吧。
- 效果图
模拟三球仪
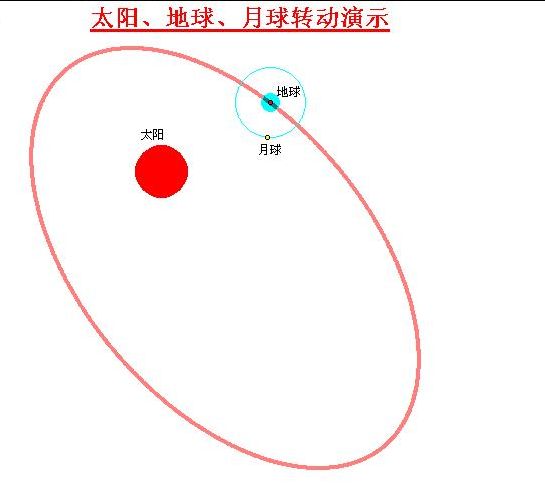
三球仪是天体文学中的星象仪器,用来模拟地球,月亮和太阳的运行轨迹,如图。
实现过程如下:
- 定义我们的VectorDrawable
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="200dp"
android:height="200dp"
android:viewportHeight="100"
android:viewportWidth="100">
<group
android:name="sun"
android:pivotX="60"
android:pivotY="50"
android:rotation="0">
<path
android:name="path_sun"
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:pathData="
M 50,50
a 10,10 0 1,0 20,0
a 10,10 0 1,0 -20,0" />
<group
android:name="earth"
android:pivotX="75"
android:pivotY="50"
android:rotation="0">
<path
android:name="path_earth"
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark"
android:pathData="
M 70,50
a 5,5 0 1,0 10,0
a 5,5 0 1,0 -10,0" />
<group>
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:pathData="
M 90,50
m -5 0
a 4,4 0 1,0 8 0
a 4,4 0 1,0 -8,0" />
group>
group>
group>
vector>
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="200dp"
android:height="200dp"
android:viewportHeight="100"
android:viewportWidth="100">
<group
android:name="sun"
android:pivotX="60"
android:pivotY="50"
android:rotation="0">
<path
android:name="path_sun"
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:pathData="
M 50,50
a 10,10 0 1,0 20,0
a 10,10 0 1,0 -20,0" />
<group
android:name="earth"
android:pivotX="75"
android:pivotY="50"
android:rotation="0">
<path
android:name="path_earth"
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark"
android:pathData="
M 70,50
a 5,5 0 1,0 10,0
a 5,5 0 1,0 -10,0" />
<group>
<path
android:fillColor="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:pathData="
M 90,50
m -5 0
a 4,4 0 1,0 8 0
a 4,4 0 1,0 -8,0" />
group>
group>
group>
vector>- 定义两个objectAnimator,代码都是一样的
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="4000"
android:propertyName="rotation"
android:valueFrom="0"
android:valueTo="360" />- 定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@drawable/earth_moon_system">
<target
android:name="sun"
android:animation="@anim/anim_sun" />
<target
android:name="earth"
android:animation="@anim/anim_earth" />
animated-vector>- 布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/sun_system" />- 代码中启动动画
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable();
if (drawable instanceof Animatable) {
((Animatable) drawable).start();
}- 效果图
- 解释
可以在代码中发现“sun”在这个group中,有一个“earth”的group,同时使用android:pivotX和android:pivotY属性来设置其旋转中心,分别代表太阳系统和地月系统,分别对这两个group进行SVG动画。
轨迹动画
使用轨迹动画:
- 定义我们的VectorDrawable
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:width="160dp"
android:height="30dp"
android:viewportHeight="30"
android:viewportWidth="160">
<path
android:name="search"
android:pathData="M141 , 17 A9 ,9 0 1 , 1 ,142 , 16 L149 ,23"
android:strokeAlpha="0.8"
android:strokeColor="#ff3570be"
android:strokeLineCap="square"
android:strokeWidth="2" />
<path
android:name="bar"
android:pathData="M0,23 L149 ,23"
android:strokeAlpha="0.8"
android:strokeColor="#ff3570be"
android:strokeLineCap="square"
android:strokeWidth="2"
/>
vector>- 定义objectAnimator
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="1000"
android:interpolator="@android:interpolator/accelerate_decelerate"
android:propertyName="trimPathStart"
android:valueFrom="0"
android:valueTo="1"
android:valueType="floatType" />- 定义AnimatedVectorDrawable连接VectorDrawable和objectAnimator
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@drawable/searchbar">
<target
android:name="search"
android:animation="@anim/anim_searchbar" />
animated-vector>- 布局文件中使用这个AnimatedVectorDrawable
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/search_anim" />- 代码中启动动画
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
Drawable drawable = image.getDrawable();
if (drawable instanceof Animatable) {
((Animatable) drawable).start();
}- 效果图
- 解释
还是利用属性动画,只是将propertyName改为trimPathStart,这个属性就是利用0-1的百分比来按照绘制轨迹绘制SVG图像。类似的还有trimPathEnd这个属性,可以从无到有。
总结
- 大概了解SVG的机制。
- 注意启动动画的代码与以前有所不同。
- 理解SVG动画实例。
进入我的CSDN戳这里(我的博客导航)