RabbitMQ自学之路(六)——-RabbitMQ实战场景(一)异步记录用户操作日志
传统的项目开发中业务流程以串行方式,执行了模块1—》模块2–》模块3
而我们知道,这个执行流程其实对于整个程序来讲是有一定的弊端的,主要有几点:
(1)整个流程的执行响应等待时间比较长;
(2)如果某一个模块发生异常,可能会影响其他 模块甚至整个系统的执行流程与结果;
(3)程序的代码上造成冗余,模块与模块需要进行强通信以及数据的交互,出现问题时难以定位与维护。耦合度过高!
因此需要进行优化,将强关联的业务模块解耦以及某些模块之间实行异步通信!
下面我将通过一些实际案例来进行一个介绍
一、异步记录用户操作日志
用户操作日志对于每一个系统来说是不可或缺的,并且操作日志应该单独抽取为一个模块业务,不应该与主业务系统之间耦合在一起。
故而我们需要将其单独抽出并以异步的方式与主模块进行异步通信交互数据。
要求:采用 RabbitMQ 的 DirectExchange+RoutingKey 消息模型来实现【异步记录用户操作日志】
前提:SpringBoot与RabbitMQ的整合前面章节已经讲述过了,就不再重述了。
第一步:创建消息模型:包括 Queue、Exchange、RoutingKey 等的建立
package com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
*
* Direct Exchange(路由模式)—异步记录用户操作日志
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfigDemo1 {
//消息队列名称
final static String queue = "queue_demo1";
/**
* 交换机名称
*/
final static String exchange = "deom1Exchange";
@Bean
public Queue queueDemo1() {
return new Queue(RabbitConfigDemo1.queue);
}
/**
*
* @method 声明一个direct类型的交换机
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
* @return
*/
@Bean
DirectExchange exchangeDemo1() {
return new DirectExchange(RabbitConfigDemo1.exchange);
}
/**
*
* @method 绑定Queue队列到交换机,并且指定routingKey
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
* @param queueDemo1 对应注入queueDemo1()方法
* @param exchangeDemo1 对应exchangeDemo1()
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectExchangeDemo1(Queue queueDemo1, DirectExchange exchangeDemo1) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueDemo1).to(exchangeDemo1).with("keyDemo1");
}
}
第二步:创建生产者,这里的生产者负责发送用户日志信息到rabbitmq
其中需要建立User 用户实体类、UserLog用户日志实体类,这里就不介绍了。
注意一点:rabbitmq消息队列可以接受任何形式的消息数据。
package com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.producers;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.entity.UserLog;
/**
*
* @method 生产者
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
*/
@Component
public class ProducersDemo1 {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
/**
*
* @method 生产者发送消息,direct模式下需要传递一个routingKey
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
* @throws Exception
*/
public void send(UserLog userLog) throws Exception {
System.out.println("发送用户日志信息到rabbitmq: " + userLog.toString());
this.amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("deom1Exchange", "keyDemo1", userLog);
}
}
第三步:创建消费者,即接受到rabbitmq传过来的消息后进行操作(如持久化用户日志信息)
我这里只提供了核心代码,如持久化操作模拟执行即可。
package com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.consumers;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.entity.UserLog;
/**
*
* @method 抽离日志系统为一个消费者
* @author Mr yi
* @time 2019年6月19日
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_demo1")
public class ConsumersLogDemo1 {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(UserLog userLog) {
System.out.println("log_name="+userLog.getLog_name());
System.out.println("user_name="+userLog.getUser_name());
System.out.println("log_type="+userLog.getLog_type());
//将日志信息进行持久化操作(这里没有写操作数据库方法,模拟执行)
//save(userLog);
System.out.println("用户日志成功录入!");
}
}
第四步:在 Controller 中执行用户登录逻辑
我们这里模拟用户登录操作,用户登录后,会发送用户登录操作日志到rabbitmq队列中,由绑定了此队列的消费者(即用户日志模块系统)接受消息
package com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.entity.UserLog;
import com.springboot.rabbitmq.example.demo1.producers.ProducersDemo1;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Controller
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/userdemo1")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProducersDemo1 producers;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login() throws Exception {
String user_name = "admin";
String pwd = "123456";
if(user_name=="admin" && pwd=="123456") {
log.info("用户登录成功!");
UserLog userLog = new UserLog();
userLog.setLog_name("用户登录").setLog_type("login").setUser_name(user_name);
producers.send(userLog);
log.info("异步记录用户操作日志!");
}
return "success";
}
}
控制台数据结果

队列

队列绑定的routing key
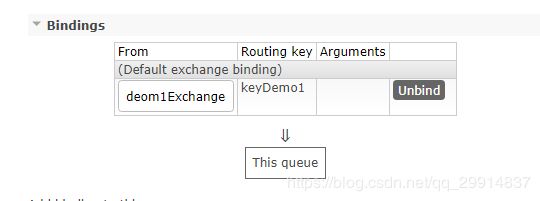
exchange交换机
![]()
源码下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_29914837/11252985
如果你觉得本篇文章对你有所帮助的话,麻烦请点击头像右边的关注按钮,谢谢!
技术在交流中进步,知识在分享中传播
