filebeat学习笔记
filebeat学习笔记
主要供自己记录学习笔记,有一部分是摘录的参考文章的内容,如有问题,欢迎留言
文章目录
- filebeat学习笔记
- filebeat是什么
- filebeat配置
- filebeat性能测试及优化
- filebeat数据收集时丢失问题
- filebeat源码简单解析
- 模块结构
- filebeat组织结构
- 重要数据结构
- 执行逻辑
- 日志收集
- 参考
filebeat是什么
filebeat是beat的一种
官网是这样介绍beat的:The Lightweight Shippers of the Elastic Stack
Lightweight就是轻量级,是指Beats的安装占用空间小,使用的系统资源有限并且没有运行时依赖性。
我的理解就是轻量级的数据采集器,可以简单的处理、加工数据。
下面是所有的beat和功能。可根据需要去学习使用,我主要使用filebeat去采集日志文件。
| Beat | Description |
|---|---|
| Auditbeat | Collect your Linux audit framework data and monitor the integrity of your files. |
| Filebeat | Tails and ships log files |
| Functionbeat | Read and ships events from serverless infrastructure. |
| Heartbeat | Ping remote services for availability |
| Journalbeat | Read and ships event from Journald. |
| Metricbeat | Fetches sets of metrics from the operating system and services |
| Packetbeat | Monitors the network and applications by sniffing packets |
| Winlogbeat | Fetches and ships Windows Event logs |
filebeat配置
安装filebeat官网
这里简单说一下配置,配置文件主要是filebeat.yml
文件结构很容易理解,主要了解一下filebeat的参数,知道filebeat可以实现哪些功能
| 参数 | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Paths | 要监控的日志 | - /var/log/*.log |
| input_type | 文件的输入类型 | log,stdin |
| encoding | 监控的文件的编码类型 | plain, utf-8 |
| exclude_lines | 排除符合正则表达式列表的那些行 | [.log.] |
| include_lines | 包含输入中符合正则表达式列表的那些行默认包含所有行 | ["^ERR", “^WARN”] |
| fields | 添加额外的信息 | topic: syslog |
| fields_under_root | 如果该选项设置为true则新增fields成为顶级目录而不是将其放在fields目录下 | true |
| ignore_older | Filebeat忽略指定时间段以外修改的日志内容 | 2h |
| document_type | 设定Elasticsearch输出时的document的type字段 | log |
| scan_frequency: | Filebeat以多快的频率去prospector指定的目录下面检测文件更新(新增) | 10s |
| close_older | 如果一个文件在某个时间段内没有发生过更新则关闭监控的文件** | 1h |
| harvester_buffer_size | 每个harvester监控文件时使用的buffer的大小 | 16384 |
| max_bytes | 日志文件中增加一行算一个日志事件max_bytes限制在一次日志事件中最多上传的字节数多出的字节会被丢弃 | 10485760 |
| multiline | 适用于日志中每一条日志占据多行的情况,比如各种语言的报错信息调用栈 | **** |
| publish_async | 异步发送模式(实验!) | False |
| registry_file | 记录filebeat处理日志文件的位置的文件 | /var/lib/filebeat/registry |
| tail_files | 如果设置为true,Filebeat从文件尾开始监控文件新增内容,把新增的每一行文件作为一个事件依次发送 | True |
| max_procs | 最大使用c数 | 1 |
filebeat性能测试及优化
我对于filebeat做了一个性能测试
数据待续
filebeat数据收集时丢失问题
我们在使用filebeat收集业务日志的过程中,发现少部分日志没有被收集。
经排查,原因如下:
业务日志文件在固定时间或者固定大小会进行压缩处理,压缩处理之后,文件的I_node改变无法继续收集,而filebeat的采集间隔一般为10s,这个间隔内的日志就没有收集到。
解决办法如下:
修改业务日志的压缩方式,在达到压缩条件后,先不压缩,等待一段时间后在再进行压缩。
filebeat源码简单解析
模块结构
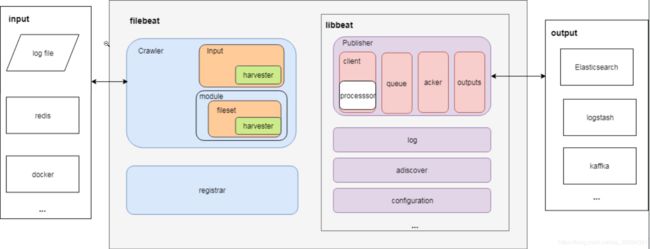
下图是filebeat及使用libbeat的一些主要模块,图片地址
-
Crawler: 管理所有Input收集数据并发送事件到libbeat的Publisher(发布者)
-
Input: 对应可配置的一种输入类型,每种类型都有具体的Input和Harvester(收割机)实现。
配置项
- Harvester: 对应一个输入源,是收集数据的实际工作者。配置中,一个具体的Input可以包含多个输入源(Harvester)
-
module: 简化了一些常见程序日志(比如nginx日志)收集、解析、可视化(kibana dashboard)
配置项
- fileset: module下具体的一种Input定义(比如nginx包括access和error log),包含:1)输入配置;2)es ingest node pipeline定义;3)事件字段定义;4)示例kibana dashboard
-
Registrar:用于在事件发送成功后记录文件状态
-
Publisher:
- client: 提供
Publish接口让filebeat将事件发送到Publisher。在发送到队列之前,内部会先调用processors(包括input 内部的processors和全局processors)进行处理。 - processor: 事件处理器,可对事件按照配置中的条件进行各种处理(比如删除事件、保留指定字段等)。配置项
- queue: 事件队列,有memqueue(基于内存)和spool(基于磁盘文件)两种实现。配置项
- outputs: 事件的输出端,比如ES、Logstash、kafka等。配置项
- acker: 事件确认回调,在事件发送成功后进行回调
- client: 提供
-
autodiscover:用于自动发现容器并将其作为输入源
filebeat组织结构
├── autodiscover # 包含filebeat的autodiscover适配器(adapter),当autodiscover发现新容器时创建对应类型的输入
├── beater # 包含与libbeat库交互相关的文件
├── channel # 包含filebeat输出到pipeline相关的文件
├── config # 包含filebeat配置结构和解析函数
├── crawler # 包含Crawler结构和相关函数
├── fileset # 包含module和fileset相关的结构
├── harvester # 包含Harvester接口定义、Reader接口及实现等
├── input # 包含所有输入类型的实现(比如: log, stdin, syslog)
├── inputsource # 在syslog输入类型中用于读取tcp或udp syslog
├── module # 包含各module和fileset配置
├── modules.d # 包含各module对应的日志路径配置文件,用于修改默认路径
├── processor # 用于从容器日志的事件字段source中提取容器id
├── prospector # 包含旧版本的输入结构Prospector,现已被Input取代
├── registrar # 包含Registrar结构和方法
└── util # 包含beat事件和文件状态的通用结构Data
重要数据结构
beats通用事件结构(libbeat/beat/event.go):
type Event struct {
Timestamp time.Time // 收集日志时记录的时间戳,对应es文档中的@timestamp字段
Meta common.MapStr // meta信息,outpus可选的将其作为事件字段输出。比如输出为es且指定了pipeline时,其pipeline id就被包含在此字段中
Fields common.MapStr // 默认输出字段定义在field.yml,其他字段可以在通过fields配置项指定
Private interface{} // for beats private use
}
Crawler(filebeat/crawler/crawler.go):
// Crawler 负责抓取日志并发送到libbeat pipeline
type Crawler struct {
inputs map[uint64]*input.Runner // 包含所有输入的runner
inputConfigs []*common.Config
out channel.Factory
wg sync.WaitGroup
InputsFactory cfgfile.RunnerFactory
ModulesFactory cfgfile.RunnerFactory
modulesReloader *cfgfile.Reloader
inputReloader *cfgfile.Reloader
once bool
beatVersion string
beatDone chan struct{}
}
log类型Input(filebeat/input/log/input.go)
// Input contains the input and its config
type Input struct {
cfg *common.Config
config config
states *file.States
harvesters *harvester.Registry // 包含Input所有Harvester
outlet channel.Outleter // Input共享的Publisher client
stateOutlet channel.Outleter
done chan struct{}
numHarvesters atomic.Uint32
meta map[string]string
}
log类型Harvester(filebeat/input/log/harvester.go):
type Harvester struct {
id uuid.UUID
config config
source harvester.Source // the source being watched
// shutdown handling
done chan struct{}
stopOnce sync.Once
stopWg *sync.WaitGroup
stopLock sync.Mutex
// internal harvester state
state file.State
states *file.States
log *Log
// file reader pipeline
reader reader.Reader
encodingFactory encoding.EncodingFactory
encoding encoding.Encoding
// event/state publishing
outletFactory OutletFactory
publishState func(*util.Data) bool
onTerminate func()
}
Registrar(filebeat/registrar/registrar.go):
type Registrar struct {
Channel chan []file.State
out successLogger
done chan struct{}
registryFile string // Path to the Registry File
fileMode os.FileMode // Permissions to apply on the Registry File
wg sync.WaitGroup
states *file.States // Map with all file paths inside and the corresponding state
gcRequired bool // gcRequired is set if registry state needs to be gc'ed before the next write
gcEnabled bool // gcEnabled indictes the registry contains some state that can be gc'ed in the future
flushTimeout time.Duration
bufferedStateUpdates int
}
libbeat Pipeline(libbeat/publisher/pipeline/pipeline.go)
type Pipeline struct {
beatInfo beat.Info
logger *logp.Logger
queue queue.Queue
output *outputController
observer observer
eventer pipelineEventer
// wait close support
waitCloseMode WaitCloseMode
waitCloseTimeout time.Duration
waitCloser *waitCloser
// pipeline ack
ackMode pipelineACKMode
ackActive atomic.Bool
ackDone chan struct{}
ackBuilder ackBuilder // pipelineEventsACK
eventSema *sema
processors pipelineProcessors
}
执行逻辑
日志收集
从收集日志、到发送事件到publisher,其数据流如下图所示:
- Crawler根据Input配置创建并启动具体Input对象
以log类型为例
- Log input对象创建时会从registry读取文件状态(主要是offset),然后为input配置中的文件路径创建harvester并运行
- harvester启动时会通过
Setup方法创建一系列reader形成读处理链
- harvester启动时会通过
- harvester从registry记录的文件位置开始读取,组装成事件(beat.Event)后发给Publisher
参考
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1367784