获取文件属性—stat、lstat、fstat
一、函数原型
#include
#include
#include
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
二、参数
1、path :文件名或者目录名
2、fd : 文件描述符
3、 struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ // 文件的设备编号
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ // 结点
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ // 文件的类型和存取的权限
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ // 连到该文件的硬链接数目,新建的文件则硬连接数为 1
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ // 用户ID
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ // 组ID
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ // 若此文件为设备文件,则为其设备的编号
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ // 文件字节数(文件大小)
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */ // 块大小
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ // 块数
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ // 最后一次访问时间
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ // 最后一次修改时间
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ // 最后一次改变时间
};
st_mode :该变量占 2 byte,共16位
(1)、掩码的使用: st_mode & 掩码
(2)、其他人权限( 0-2 bit )
(a)、S_IROTH 00004 读权限
(b)、S_IWOTH 00002 写权限 掩码:S_IRWXO
(c)、S_IXOTH 00001 执行权限
(3)、所属组权限(3-5bit)
(a)、S_IRWXG 00070 读权限
(b)、S_IRGRP 00040 写权限 掩码:S_RWXG
(c)、S_IXGRP 00010 执行权限
(4)、文件所有者权限(6-8bit)
(a)、S_IRUSR 00400 读权限
(b)、S_IWUSR 00200 写权限 掩码:S_IRWXU
(c)、S_IXUSR 00100 执行权限
(5)、文件特权位(9-11bit)
(a)、 S_ISUID 0004000 设置用户ID
(b)、 S_ISGID 0002000 设置组ID 文件特权位很少用
(6)、文件类型(12-15bit)
(a) 、S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket(套接字)
(b) 、S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link(符号链接--软连接)
(c) 、S_IFREG 0100000 regular file(普通文件)
(d)、 S_IFBLK 0060000 block device(块设备) 掩码:S_IFMT
(e) 、S_IFDIR 0040000 directory(目录)
(f) 、 S_IFCHR 0020000 character device(字符设备)
(g)、 S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO(管道)
三、返回值
以上三个获取文件属性的函数 若成功,返回0;若失败,返回 -1;
四、stat、lstat、fstat之间的区别
1、fstat 函数:系统调用的是一个 ”文件描述符”,而另外两个则直接接收“文件路径”。文件描述符是我们用 open 系统调用后得到的,而文件全路径直接写就可以了。
2、stat 函数与 lstat 函数的区别: 当一个文件是符号链接时,lstat 函数返回的是该符号链接本身的信息;而 stat 函数返回的是该链接指向文件的信息。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if( argc<2 )
{
perror("a.out ");
exit(1);
}
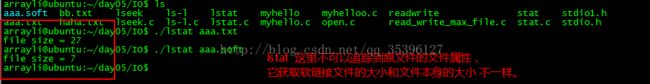
struct stat st;
int ret = lstat(argv[1],&st);
if( ret == -1)
{
perror("lstat");
exit(1);
}
int size = st.st_size;
printf("file size = %d\n",size);
return 0;
}
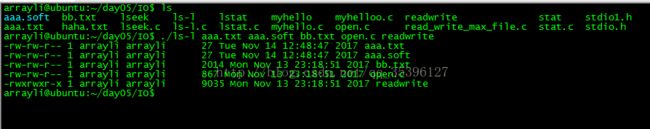
五、使用 stat() 函数实现一个简单的 ls -l Shell 命令:
#include
#include
#include
#include // 所有者信息
#include // 所属组信息
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if( argc<2 )
{
perror("./a.out filename\n");
exit(1);
}
struct stat st;
int i;
for( i = 1; ipw_name;
// 文件所属组
char *filegroup = getgrgid(st.st_gid)->gr_name;
// 文件大小
int size = (int)st.st_size;
// 文件修改时间
char *time = ctime(&st.st_mtime);
char mtime[512]="";
strncpy(mtime,time,strlen(time)-1);
// 保存输出信息格式
char buf[1024]={0};
// 把对应信息按格式输出到 buf 中
sprintf(buf,"%s %d %s %s %d %s %s",perms,nums,fileuser,filegroup,size,mtime,argv[i]);
// 打印 buf
printf("%s\n",buf);
// drwxrwxr-x 3 arrayli arrayli 4096 11月 13 23:19 day05
// -rw-r--r-- 1 arrayli arrayli 8980 11月 7 22:05 examples.desktop
}
return 0;
}