(算法)java完成解析数学算式(计算器)三 —— 用栈解析
一、程序要求
解析一般数学算式,实现简单的带括号的加减乘除运算。
二、基本思路
前面两篇介绍了直接解析字符串和用数组容器辅助解析的两种方式,这次再介绍最常用的解析算法——解析后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)。
三、逆波兰表达式及其得到算法
1、逆波兰表达式
也即后缀表达式,指的是不包含括号,运算符放在两个运算对象的后面,所有的计算按运算符出现的顺序,严格从左向右进行(不再考虑运算符的优先规则)。(摘自百度),既然没了运算符的优先规则,那么计算机解析起来自然容易的多。
对于我们常见的表达式,称为中缀表达式,每个中缀表达式都有对应的后缀表达式。如:
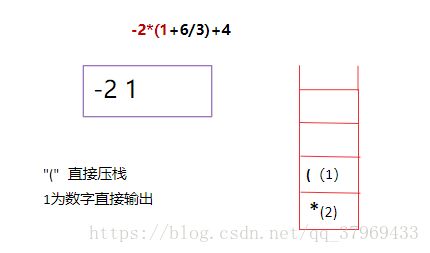
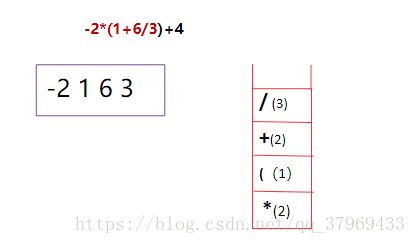
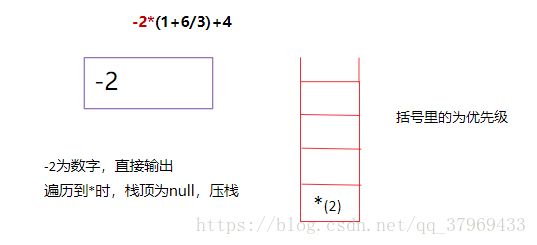
中缀表达式:-2*(1+6/3)+4
后缀表达式:-2 1 6 3 / + * 4 +(这里为了区分负号和减号,我在数字与数字、数字与符号之间都加了空格,至于怎么从中缀表达式得到后缀表达式,后面有介绍及参考程序)
而在解析后缀表达式时,只需要遵守以下原则即可:
- 从左往右遍历
- 遇到数字直接放入容器
- 遇到运算符,将最后两个数字取出,进行该运算,将结果再放入容器
- 遍历结束后,容器中的数字即为运算结果
按这个过程走下来,自然而然的想到用栈是最合适的。
现只需想办法由输入的中缀表达式转为后缀表达式即可完成解析。
2、由中缀表达式得到后缀表达式的算法
由中缀表达式得到后缀表达式,只要遵守以下步骤即可:
- 首先设置运算符的优先级(这样设置也是为了简化程序):
- ”null” 栈顶若为空,假设优先级为0
- “(” 优先级设为1
- “+-” 优先级设为2
- “*/” 优先级设为3
- 从左向右遍历中缀表达式
- 遇到数字直接输出
- 遇到符号
- 遇到左括号,直接压栈
- 遇到右括号,弹栈输出直到弹出左括号(左括号不输出)
- 遇到运算符,比较栈顶符号,若该运算符优先级大于栈顶,直接压栈;若小于栈顶,弹栈输出直到大于栈顶,然后将改运算符压栈。
- 最后将符合栈弹栈并输出
现根据这个原则,手动模拟一遍转换过程:
还是以-2*(1+6/3)+4为例

四、代码一
环境:
- Eclipse Java EE IDE(Version: Oxygen.1a Release (4.7.1a))
- jdk1.8.0_131
先写一个最基本的两位数四则运算方法,比较简单,没有写注释:
private static double doubleCal(double a1, double a2, char operator) throws Exception {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
return a1 + a2;
case '-':
return a1 - a2;
case '*':
return a1 * a2;
case '/':
return a1 / a2;
default:
break;
}
throw new Exception("illegal operator!");
}写一个获得优先级的方法:
private static int getPriority(String s) throws Exception {
if(s==null) return 0;
switch(s) {
case "(":return 1;
case "+":;
case "-":return 2;
case "*":;
case "/":return 3;
default:break;
}
throw new Exception("illegal operator!");
}将中缀表达式转变为后缀表达式:
private static String toSufExpr(String expr) throws Exception {
System.out.println("将"+expr+"解析为后缀表达式...");
/*返回结果字符串*/
StringBuffer sufExpr = new StringBuffer();
/*盛放运算符的栈*/
Stack operator = new Stack();
operator.push(null);//在栈顶压人一个null,配合它的优先级,目的是减少下面程序的判断
/* 将expr打散分散成运算数和运算符 */
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(?);//这个正则为匹配表达式中的数字或运算符
Matcher m = p.matcher(expr);
while (m.find()) {
String temp = m.group();
if (temp.matches("[+\\-*/()]")) { //是运算符
if (temp.equals("(")) { //遇到左括号,直接压栈
operator.push(temp);
System.out.println("'('压栈");
} else if (temp.equals(")")) { //遇到右括号,弹栈输出直到弹出左括号(左括号不输出)
String topItem = null;
while (!(topItem = operator.pop()).equals("(")) {
System.out.println(topItem+"弹栈");
sufExpr.append(topItem+" ");
System.out.println("输出:"+sufExpr);
}
} else {//遇到运算符,比较栈顶符号,若该运算符优先级大于栈顶,直接压栈;若小于栈顶,弹栈输出直到大于栈顶,然后将改运算符压栈。
while(getPriority(temp) <= getPriority(operator.peek())) {
sufExpr.append(operator.pop()+" ");
System.out.println("输出sufExpr:"+sufExpr);
}
operator.push(temp);
System.out.println("\""+temp+"\""+"压栈");
}
}else {//遇到数字直接输出
sufExpr.append(temp+" ");
System.out.println("输出sufExpr:"+sufExpr);
}
}
String topItem = null;//最后将符合栈弹栈并输出
while(null != (topItem = operator.pop())) {
sufExpr.append(topItem+" ");
}
return sufExpr.toString();
} 解析中缀表达式的方法:
public static String getResult(String expr) throws Exception {
String sufExpr = toSufExpr(expr);// 转为后缀表达式
System.out.println("开始计算后缀表达式...");
/* 盛放数字栈 */
Stack number = new Stack();
/* 这个正则匹配每个数字和符号 */
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("-?\\d+(\\.\\d+)?|[+\\-*/]");
Matcher m = p.matcher(sufExpr);
while (m.find()) {
String temp = m.group();
if (temp.matches("[+\\-*/]")) {// 遇到运算符,将最后两个数字取出,进行该运算,将结果再放入容器
System.out.println("符号"+temp);
double a1 = number.pop();
double a2 = number.pop();
double res = doubleCal(a2, a1, temp.charAt(0));
number.push(res);
System.out.println(a2 + "和" + a1 + "弹栈,并计算" + a2 + temp + a1);
System.out.println("数字栈:" + number);
} else {// 遇到数字直接放入容器
number.push(Double.valueOf(temp));
System.out.println("数字栈:" + number);
}
}
return number.pop() + "";
} 主方法,以-3.5*(4.5-(4+(-1-1/2)))测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "-3.5*(4.5-(4+(-1-1/2)))";
System.out.println(getResult(str));
}五、执行结果
六、简化过程分析
根据这个算法,在不需要解出后缀表达式的情况下,还可以将代码进一步简化。
在解析的过程的中,我们只需要按照以下原则:
- 使用两个栈,一个数字栈,一个符号栈
- 从左往右遍历表达式字符串
- 遇到数字,直接压入数字栈
- 遇到符号
- 遇到左括号,直接入符号栈
- 遇到右括号,”符号栈弹栈取栈顶符号b,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a1,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a2,计算a2 b a1 ,将结果压入数字栈”,重复引号步骤至取栈顶为左括号,将左括号弹出
- 遇到运算符,1)若该运算符的优先级大于栈顶元素的优先级,直接入符号栈。2)若小于,”符号栈弹栈取栈顶符号b,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a1,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a2,计算a2 b a1 ,将结果压入数字栈”,重复引号步骤至该运算符的优先级大于符号栈顶元素的优先级,然后将该符号入符号栈
- 遍历结束后,”符号栈弹栈取栈顶符号b,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a1,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a2,计算a2 b a1 ,将结果压入数字栈”,重复引号步骤至符号栈无符号(或数字栈只有一个元素),则数字栈的元素为运算结果
七、代码二
环境:
- Eclipse Java EE IDE(Version: Oxygen.1a Release (4.7.1a))
- jdk1.8.0_131
先写一个最基本的两位数四则运算方法,比较简单,没有写注释:
private static double doubleCal(double a1, double a2, char operator) throws Exception {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
return a1 + a2;
case '-':
return a1 - a2;
case '*':
return a1 * a2;
case '/':
return a1 / a2;
default:
break;
}
throw new Exception("illegal operator!");
}写一个获得优先级的方法:
private static int getPriority(String s) throws Exception {
if(s==null) return 0;
switch(s) {
case "(":return 1;
case "+":;
case "-":return 2;
case "*":;
case "/":return 3;
default:break;
}
throw new Exception("illegal operator!");
}解析表达式:
public static String getResult(String expr) throws Exception {
System.out.println("计算"+expr);
/*数字栈*/
Stack number = new Stack();
/*符号栈*/
Stack operator = new Stack();
operator.push(null);// 在栈顶压人一个null,配合它的优先级,目的是减少下面程序的判断
/* 将expr打散为运算数和运算符 */
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(?);// 这个正则为匹配表达式中的数字或运算符
Matcher m = p.matcher(expr);
while(m.find()) {
String temp = m.group();
if(temp.matches("[+\\-*/()]")) {//遇到符号
if(temp.equals("(")) {//遇到左括号,直接入符号栈
operator.push(temp);
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
}else if(temp.equals(")")){//遇到右括号,"符号栈弹栈取栈顶符号b,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a1,数字栈弹栈取栈顶数字a2,计算a2 b a1 ,将结果压入数字栈",重复引号步骤至取栈顶为左括号,将左括号弹出
String b = null;
while(!(b = operator.pop()).equals("(")) {
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
double a1 = number.pop();
double a2 = number.pop();
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
System.out.println("计算"+a2+b+a1);
number.push(doubleCal(a2, a1, b.charAt(0)));
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
}
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
}else {//遇到运算符,满足该运算符的优先级大于栈顶元素的优先级压栈;否则计算后压栈
while(getPriority(temp) <= getPriority(operator.peek())) {
double a1 = number.pop();
double a2 = number.pop();
String b = operator.pop();
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
System.out.println("计算"+a2+b+a1);
number.push(doubleCal(a2, a1, b.charAt(0)));
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
}
operator.push(temp);
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
}
}else {//遇到数字,直接压入数字栈
number.push(Double.valueOf(temp));
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
}
}
while(operator.peek()!=null) {//遍历结束后,符号栈数字栈依次弹栈计算,并将结果压入数字栈
double a1 = number.pop();
double a2 = number.pop();
String b = operator.pop();
System.out.println("符号栈更新:"+operator);
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
System.out.println("计算"+a2+b+a1);
number.push(doubleCal(a2, a1, b.charAt(0)));
System.out.println("数字栈更新:"+number);
}
return number.pop()+"";
} 主方法,以-3.5*(4.5-(4+(-1-1/2)))测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "-3.5*(4.5-(4+(-1-1/2)))";
System.out.println(getResult(str));
}