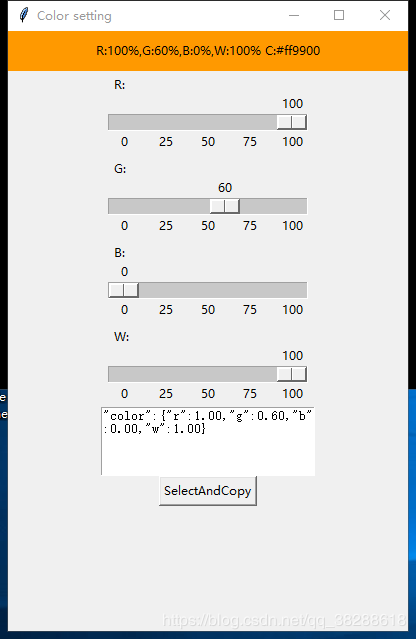
python tkinter调整label背景颜色的测试
调整label背景颜色测试截图
我们都知道,一般来说每个像素的数据包括rgb三个通道用三个字节来表示
如0xff9900 中 ff是红色的量 99是绿色的量 00是蓝色的量
代码实现了用 scale滑动条来调节 rgb的占比,从而调节颜色
源码
import tkinter as tk
window = tk.Tk() # 实例化一个窗口
window.title('Color setting') # 定义窗口标题
window.geometry('400x600') # 定义窗口大小
l = tk.Label(window, bg='yellow', width=200, height=2, text='empty')
l.pack()
r,g,b,w=100,100,100,100
def print_selection():
global r,g,b,w
#转化16进制并格式化
rv =hex(int(255.0*(float(r)*float(w)/10000.0)))#0x xx 不合适
srv='%02x'%int(255.0*(float(r)*float(w)/10000.0))
sgv = '%02x' % int(255.0 * (float(g) * float(w) / 10000.0))
sbv = '%02x' % int(255.0 * (float(b) * float(w) / 10000.0))
#print(srv)
bgstr="#"+srv+sgv+sbv
l.configure(bg=bgstr)
l.config(text='R:' + str(r) + '%,G:' + str(g) + '%,B:' + str(b) + '%,W:' + str(w)+"% C:"+bgstr)
jsonstr="\"color\":{\"r\":%1.2f,\"g\":%1.2f,\"b\":%1.2f,\"w\":%1.2f}"%(float(r)/100.0,float(g)/100.0,float(b)/100.0,float(w)/100.0)
fresh(jsonstr)
def setR(v):
global r
r=v
print_selection()
def setG(v):
global g
g=v
print_selection()
def setB(v):
global b
b=v
print_selection()
def setW(v):
global w
w=v
print_selection()
rs = tk.Scale(window, label='R:', from_=0, to=100, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200, showvalue=1, tickinterval=25,
resolution=1, command=setR)
rs.pack() # 显示名字 从5-11 条方向 长度(像素),是否直接显示值,标签的单位长度,保留精度 ,定义功能
rs.set(r)
gs = tk.Scale(window, label='G:', from_=0, to=100, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200, showvalue=1, tickinterval=25,
resolution=1, command=setG)
gs.pack()
gs.set(g)
bs = tk.Scale(window, label='B:', from_=0, to=100, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200, showvalue=1, tickinterval=25,
resolution=1, command=setB)
bs.pack()
bs.set(b)
ws = tk.Scale(window, label='W:', from_=0, to=100, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, length=200, showvalue=1, tickinterval=25,
resolution=1, command=setW)
ws.pack()
ws.set(w)
text1 = tk.Text(window,width=30,height=5)
text1.pack()
text1.insert(tk.INSERT,'I love you')
def fresh(t):
text1.delete(1.0, tk.END)
text1.insert(tk.INSERT, t)
def show():
T1 = text1.get(0.0, tk.END)
print(T1)
def cut(event=None):
text1.event_generate("<>")
def copy(event=None):
text1.get('sel.first', 'sel.last')
text1.event_generate("<>")
def paste(event=None):
text1.event_generate('<>')
# Select all the text in textbox
def select_all(event=None):
text1.tag_add(tk.SEL, "1.0", tk.END)
text1.mark_set(tk.INSERT, "1.0")
text1.see(tk.INSERT)
copy()
return 'break'
button = tk.Button(window,text="SelectAndCopy",command=select_all)
button.pack()
text1.focus_set()
#button.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=1)
#text1.window_create(tk.INSERT,window=button)
window.mainloop()