Concurrent并发包
1.Executor
为什么使用线程池:
降低资源消耗:通过重用已经创建的线程来降低线程创建和销毁的消耗
提高响应速度:任务到达时不需要等待线程创建就可以立即执行
提高线程的可管理性:线程池可以统一管理、分配、调优和监控
说说几种常见的线程池及使用场景
1.newFixedThreadPool(固定大小的线程池)
2.newSingleThreadExecutor(单线程线程池)
3.newCachedThreadPool(可缓存线程的线程池)
4.newScheduledThreadPool(固定调度线程池)
四种线程池的常用创建
ExecutorService Cachedservice= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
从源码看到,这些实例化线程池的代码,其实都调用了ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledExecutorService的构造方法,ScheduledExecutorService继承自ThreadPoolExecutor,因此最终所有线程池的构造函数都调用了ThreadPoolExecutor的构造函数。
每种线程池的特点:
newFixThreadPool:创建一个固定线程的线程池。线程的存活时间是0L,可以一直存活,队列使用LinkdedBlockingQueue(无界队列)。所以可以使用在任务量固定,耗时较长的任务。
newSingleThreadExecutor:创建一个线程的线程池,存活时间0L,使用无界队列。所以适用于多个任务顺序执行的场景。
newCachedThreadPool:创建一个核心线程为0,最大线程数为Integer最大值,队列使用同步队列,线程存活时间为60s,所以该线程池适合数量大但是耗时短的任务。
newScheduledThreadPool:创建固定大小的线程池,存活时间为0,队列使用DelayWorkQueue,一个按超时时间排序的队列。所以它适用与定时任务或者周期性任务
ConcurrentHashmap
BlockQueue:
ArrayBlockingQueue与LinkedBlockingQueue。
locks部分
主要就是AQS,重入锁。
AQS:操作资源的方式有独占和共享两种方式,在理解它之前,先去了解它如何使用,我们随便写一个类,再写一个内部类继承AQS,重写特定的方法就可以使用,因为有独占和共享两种方式所以也有对应的方法,独占有tryAcquire和tryRelease。共享有tryAcquireShared和tryReleaseShared。AQS的核心由一个阻塞队列和一个volatile修饰的state变量组成。AQS可以通过cas对state变量进行修改,一般来说,state为0时表示无锁状态,state大于0时表示有线程获得锁。从代码上看,如果我们调用lock方法是,触发Acquire方法,该方法又会去调用tryAcquire方法以cas的方式尝试获取锁,如果获取失败,就调用addWaiter方法把当前线程包装为Node对象添加到阻塞队列中。然后调用acquireQueued方法通过自旋去获取锁。
什么叫公平锁与非公平锁呢?
公平锁意思就是根据线程请求锁的顺序来获取锁,先来后到。
非公平锁意思就是多个线程获取锁的顺序不是按照申请锁的顺序,可能后申请的线程先拿到锁。
同步工具:一次性栅栏:CountDownLatch
我们可以启动多个线程来调用CountDownLatch对象的await方法,来等待条件的满足,我们可以在countdownlatch的构造方法中定义要满足多少个条件。如果说有条件满足,就可以调用CountdownLatch的countdown()方法,使得要满足的条件减一,当所有的条件满足时,也就是构造方法中的值减为0,那么所有的线程都被唤醒。
CountDownLatch底层实现还是AQS,用一个内部类继承AQS然后重写tryAcquireShared和tryReleaseShared。将实例化输入的参数设置到state上去,当满足条件调用countDown方法时u,status值减一,当减到0的时候,唤醒线程继续运行。
atomic
原子变量:
原子引用AtomicReference:实现对引用类型的原子性更改
映射到代码上如何使用呢?
先创建一个AtomicReference对象,在构造方法中实例化一个我们需要进行原子更改的引用类型。
然后使用for循环启动十个线程,使用AtomicReference对象的get方法获取原先初始化好的对象,然后再额外实例化一个该对象,在构造方法中对两个属性进行+1操作,然后调用AtomicReference的compareandSet方法,传入原先的对象和新对象。等累加操作完成后调用AtomicReference的get方法获取对象的属性,可以看到其中的属性累加成功。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
AtomicReference<Element> reference = new AtomicReference<>(new Element(0,0));
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executorService.execute(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
boolean flag=false;
while(!flag){
Element e1=reference.get();
Element e2=new Element(e1.x+1,e1.y+1);
flag=reference.compareAndSet(e1,e2);
}
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("element.x="+reference.get().x+ ",element.y=" + reference.get().y);
}
}
class Element{
int x;
int y;
public Element(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
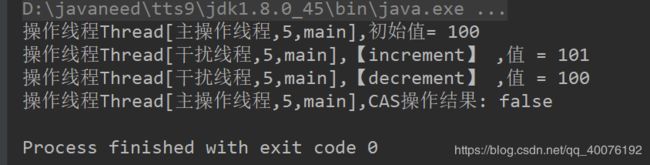
AtomicStampedReference解决ABA问题
//构造方法, 传入引用和戳
public AtomicStampedReference(V initialRef, int initialStamp)
//返回引用
public V getReference()
//返回版本戳
public int getStamp()
//如果当前引用 等于 预期值并且 当前版本戳等于预期版本戳, 将更新新的引用和新的版本戳到内存
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp)
示例代码:
public class AtomicStampedTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference
= new AtomicStampedReference(100,0);
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() +",初始值= " + atomicStampedReference.getReference());
int stamp=atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isCASSuccess=atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,101,
stamp,stamp+1);
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() +",CAS操作结果: " + isCASSuccess);
},"主操作线程").start();
new Thread(()->{
Thread.yield();
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,101,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1);
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() +
",【increment】 ,值 = "+ atomicStampedReference.getReference());
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(101,100,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1);
System.out.println("操作线程" + Thread.currentThread() +
",【decrement】 ,值 = "+ atomicStampedReference.getReference());
},"干扰线程").start();