【小王的安卓之路】自定义控件开发(二)之“蛋黄的长裙,蓬松的头发,你想要的样子我都有”
自定义控件开发
想象一下这样一个场景,在电视剧中:
- 男主:“亲爱的,我不在乎你的外貌,也不在乎你的高矮胖瘦,我只在乎你这个人,我爱你”。
- 话音一落,漂亮的女主妹子被感动的稀里哗啦。
- 女主:“555,好感动,我也爱你”
然而在现实生活中:
- 男生:“亲爱的,我不在乎你的外貌,也不在乎你的高矮胖瘦,我只在乎你这个人,我爱你”
- 女生勃然大怒,一巴掌呼了上去
- 女生:“你是觉得老娘长得不好看了?你不爱我了,555”
- 男生:“听我解释,@#¥%#@¥……@#¥@”
又或者是:
- 男生(妹子):“小哥哥(小姐姐),你长得真好看,我能做你男(女)朋友吗?”
- 女生(男生):“哈哈哈谢谢,你是个好人,我要去洗澡了,以后再聊”
你看看,外观无疑是现在人们最先从另外一个人的身上看到的东西,也是最容易给别人留下好感的东西,手机APP也是。比如某音,如果功能照旧,按钮什么别的东西都是不加修饰的原生按钮,那相比用的人也 不会很多。然而,谷歌提供给我们的控件就那么多,终究会遇到找不到合适的控件的情况。在上篇文章里我提到了用组合的方式创造了一个新的控件,这次我来和大家分析新的一招:
无中生有
-----摘自《郭语·第一章》
想要自定义控件,首先我们得明确一点,我的需求是什么:
我想要一个会渐变色的按钮?还是能感应手机壳颜色的的背景色?还是五彩斑斓的黑色头像?
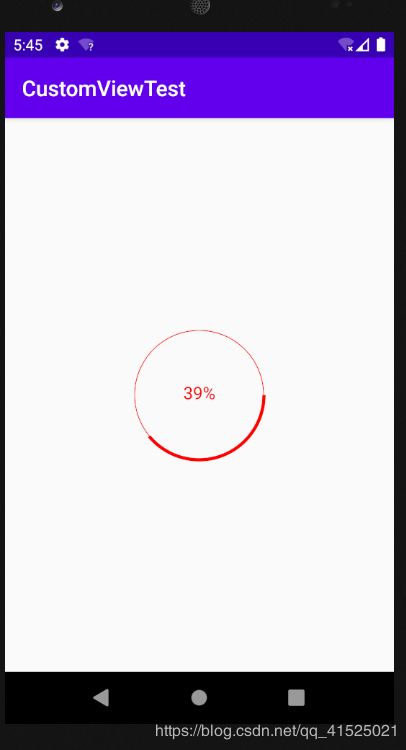
那么假设现在有这样一个需求:安卓原生的进度条太难看了,我想要自定义一个,圆形的,会动的,能显示百分比的。
好的我们先分析一下,得出以下几点要素:
- 是一个进度条
- 圆的
- 能显示百分比
- 会动的
安排!!!
首先要明确自定义控件的开发步骤:
- 自定义属性的声明和获取
- 测量
- 绘制
- 状态的存储和恢复
.
.
.
步骤一:定义属性
我们在新建一个类,叫做:RoundProgressBar,并让他继承自View类,然后重写它的构造方法
public class RoundProgressBar1 extends View {
//一般情况下重写两个参数的构造函数就行
public RoundProgressBar1(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
}
然后我们在values文件夹中新建一个叫做attrs.xml文件(如果有就直接用就行)
开始定义这个控件的属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="RoundProgressBar"> //name要和我们的类名对应
<attr name="color" format="color"/> //进度条的颜色
<attr name="line_width" format="dimension"/>//进度条的宽度
<attr name="radius" format="dimension"/>//圆形的半径
<attr name="android:progress" />//进度(这里我们用了原生的属性)
<attr name="android:textSize" />//显示百分比的字体大小
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
然后我们在类中定义属性来记录这些变量
private int mColor;
private int mRadius;
private int mLineWidth;
private int mTextSize;
private int mProgress ;
然后在构造方法中,我们获取这些属性:
public RoundProgressBar(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//获取TypedArray 对象
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.RoundProgressBar);
//获取半径,默认值为dp2px(30)
mRadius = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_radius,dp2px(30));
//获取颜色,默认值为红色
mColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_color,0xffff0000);
//获取线的宽度
mLineWidth = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_line_width,dp2px(3));
//获取字体大小
mTextSize = (int)ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_textSize,dp2px(16));
//获取进度
mProgress = ta.getInt(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_progress,0);
//回收TypedArray 对象
ta.recycle();
}
其中dp2px()方法长这样:
private float dp2px(int i) {
return TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP,i,getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
然后再布局文件里我们就可以使用这个控件的属性了:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:wang="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" ///这个命名控件是一定要写的,前面的wang可以随意替换
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.example.customviewtest.RoundProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressbar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
wang:radius="60dp"
android:progress="10"
wang:line_width="3dp"
android:padding="10dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
我们可以尝试在构造方法中打一个log,看看是否能正常获取到我们赋值的属性。
步骤二:测量
这里直接开始写测量,不知道View绘制流程的可以看看我之前的一片文章:安卓View绘制的相关知识点
我们直接在RoundProgressBar这个类中重写onMeasure()这个方法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int with_mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);//获取测量模式
int width_size = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);//获取父控件测量出来的宽度值
//测量宽度
int width = 0;
if(with_mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
{
//如果测量模式是EXACTLY,那宽度就取决于xml里写的值
width = width_size;
}
else
{
int width_measure = meaasureWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (width == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
{
//如果测量模式是AT_MOST,就选取较小的
width = Math.min(width_size,width_measure);
}
else
{
//如果测量模式是UNSPECIFICED,则是需要你自己测量
width = width_measure;
}
}
//测量高度
int height_mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int height_size = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int height = 0;
if(height_mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
{
height = height_size;
}
else
{
int height_measure = meaasureHeight() +getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
if (height_mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
{
height = Math.min(height_size,height_measure);
}
else
{
height = height_measure;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(width,height);
}
//因为我们测量的是一个圆,所以宽度和高度都是圆的半径*2
private int meaasureHeight() {
return mRadius*2;
}
private int meaasureWidth() {
return mRadius*2;
}
大多数控件的测量方式就是这样,一般情况下我们只需改动meaasureHeight()和meaasureWidth()方法即可。
步骤三:绘制
首先我们需要一支笔,
private Paint mPaint;
然后在构造方法中,在对ra进行回收后,对笔进行初始化:
private void initPaint() {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);//设置抗锯齿
}
重写onDraw()方法:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//设置笔的空心/实心
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth/4);//设置笔的宽度
int width = getWidth();//获取控件宽度
int height = getHeight();//获取控件高度
//先画一个比较细的圆
canvas.drawCircle(width/2,height/2,width/2-getPaddingLeft()-mPaint.getStrokeWidth()/2,mPaint);
//画一个粗一些的圆
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth);
canvas.save();
//移动画笔的中心点
canvas.translate(getPaddingLeft(),getPaddingTop());
float angle = mProgress*1.0f/100*360;//计算绘制的弧度
//绘制弧线
canvas.drawArc(new RectF(0,0,width-getPaddingLeft()*2,height-getPaddingLeft()*2),0,angle,false,mPaint);
canvas.restore();
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
String text = mProgress+"%";
mPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
int y = getHeight()/2;
Rect bound = new Rect();
mPaint.getTextBounds(text,0,text.length(),bound);
int textHeight = bound.height();
//绘制字体
canvas.drawText(text,0,text.length(),getWidth()/2,y+textHeight/2-mPaint.descent()/2,mPaint);
}
在onDraw()方法中,最重要的就是canvas对象和paint对象的相关API,不管绘制什么控件都是一样的步骤。
步骤四:状态的存储和恢复
重写这两个方法就行:
public static final String KEY_PROGRESS = "progress";
public static final String KEY_INSTANCE = "instance";
@Nullable
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt(KEY_PROGRESS,mProgress);
bundle.putParcelable(KEY_INSTANCE,super.onSaveInstanceState());
return bundle;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (state instanceof Bundle)
{
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) state;
mProgress = bundle.getInt(KEY_PROGRESS);
Parcelable parcelable = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INSTANCE);
super.onRestoreInstanceState(parcelable);
return;
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
最后给这个控件加上获取和设置进度的方法:
public void setProgress(int progress)
{
mProgress = progress;
invalidate();//重新绘制
}
public int getProgress()
{
return mProgress;
}
然后再Activity中,我们只需获取这个控件,然后给他设置属性动画即可:
final View progress = findViewById(R.id.progressbar);
ObjectAnimator.ofInt(progress,"progress",0,100).setDuration(3000).start();