Frames in networking
Q:Which layer of Tcp/Ip stack works with frames?
A:
From above figure,we can know easily know it that frames works in Layer 2 of Tcp/Ip stack model. Layer 2 is also known as Data Link layer.Above figure,Tcp/ip model has 5 layers,but sometimes it has 4 layers.Get further reading,you can click this link:Does Tcp/Ip model has 4 layers or 5 layers .Layer 1 is also known as Physical layer.
Q: What's difference between frame and packet?
A:Frame only works within Lan but can't work outside Lan.Each mac address is only meaningful within its layer segment (layer 2),mac address of frame is assigned by device manufactuer.
Packet only works in Wan(aka outside Lan),ip adress of packet is assigned by ISP.
Q:How physical address change hop to hop?
A:It's the mac address of data packet which change from hop to hop.
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/74343
Q:Format of frames in networking that captured using wireshark.
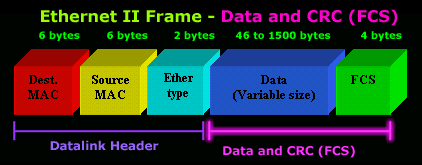
A:The following is a description of the frame format describled by the original Ethernet Version 2 specification as released by DEC,Intel,and Xerox.Like the 802.3 spec,the Version 2 spec defines a Datalink Header consisting of 14 bytes(6+6+2) of information,but the Version 2 spec does not specify an LLC Header.
Let's now have a closer look at the Ethernet 2 frame format.
The Data Link Header
Now ,I show a screenshot related Ethernet 2 frame.
OFFSET 0-5 The Destination Address
- The first six bytes of an Ethenet frame make up the Destination Address.The Destination specifies to which adapter the data frame is being sent.A Destination Address of all ones specifies a Broadcast Message that is read in by all receiving Ethernet adapters.
- The first three bytes of the Destinaiotn Address are assigned by the IEEE to the vendor of the adapter and are specific to the vendor.
- TheDestination Address format is indentical in all implementations of Etherenet.
- From above figure.we can know it that frame's destination address is 04:40:a9:65:f8:02
Offset 6-11:The Source Address
- The next six bytes of an Ethernet frame make up the Source Address.The Source Address specifies from which adapter the message originated Like the Destination Address,the first three bytes specify the vendor of the card.
- The Source Address format is identical in all implementations of Ethernet.
- From above figure.we can know it that frame's source destination is 80:a5:89:ca:ee:63
Offset 12-13:The Ethertype
- Following the Source Address is a 2 byte field called the Ethertype.The Ethertype is analogous to SAPs in the 802.3 frame in that it specifies the memory buffer in which to place this frame.
- From above figure,we can know it that frame 's thertype is IPV4.
User Data and FCS
Data:46-1500 Bytes
- Followng the Ethertype are 46 to 1500 bytes of data,generally consisting of upper layer header such as TCP/IP or IPX and then the actual user data.
FCS:Last 4 Bytes
- The last 4 bytes that the adapter reads in are the Frame Check Sequence of CRC.When the voltage on the wire returns to zero,the adapter checks the last 4 bytes it received against a checksum that is generate via a complex polynomial.If the calculated checksum does not match the check sum on the frame,the frame is discarded and never reaches the memory buffer in the station.
- Most NIC(drivers) strip CRC(FCS) ,before passing to the system.That means wireshark does not toget to see the CRC(FCS). So we can't see CRC(FCS) in wireshark.
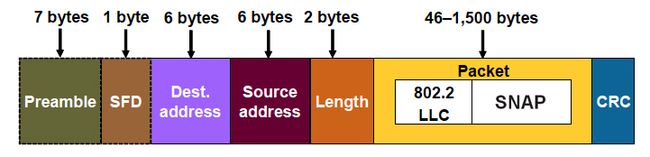
Q:What's the difference between Ethernet 802.3 and Ethernet 2?
A:The biggest difference Ethenet 2 and 802.3 is the fields of their Ethernet headers.Ethernet 2 and 802.3 is the fields of their
Ehernet headers.Ethernet 2 is much more popular for reasons that I'll make clear shortly.Its header fields are:
- Preamble:This offers synchronization since both sender and receiver interface cards are running with different system clocks.
- Start frame delimiter: This tells the Ethernet software where to start reading the frame.
- Source address: The MAC address of the sending device.
- Type field: Sets the kind of packet that is in the data field. Its also called Ether Type.
- Data field: Carries the data application data plus networking overhead.
- Frame check sequence: The sending NIC does a calculation on the bit stream and puts the result in this field. The receiver of the frame then does the same calculation on the bit stream that it received and compares the two values. If the bit stream has been changed, the match will fail, and the frame will be throwaway.
There are frame formats from the IEEE:IEEE 802.3,IEEE 802.0 with SNAP,and 802.3 with 802.2 Modem operating systems can send and receive any of these frame formats.The main difference between Version 2 and IEEE frames is that the Type field in Version 2 has beeb replaced with a with a 2-byte Length field in the IEEE formats. To run TCP/IP over IEEE 802.3, the SNAP format has to be used. That requires 8 bytes of the data field to identify the kind of data the frame is carrying: three bytes for the Logical Link Control, three bytes for the SNAP header, and two bytes for the Protocol Type field. That means the data field shrinks from the standard range of 46 to 1500 bytes down to a range of 38 to 1492. This is the reason most network managers stay with Ethernet II. The Ether Type field contains two bytes of hexadecimal code. This table translates the codes to some of the more commonly used codes:
| Ether Type | Protocol |
| 0x0800 | Internet Protocol, Version 4 (IPv4) |
| 0x0806 | Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) |
| 0x8035 | Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) |
| 0x8100 | VLAN-tagged frame (IEEE 802.1Q) |
| 0x814C | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) |
| 0x86DD | Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) |
| 0x8847 | MPLS unicast |
| 0x8848 | MPLS multicast |
| 0x8870 | Jumbo Frames |
| 0x888E | EAP over LAN (IEEE 802.1X) |
| 0x88E5 | MAC security (IEEE 802.1AE) |
| 0x88F7 | Precision Time Protocol (IEEE 1588) |
References:
https://networkengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/49427/how-physical-addresses-change-hop-to-hop
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/74343
https://superuser.com/questions/647016/does-tcp-ip-model-has-4-layers-or-5-layers
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_layer
https://www.globalknowledge.com/us-en/resources/resource-library/articles/what-is-the-difference-between-ethernet-ii-and-ieee-8023/
https://osqa-ask.wireshark.org/questions/20862/how-to-display-the-packets-crc-in-the-gui-and-how-to-edit-crc-with-bad-value
http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/ethernet/ethernet-frame-formats/201-ethernet-ii.html