并发编程-Thread类源码解析及线程状态分析
并发编程-Thread类源码解析及线程状态分析
1、常用方法 源码解析
2、线程状态详细分析
构造函数源码解析:
Thread类对外开放的 public 构造
public Thread() {
this((ThreadGroup)null, (Runnable)null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0L);
}
public Thread(Runnable target) {
this((ThreadGroup)null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0L);
}
Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) {
this((ThreadGroup)null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0L, acc, false);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) {
this(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0L);
}
public Thread(String name) {
this((ThreadGroup)null, (Runnable)null, name, 0L);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) {
this(group, (Runnable)null, name, 0L);
}
public Thread(Runnable target, String name) {
this((ThreadGroup)null, target, name, 0L);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) {
this(group, target, name, 0L);
}
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) {
this(group, target, name, stackSize, (AccessControlContext)null, true);
}
/**
* @param g 指定此线程属于线程组
* @param target runnable 对象
* @param name 线程名
* @param stackSize 最大线程栈 大小
* @param inheritThreadLocals 是否继承 父线程的 threadlocal 属性值
*/
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
this(group, target, name, stackSize, (AccessControlContext)null, inheritThreadLocals);
}
私有 构造
/**
* @param g 指定此线程属于线程组
* @param target runnable 对象
* @param name 线程名
* @param stackSize 最大线程栈 大小
* @param acc
* @param inheritThreadLocals
*/
private Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc, boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
this.daemon = false;
this.stillborn = false;
this.threadLocals = null;
this.inheritableThreadLocals = null;
this.blockerLock = new Object();
// 所有的线程必须有名字
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
} else {
this.name = name;
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
// 如果线程组为 null
// 1 首先从 当前安全管理器中 获取 线程组
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
// 2 如果 仍没有 线程组
// 从 当前线程(很大可能 mian 线程) 获取 线程组
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
// 线程组校验
g.checkAccess();
if (security != null && isCCLOverridden(this.getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
// 线程组 添加未开始的 线程数
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
// 线程是否是守护线程 和 优先级 都有继承性
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security != null && !isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) {
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
} else {
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
}
this.inheritedAccessControlContext = acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
this.setPriority(this.priority);
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) {
//InheritableThreadLocal主要用于子线程创建时,自动继承父线程的ThreadLocal变量,方便必要信息的进一步传递。
this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
}
this.stackSize = stackSize;
this.tid = nextThreadID();
}
}
线程默认名称
private static int threadInitNumber;
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {
return threadInitNumber++;
}
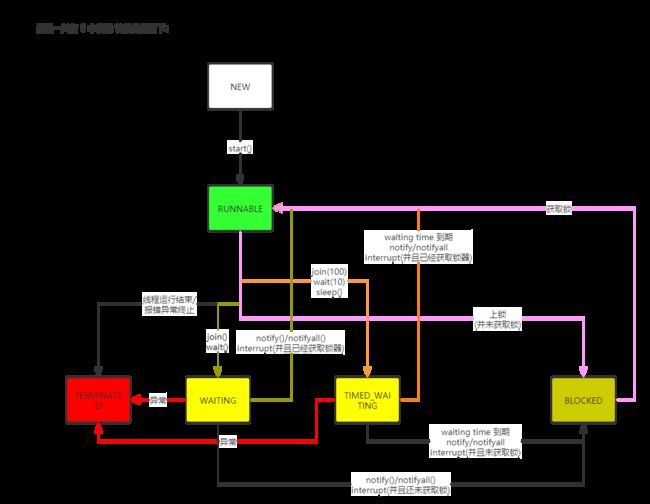
线程状态
/** Thread 类 内部 枚举
* 线程状态一共有 6 种
*/
public static enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
private State() {
}
}
线程状态图
线程实例方法源码解析
start()
Description
Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine calls the run method of this thread.
Code
/**
*/
public synchronized void start() {
if (this.threadStatus != 0) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
} else {
// 往线程组中添加 该线程
this.group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
// 线程开始 是 native 方法
this.start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
// 如果 线程启动失败 从 该 线程组中 remove 掉 此线程
if (!started) {
this.group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable var8) {
}
}
}
}
private native void start0();
run()
Description
If this thread was constructed using a separate Runnable run object, then that Runnable object’s run method is called; otherwise, this method does nothing and returns.
Code
/**
*/
public void run() {
// 直接调用 runnable 中的 run() 方法体的逻辑
if (this.target != null) {
this.target.run();
}
}
interrupt()
Description
Interrupts this thread.
Code
/**
* 添加 中断标识
* interrupt() 方法只是改变中断状态而已,它不会中断一个正在运行的线程
* 如果线程被Object.wait, Thread.join和Thread.sleep三种方法之一阻塞,此时调用该线程的interrupt()方
* 法,那么该线程将抛出一个 InterruptedException中断异常(该线程必须事先预备好处理此异常)从而提早地终结
* 被阻塞状态
*/
public void interrupt() {
if (this != currentThread()) {
// Determines if the currently running thread has permission to modify this thread.
// 校验 是否有权限 线程修改
this.checkAccess();
synchronized(this.blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = this.blocker;
if (b != null) {
this.interrupt0();
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
}
this.interrupt0();
}
setPriority(int newPriority)
/**
* 设置线程优先级
* newPriority 越大 优先级越高
*/
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
// 校验 你是否有权限 线程修改
this.checkAccess();
// 线程优先级 区间[1,10]
if (newPriority <= 10 && newPriority >= 1) {
ThreadGroup g;
if ((g = this.getThreadGroup()) != null) {
// 调整 线程优先级 最大 不超过 所在线程组的最大值(默认10 可能小于10)
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
this.setPriority0(this.priority = newPriority);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
getPriority()
/**
* 获取线程优先级
**/
public final int getPriority() {
return this.priority;
}
join()
Description
Waits for this thread to die.
Code
/**
* 让线程进入 waiting 状态
* 如果 millis == 0L 线程进入 waiting
* 如果 millis > 0L 线程进入 timed waiting
**/
public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0L;
if (millis < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
} else {
if (millis == 0L) {
while(this.isAlive()) {
this.wait(0L);
}
} else {
while(this.isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0L) {
break;
}
// 使用wait 方法 所以 会 释放 cpu占用
this.wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
}
// 等待这个线程死亡的时间最多是毫秒 加 纳秒。
public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
} else if (nanos >= 0 && nanos <= 999999) {
if (nanos >= 500000 || nanos != 0 && millis == 0L) {
++millis;
}
this.join(millis);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
}
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
this.join(0L);
}
线程static方法
sleep(long var0)
Description
Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers.
Code
// 线程 进入 waitting timed 状态
// 不会释放cpu 资源(这是和 wait 和 join 很大 区别)
public static native void sleep(long var0) throws InterruptedException;
public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
} else if (nanos >= 0 && nanos <= 999999) {
if (nanos >= 500000 || nanos != 0 && millis == 0L) {
++millis;
}
sleep(millis);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
}
yield()
Description
A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of a processor.
Code
/**
* Java线程中的Thread.yield( )方法,译为线程让步。顾名思义,就是说当一个线程使用了这个方法之后,它就会把自* 己CPU执行的时间让掉,让自己或者其它的线程运行,注意是让自己或者其他线程运行,并不是单纯的让给其他线程
*
* example 小朋友们 一起抢一个球 现在被我抢到了,我突然大喊“我把球重新丢出去,谁先抢到是谁的”(注意是我
* 们,包含自己),然后大家重新进入抢球大战
* 与wait 区别是 wait 让出 cpu资源 自己不在加入 抢资源的 大军
*/
public static native void yield();
note: 文章用于学习交流,如有错误之处,请大家指正