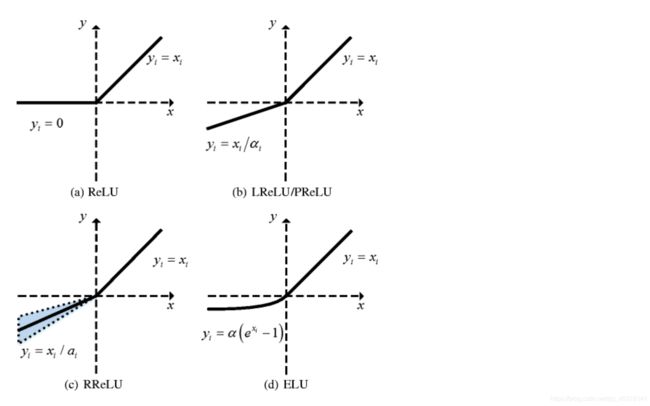
图注意力网络(GAT)
@TOC
一、INTRODUCTION
图注意力网络(GAT)Graph attention network缩写为GAT,若按照首字母大写,会与对抗生成网络GAN混淆。所以后面GAT即本文的图注意力网络。
论文地址 https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
代码地址: https://github.com/Diego999/pyGAT
1.1 相关研究
- Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks,ICLR 2017,图卷积网络
- Graph Attention Networks,ICLR 2018. 图注意力网络
- Relational Graph Attention Networks ,ICLR2019 关联性图注意力网络,整合了GCN+Attention+Relational
1.2. attention 引入目的
- 为每个节点分配不同权重
- 关注那些作用比较大的节点,而忽视一些作用较小的节点
- 在处理局部信息的时候同时能够关注整体的信息,不是用来给参与计算的各个节点进行加权的,而是表示一个全局的信息并参与计算
2 GAT ARCHITECTURE
本文作者提出GATs方法,利用一个隐藏的self-attention层,来处理一些图卷积中的问题。不需要复杂的矩阵运算或者对图结构的事先了解,通过叠加self-attention层,在卷积过程中将不同的重要性分配给邻域内的不同节点,同时处理不同大小的邻域。作者分别设计了inductive setting和transductive setting的任务实验,GATs模型在基线数据集Cora、Citeseer、Pubmed citation和PPI数据集上取得了state-of-the-art的结果。
2.1 Graph Attentional Layer
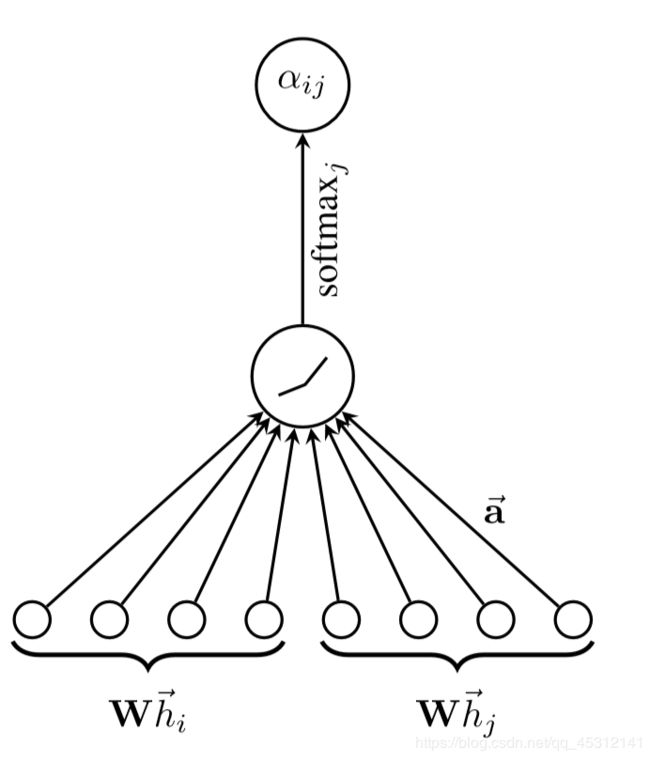
和所有的attention mechanism一样,GAT的计算也分为两步:计算注意力系数(attention coefficient)和加权求和(aggregate)

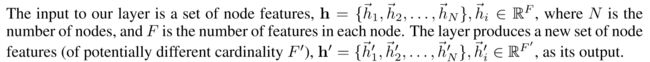
2.2. 计算相互关注
def forward(self, x):
# [B_batch,N_nodes,C_channels]
B, N, C = x.size()
# h = torch.bmm(x, self.W.expand(B, self.in_features, self.out_features)) # [B,N,C]
h = torch.matmul(x, self.W) # [B,N,C]
a_input = torch.cat([h.repeat(1, 1, N).view(B, N * N, C), h.repeat(1, N, 1)], dim=2).view(B, N, N,
2 * self.out_features) # [B,N,N,2C]
# temp = self.a.expand(B, self.out_features * 2, 1)
# temp2 = torch.matmul(a_input, self.a)
attention = self.leakyrelu(torch.matmul(a_input, self.a).squeeze(3)) # [B,N,N]
attention = F.softmax(attention, dim=2) # [B,N,N]
attention = F.dropout(attention, self.dropout, training=self.training)
h_prime = torch.bmm(attention, h) # [B,N,N]*[B,N,C]-> [B,N,C]
out = F.elu(h_prime + self.beta * h)
return out
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GATLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, g, in_dim, out_dim):
super(GATLayer, self).__init__()
self.g = g
# equation (1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(in_dim, out_dim, bias=False)
# equation (2)
self.attn_fc = nn.Linear(2 * out_dim, 1, bias=False)
def edge_attention(self, edges):
# edge UDF for equation (2)
z2 = torch.cat([edges.src['z'], edges.dst['z']], dim=1)
a = self.attn_fc(z2)
return {'e': F.leaky_relu(a)}
def message_func(self, edges):
# message UDF for equation (3) & (4)
return {'z': edges.src['z'], 'e': edges.data['e']}
def reduce_func(self, nodes):
# reduce UDF for equation (3) & (4)
# equation (3)
alpha = F.softmax(nodes.mailbox['e'], dim=1)
# equation (4)
h = torch.sum(alpha * nodes.mailbox['z'], dim=1)
return {'h': h}
def forward(self, h):
# equation (1)
z = self.fc(h)
self.g.ndata['z'] = z
# equation (2)
self.g.apply_edges(self.edge_attention)
# equation (3) & (4)
self.g.update_all(self.message_func, self.reduce_func)
return self.g.ndata.pop('h')
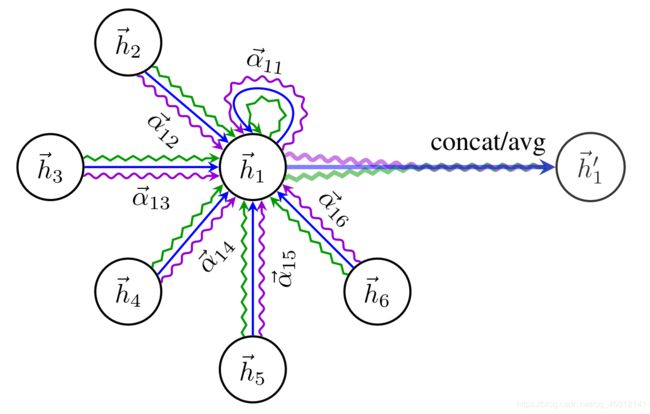
加权求和(aggregate)
2.3.multi-head attention机制
Conclusion
本文提出了一种基于self-attention的图模型。总的来说,GAT的特点主要有以下两点:
- 与GCN类似,GAT同样是一种局部网络。因此,(相比于GNN或GGNN等网络)训练GAT模型无需了解整个图结构,只需知道每个节点的邻节点即可。
3 利用相似度

论文:Attention-based Graph Neural Network for semi-supervised learning
代码:dawnranger/pytorch-AGNN
参考:
1、DGL博客 | 深入理解图注意力机制