python绘图汇总
绪论
机器学习,我们一般需要先对数据进行分析,又称EDA( Exploratory Data Analysis ). 分类、回归等问题Eda方法会有所偏差。而EDA一般都是通过绘制图进行展示。
本文主要收集常用的Eda方法。
1、数据相关性分析
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
correlations = data.corr() #计算变量之间的相关系数矩阵
# plot correlation matrix
fig = plt.figure() #调用figure创建一个绘图对象
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
cax = ax.matshow(correlations, vmin=-1, vmax=1) #绘制热力图,从-1到1
fig.colorbar(cax) #将matshow生成热力图设置为颜色渐变条
#ticks = np.arange(10)
# ax.set_xticks(ticks) #生成刻度
# ax.set_yticks(ticks)
names = data.columns.tolist()
ax.set_xticklabels(names) #生成x轴标签
ax.set_yticklabels(names)
plt.show()
此外,如果想获得较为精确的数值时,可以考虑:
#比较不同df, 同一个column下的相关性。
import numpy as np
for col in [‘a’, 'b']:
print(col)
print(np.corrcoef(sub1[col],sub2[col])[0,1])
其他绘制相关性图:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
data_corr=dataset.corr().abs()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
print(" the correlation between features :")
sns.heatmap(data_corr,annot=True,cmap='Blues')
更新2018.12.31
2、4种可视化方法
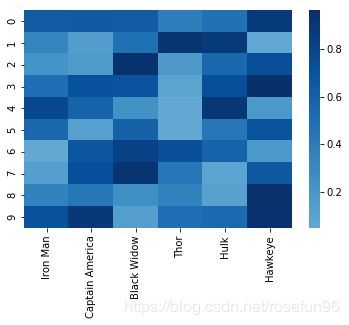
2.1 热力图
# Importing libs
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create a random dataset
data = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random((10,6)), columns=["Iron Man","Captain America","Black Widow","Thor","Hulk", "Hawkeye"])
print(data)
# Plot the heatmap
heatmap_plot = sns.heatmap(data, center=0, cmap='Blues')
plt.show()
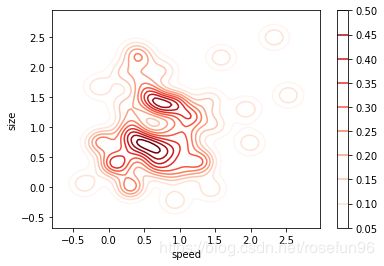
2.2 二维密度图
二维密度图可以看到两个变量的概率分布。
# Importing libs
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import skewnorm
# Create the data
speed = skewnorm.rvs(4, size=50)
size = skewnorm.rvs(4, size=50)
# Create and shor the 2D Density plot
ax = sns.kdeplot(speed, size, cmap="Reds", shade=False, bw=.15, cbar=True)
ax.set(xlabel='speed', ylabel='size')
plt.show()
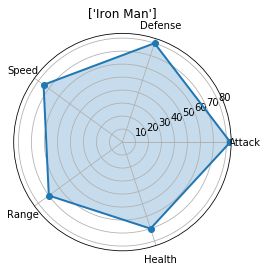
2.3 蜘蛛网图
蜘蛛网图可以显示一对多关系。
# Import libs
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Get the data
df=pd.DataFrame(index = [0], columns = ['Name', 'Attack', 'Defense', 'Speed',
'Range', 'Health'], data = [['Iron Man',83, 80, 75, 70, 70]])
print(df)
"""
# Name Attack Defense Speed Range Health
0 1 Iron Man 83 80 75 70 70
1 2 Captain America 60 62 63 80 80
2 3 Thor 80 82 83 100 100
3 3 Hulk 80 100 67 44 92
4 4 Black Widow 52 43 60 50 65
5 5 Hawkeye 58 64 58 80 65
"""
# Get the data for Iron Man
labels=np.array(["Attack","Defense","Speed","Range","Health"])
stats=df.loc[0,labels].values
# Make some calculations for the plot
angles=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, len(labels), endpoint=False)
stats=np.concatenate((stats,[stats[0]]))
angles=np.concatenate((angles,[angles[0]]))
# Plot stuff
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True)
ax.plot(angles, stats, 'o-', linewidth=2)
ax.fill(angles, stats, alpha=0.25)
ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels)
ax.set_title([df.loc[0,"Name"]])
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
2.4 树状图
# Import libs
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy.cluster import hierarchy
import numpy as np
# Read in the dataset
# Drop any fields that are strings
# Only get the first 40 because this dataset is big
df = pd.read_csv('Pokemon.csv')
df = df.set_index('Name')
del df.index.name
df = df.drop(["Type 1", "Type 2", "Legendary"], axis=1)
df = df.head(n=40)
# Calculate the distance between each sample
Z = hierarchy.linkage(df, 'ward')
# Orientation our tree
hierarchy.dendrogram(Z, orientation="left", labels=df.index)
plt.show()
这里没有数据,原链接;
2 matplotlib 绘图
此外,使用 python Matploblib绘图。
参考:
- python 作图;
- python 4中可视化方法;