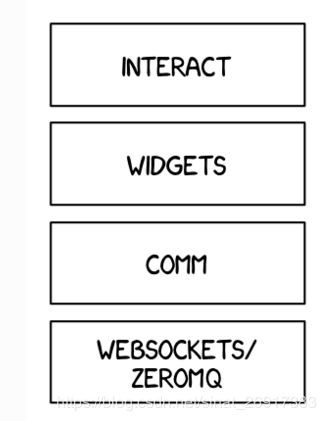
Jupyter notebook最简原型界面设计 - ipywidgets与lineup_widget
Tkinter的GUI设计 和 django页面设计,那么笔者只是想快速做个demo原型,以上的内容能不能结合着来,有一些简单的交互 + web可以快速访问的到,于是就看到了jupyter notebook这两个库,非常简单的玩具,来看看呗~
ipywidgets比较强调输入项的各式花样,但是其对输出内容的格式的花样非常少。
文章目录
- 一 ipywidgets
- 1.1 基础组件
- 1.1.1 button 按钮
- 1.1.2 IntSlider、FloatSlider
- 1.1.3 FloatProgress / IntProgress
- 1.1.4 Text、Textarea
- 1.1.5 图片Image
- 1.2 单控件 - interact 简单交互
- 1.3 单控件 - interact_manual简单交互
- 1.4 单控件 - interactive_output + HBox交互
- 1.5 单控件 - 文本交互
- 1.6 两个控件 - 组合交互jslink
- 1.7 多模块 - 控件独立分屏Accordion
- 1.8 一些小案例
- 1.8.1 图形 + 滑块
- 1.8.2 一个可控的进度读条
- 1.8.3 颜色筛选器
- 1.8.4 复杂输入框
- 二 lineup_widget
- 2.1 安装
- 2.2 主函数
- 2.3 案例
- 案例一:
- 案例二:
- 2.4 ipywidgets与lineup_widget共同使用的案例
- 三 相似的Jupyter画图小模块
- 3.1 d3-slider widget
- 3.2 drawing-pad
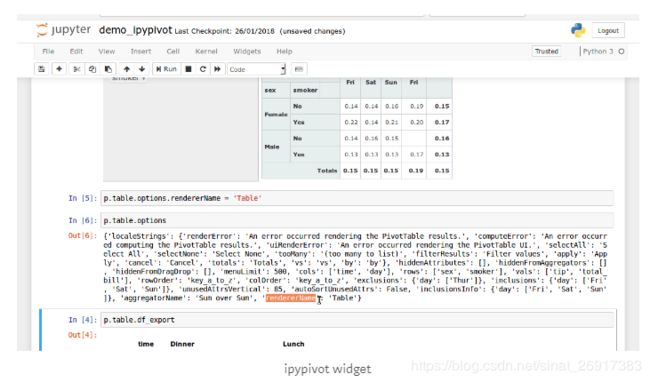
- 3.3 ipypivot
一 ipywidgets
文档:https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html
github:https://github.com/jupyter-widgets/ipywidgets
安装:
# 方式一
pip install ipywidgets
jupyter nbextension enable --py widgetsnbextension
# 方式二
conda install -c conda-forge ipywidgets
效果:
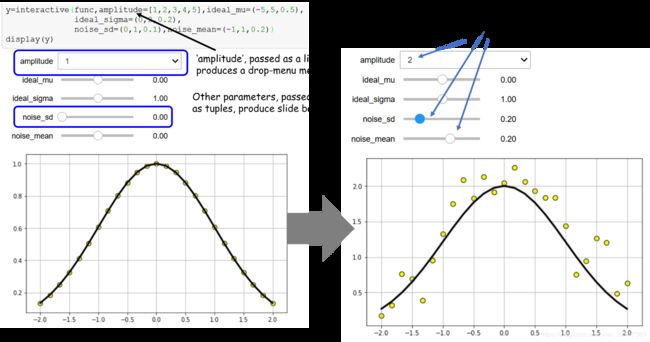
(参考自:A very simple demo of interactive controls on Jupyter notebook)
(参考于:Interactive Visualizations In Jupyter Notebook)
来看一些组件与模块。
1.1 基础组件
主要参考:Widget List
1.1.1 button 按钮
widgets.Button(
description='Click me',
disabled=False,
button_style='success', # 'success', 'info', 'warning', 'danger' or ''
tooltip='Click me',
icon='check'
)
# 调整按钮
from ipywidgets import Button, Layout
b = Button(description='(50% width, 80px height) button',
layout=Layout(width='50%', height='80px'),
button_style='success')
b
1.1.2 IntSlider、FloatSlider
widgets.FloatSlider(
value=7.5,
min=0,
max=10.0,
step=0.1,
description='Test:',
disabled=False,
continuous_update=False,
orientation='horizontal',
readout=True,
readout_format='.1f',
)
1.1.3 FloatProgress / IntProgress
widgets.IntProgress(
value=7,
min=0,
max=10,
step=1,
description='Loading:',
bar_style='', # 'success', 'info', 'warning', 'danger' or ''
orientation='horizontal'
)
widgets.FloatProgress(
value=7.5,
min=0,
max=10.0,
step=0.1,
description='Loading:',
bar_style='info',
orientation='horizontal'
)
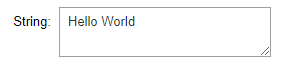
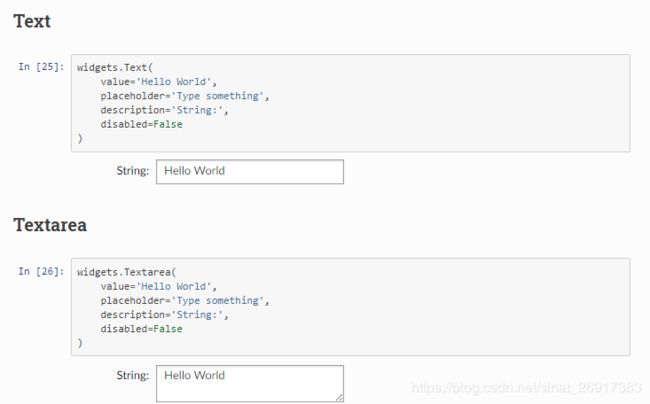
1.1.4 Text、Textarea
widgets.Text(
value='Hello World',
placeholder='Type something',
description='String:',
disabled=False
)
widgets.Textarea(
value='Hello World',
placeholder='Type something',
description='String:',
disabled=False
)
一般来说,textarea比text更好用,模块是可伸缩的。
1.1.5 图片Image
file = open("images/WidgetArch.png", "rb")
image = file.read()
widgets.Image(
value=image,
format='png',
width=300,
height=400,
)
1.2 单控件 - interact 简单交互
from __future__ import print_function
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive, fixed, interact_manual
import ipywidgets as widgets
def f(segx,opt):
if opt:
return segx
else:
return 1
interact(f, segx=10, opt = True)
interact代表交互,第一个f代表函数,segx与opt都代表f函数的参数。
- segx代表滑条
- opt = True/False代表选项框
注意interact,相当于给函数f赋值,除了第一个,之后的参数都是第一个函数的参数,名字需对齐。
1.3 单控件 - interact_manual简单交互
from ipywidgets import FloatSlider
# 横轴进度可以拖拽
def slow_function(i):
print(int(i),list(x for x in range(int(i)) if
str(x)==str(x)[::-1] and
str(x**2)==str(x**2)[::-1]))
return
interact_manual(slow_function,i=FloatSlider(min=1e5, max=1e7, step=1e5));
FloatSlider表示拖拽滑块,interact_manual(函数,函数参数),此时函数参数是由拖拽滑块FloatSlider来确定。
与interact的区别:
interact是实时改变,interact_manual是人工点击RUN才能执行一次。

1.4 单控件 - interactive_output + HBox交互
from IPython.display import display, HTML
a = widgets.IntSlider()
b = widgets.IntSlider()
c = widgets.IntSlider()
ui = widgets.HBox([a, b, c])
def f(a, b, c):
print((a, b, c))
out = widgets.interactive_output(f, {'a': a, 'b': b, 'c': c})
display(ui, out)
a,b,c是三个滑块,通过widgets.HBox进行拼接成为一个Box组件。
interactive_output(函数,函数参数),函数参数是一个组合Box组件。
display是展示滑块组合以及输出项。

1.5 单控件 - 文本交互
widgets.Textarea(
value='Hello World', # 默认语句
placeholder='Type something',
description='String:', # 框的名字
disabled=False # 是否可修改
)
1.6 两个控件 - 组合交互jslink
# jslink
# 两个控件的交互
a = widgets.FloatText()
b = widgets.FloatSlider()
display(a,b)
mylink = widgets.jslink((a, 'value'), (b, 'value'))
jslink把控件a,b组合起来,a是文本控件,b是数值控件。

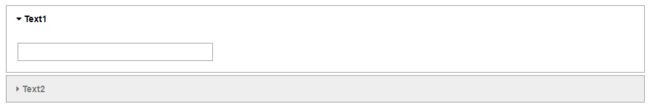
1.7 多模块 - 控件独立分屏Accordion
accordion = widgets.Accordion(children=[widgets.Text(), widgets.Text()])
accordion.set_title(0, 'Text1')
accordion.set_title(1, 'Text2')
accordion
可以把两个组件独立的链接在一起,而不是如jslink交互影响。
# 选项分屏
tab_contents = ['P0', 'P1', 'P2', 'P3', 'P4']
children = [widgets.Text(description=name) for name in tab_contents]
tab = widgets.Tab()
tab.children = children
for i in range(len(children)):
tab.set_title(i, str(i))
tab
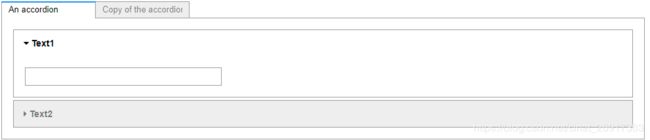
# 双模块分屏 + 选项分屏
tab_nest = widgets.Tab()
tab_nest.children = [accordion, accordion]
tab_nest.set_title(0, 'An accordion')
tab_nest.set_title(1, 'Copy of the accordion')
tab_nest
1.8 一些小案例
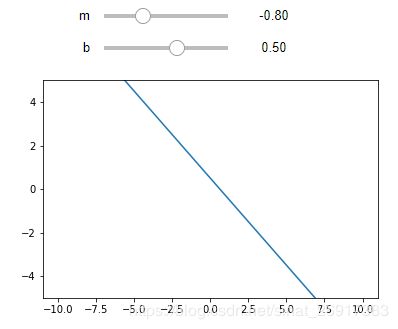
1.8.1 图形 + 滑块
%matplotlib inline
from ipywidgets import interactive
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def f(m, b):
plt.figure(2)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, num=1000)
plt.plot(x, m * x + b)
plt.ylim(-5, 5)
plt.show()
interactive_plot = interactive(f, m=(-2.0, 2.0), b=(-3, 3, 0.5))
# m代表范围
output = interactive_plot.children[-1]
output.layout.height = '350px'
interactive_plot
interactive(函数,函数参数),m/b都是可变滑块。
第二个案例:
来着:Mastering widgets in the Jupyter Notebook
@widgets.interact_manual(
color=['blue', 'red', 'green'], lw=(1., 10.))
def plot(freq=1., color='blue', lw=2, grid=True):
t = np.linspace(-1., +1., 1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 6))
ax.plot(t, np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * t),
lw=lw, color=color)
ax.grid(grid)
interact_manual是单控件函数交互,此时通过装饰器,interact_manual(函数,函数参数)中的函数被隐去。

1.8.2 一个可控的进度读条
# 一个可控的进度条
play = widgets.Play(
# interval=10,
value=0,
min=0,
max=100,
step=1,
description="Press play",
disabled=False
)
#slider = widgets.IntSlider()
slider = widgets.FloatProgress(
value=50,
min=0,
max=100.0,
step=1,
description='Loading:',
bar_style='success',
orientation='horizontal'
)
widgets.jslink((play, 'value'), (slider, 'value'))
widgets.HBox([play, slider])
Play是一个控制按钮,FloatProgress是一个数值进度条。
通过jslink将两个空间链接,点击按钮就Loading就可以开始走动。
![]()
1.8.3 颜色筛选器
# 颜色选择器
widgets.ColorPicker(
concise=False,
description='Pick a color',
value='blue',
disabled=False
)
点击之后就会出现颜色筛选内容,筛选出来的结果为该颜色的具体数值,#800080
![]()

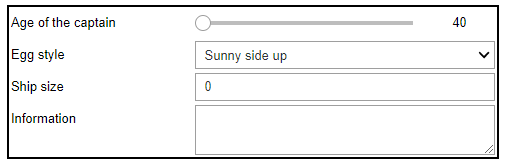
1.8.4 复杂输入框
# 复合功能
from ipywidgets import Layout, Button, Box, FloatText, Textarea, Dropdown, Label, IntSlider
form_item_layout = Layout(
display='flex',
flex_flow='row',
justify_content='space-between'
)
form_items = [
Box([Label(value='Age of the captain'), IntSlider(min=40, max=60)], layout=form_item_layout),
Box([Label(value='Egg style'),
Dropdown(options=['Scrambled', 'Sunny side up', 'Over easy'])], layout=form_item_layout),
Box([Label(value='Ship size'),
FloatText()], layout=form_item_layout),
Box([Label(value='Information'),
Textarea()], layout=form_item_layout)
]
form = Box(form_items, layout=Layout(
display='flex',
flex_flow='column',
border='solid 2px',
align_items='stretch',
width='50%'
))
form
form_item_layout统一的Box布局,
Dropdown是下拉框,一个Box是一个独立组件。
form_items是多个Box的组合,Box( [Label(),Textarea()] , layout ) => Box( [前缀名,控件函数] , 布局 )
.
二 lineup_widget
github:https://github.com/datavisyn/lineup_widget
这是一个专门为展示dataframe + ipywidgets而来的包。
参考:Jupyter Widget
2.1 安装
## install Jupyter Widgets
pip install ipywidgets
jupyter nbextension enable --py widgetsnbextension
## install library
pip install lineup_widget
jupyter nbextension enable --py --sys-prefix lineup_widget
2.2 主函数
w = lineup_widget.LineUpWidget(df, options=dict(rowHeight=20))
_data = List(trait=Dict(), default_value=[]).tag(sync=True)
_columns = List(trait=Dict(), default_value=[]).tag(sync=True)
options = Dict(traits=dict(filterGlobally=Bool(), singleSelection=Bool(), noCriteriaLimits=Bool(), animated=Bool(),
sidePanel=Enum((True, False, 'collapsed')), summaryHeader=Bool(), overviewMode=Bool(),
hierarchyIndicator=Bool(), labelRotation=Int(), ignoreUnsupportedBrowser=Bool(),
rowHeight=Int(), rowPadding=Int(), groupHeight=Int(), groupPadding=Int(),
expandLineOnHover=Bool(), defaultSlopeGraphMode=Enum(('item', 'band'))),
default_value=dict(filterGlobally=True, singleSelection=False, noCriteriaLimits=False, animated=True,
sidePanel='collapsed', summaryHeader=True, overviewMode=False,
hierarchyIndicator=True, labelRotation=0, ignoreUnsupportedBrowser=False,
rowHeight=18, rowPadding=2, groupHeight=40, groupPadding=5,
expandLineOnHover=False, defaultSlopeGraphMode='item'
)).tag(sync=True)
rankings = List(trait=Dict(traits=dict(columns=List(trait=Union((Unicode(), Dict()))), sort_by=List(trait=Unicode()),
group_by=List(trait=Unicode())),
default_value=dict(columns=['_*', '*'], sort_by=[], group_by=[])), default_value=[]).tag(
sync=True)
其中options之中有非常多的参数,由于文档也没具体说明,笔者这边只对几个参数有了解。
其中:sidePanel=Enum((True, False, 'collapsed'))代表侧边的面板是否打开,笔者觉得很碍人,一般是sidePanel = False
2.3 案例
案例一:
import lineup_widget
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,100,size=(100, 4)), columns=list('ABCD'))
w = lineup_widget.LineUpWidget(df)
w.on_selection_changed(lambda selection: print(selection))
w
非常简单,唯一需要整理的就是df,一个DataFrame的格式作为输入,其他不用调整任何东西,就可以使用了。
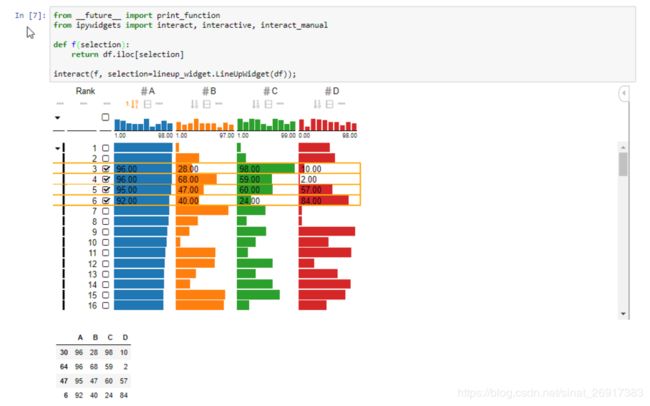
案例二:
from __future__ import print_function
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive, interact_manual
def selection_changed(selection):
return df.iloc[selection]
interact(selection_changed, selection=lineup_widget.LineUpWidget(df));
2.4 ipywidgets与lineup_widget共同使用的案例
from __future__ import print_function
from ipywidgets import interact, interactive, fixed, interact_manual
import ipywidgets as widgets
from IPython.display import display, HTML
def view(down,std):
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,100,size=(100, 4)), columns=list('ABCD'))
if down == 'overall':
df =df
elif down == 'part':
df = df[['A','B']]
if std:
display(df)
else:
w = lineup_widget.LineUpWidget(df, options=dict(rowHeight=50,sidePanel = False))
display(w)
return
down = widgets.Dropdown(
options=['overall','part'],
value='overall',
description='类型:',
disabled=False,
)
interactive(view, down = down , std = True)
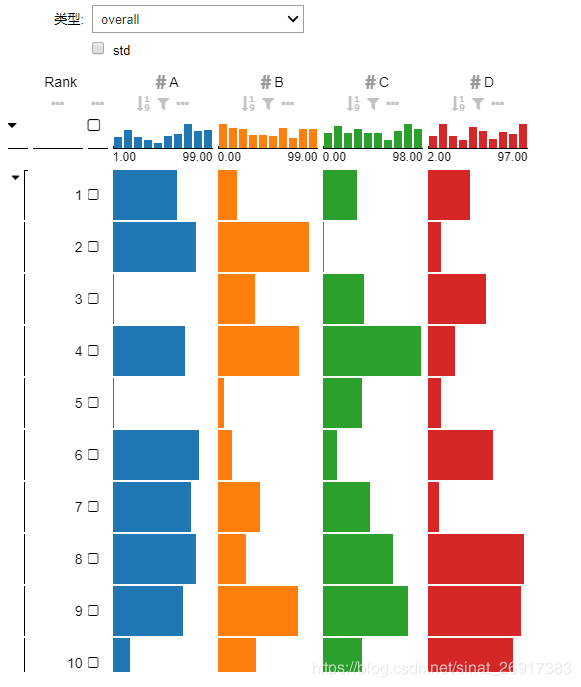
如下图,里面的内容就是可以单独对df这个数据框进行筛选,用display展示出来。
三 相似的Jupyter画图小模块
参考于:Authoring Custom Jupyter Widgets
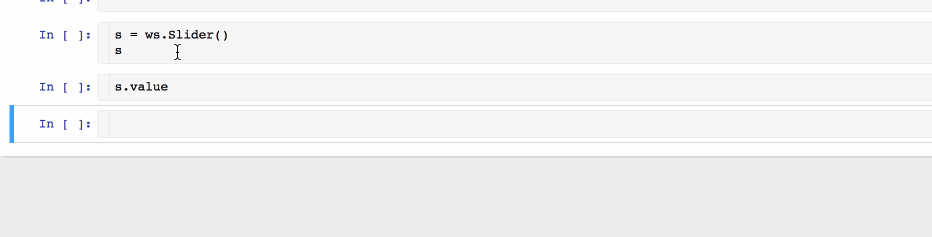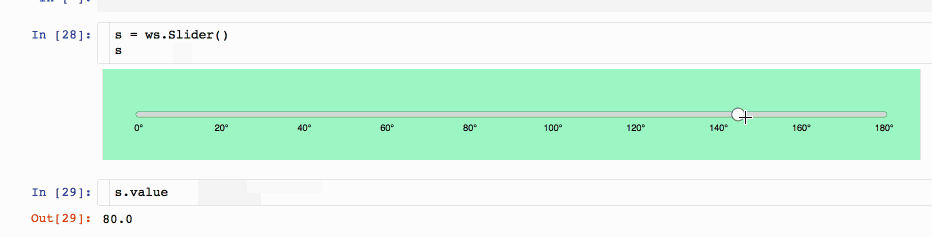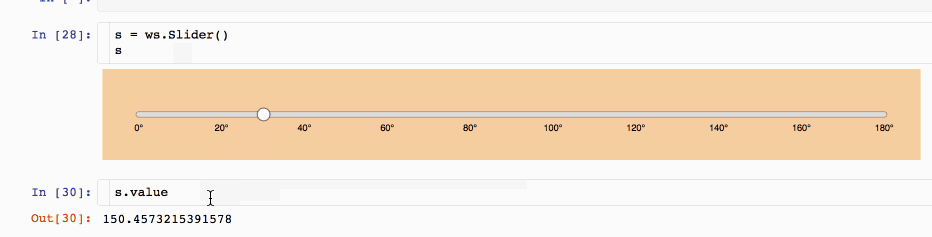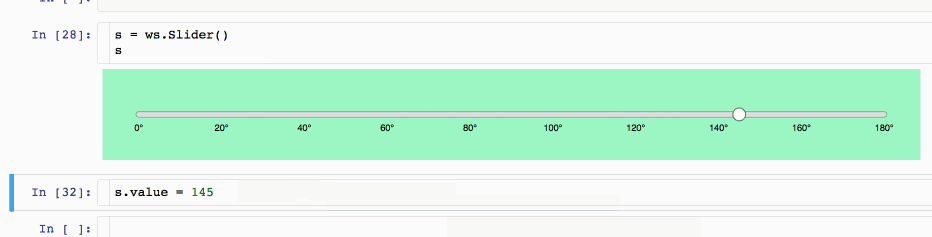
3.1 d3-slider widget
This custom d3-slider widget wraps a simple custom slider based on the fantastic d3.js library. You can run and try it on the Binder repo or watch it on nbviewer.
pip install jupyter_widget_d3_slider
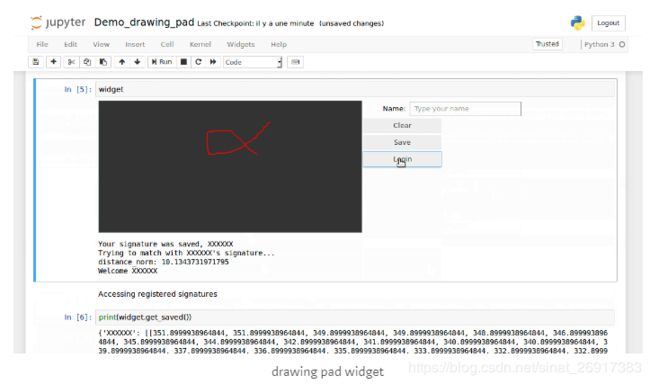
3.2 drawing-pad
This small drawing pad app, is inspired from this codepen. You can run and try it on the Binder repo or watch it on nbviewer.
pip install jupyter-drawing-pad
3.3 ipypivot
The ipypivot widget, wraps the convenient PivotTable.js library. You can run and try it on the binder repo or watch it on nbviewer.
pip install ipypivot