模拟退火(Simulate Anneal)算法
算法介绍
模拟退火算法(Simulate Anneal,SA)是一种通用概率演算法,用来在一个大的搜寻空间内找寻命题的最优解。美国物理学家 N.Metropolis 和同仁在1953年发表研究复杂系统、计算其中能量分布的文章,他们使用蒙特卡罗模拟法计算多分子系统中分子的能量分布。
模拟退火的出发点是基于物理中固体物质的退火过程与一般组合优化问题之间的相似性。模拟退火算法是一种通用的优化算法,其物理退火过程由加温过程、等温过程、冷却过程这三部分组成。
启发来源
在热力学上,退火(annealing)现象指物体逐渐降温的物理现象,温度愈低,物体的能量状态会低;够低后,液体开始冷凝与结晶,在结晶状态时,系统的能量状态最低。大自然在缓慢降温(亦即,退火)时,可“找到”最低能量状态:结晶。但是,如果过程过急过快,快速降温(亦称「淬炼」,quenching)时,会导致不是最低能态的非晶形。
如下图所示,首先(左图)物体处于非晶体状态。我们将固体加温至充分高(中图),再让其徐徐冷却,也就退火(右图)。加温时,固体内部粒子随温升变为无序状,内能增大,而徐徐冷却时粒子渐趋有序,在每个温度都达到平衡态,最后在常温时达到基态,内能减为最小(此时物体以晶体形态呈现)。
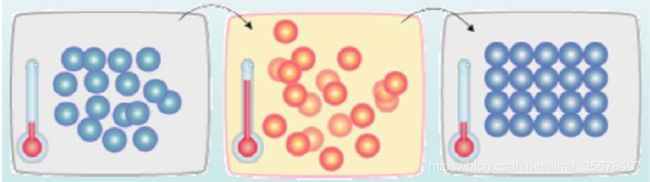
似乎,大自然知道慢工出细活:缓缓降温,使得物体分子在每一温度时,能够有足够时间找到安顿位置,则逐渐地,到最后可得到最低能态,系统最安稳。
爬山算法
爬山算法是一种Greegy算法,该算法每次从当前解的临近解空间中选择一个最优解作为当前解,直到达到一个局部最优解。

如上图:从A开始迭代搜索解空间,寻找最优解,但是该算法采用的是贪心策略,所以当搜索到B点时,发现再往后小幅度移动搜索时,不能得到比B点更好的结果了,至此停止了搜索,陷入到局部最优解的问题中。
模拟退火
介绍了以上的爬山算法,这种贪心算法往往得到的解并不是解空间中的全局最优解,如何有效的避免陷入局部最优解中,模拟退火算法应运而生。
其实模拟退火算法也是一种Greedy算法,但是在搜索最优解过程中,加入了随机的因素,一定的概率接受一个比当前解要差的解,故此,存在一定的概率跳出局部最优解,从而找到真正的全局最优解。
- 算法流程
- 由一个产生函数从当前的解空间 { x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , . . . , x n } \{x_1, x_2, x_3, ..., x_n\} {x1,x2,x3,...,xn}中产生一个新解(一般采用随机方法生成新解,比如交换顺序等)。
- 使用目标函数 f ( x ) f(x) f(x),计算出新解对应的目标值 f ( x n e w ) f(x_{new}) f(xnew)。
- 判断新解是否可以采纳,变成当前的解。采纳采用的准则——Metropolis准则:
p = { 1 , E ( x n e w ) < E ( x o l d ) e x p ( − E ( x n e w ) − E ( x o l d ) T ) , E ( x n e w ) ≥ E ( x o l d ) p = \begin{cases} 1, \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad E(x_{new}) < E(x_{old}) \\ exp(-\frac{E(x_{new}) - E(x_{old})}{T}), \quad E(x_{new}) \ge E(x_{old}) \end{cases} p={1,E(xnew)<E(xold)exp(−TE(xnew)−E(xold)),E(xnew)≥E(xold)
x n e w : 新 解 、 x o l d : 之 前 的 解 、 E ( x n e w ) : 当 前 解 的 能 量 、 T : 当 前 温 度 x_{new}: 新解、x_{old}: 之前的解、E(x_{new}): 当前解的能量、T:当前温度 xnew:新解、xold:之前的解、E(xnew):当前解的能量、T:当前温度根据以上的公式可以发现:随着温度的降低, e x p ( − E ( x n e w ) − E ( x o l d ) T ) exp(-\frac{E(x_{new}) - E(x_{old})}{T}) exp(−TE(xnew)−E(xold))即 P P P采纳比当前解差的新解的概率在不断的降低。其中的温度T,随着时间的流逝存在一个降温的过程,降温的速率可以自己定义,定义降温速率 t _ a l p h a t\_alpha t_alpha。则:温度的变化为: T = T ∗ t _ a l p h a T = T * t\_alpha T=T∗t_alpha - 新解被采纳后,使用新解替代当前解。
以上为一次算法的迭代。
- 算法参数
- 温度初始值T。(影响模拟退火算法全局搜索性能的重要因素之一、初始温度高,则搜索到全局最优解的可能性大,但因此要花费大量的计算时间;反之,则可节约计算时间,但全局搜索性能可能受到影响。)
- 温度降低速率,即退火速率 t _ a l p h a t\_alpha t_alpha。(同上,退火速率快,可节约计算时间,但全局搜索性能可能受到影响。反之)
与普通的贪心算法对比(参考一个比较有趣的解释):
- 普通贪心算法:兔子朝着比现在低的地方跳去。它找到了不远处的最低的山谷。但是这座山谷不一定最低的。
- 模拟退火:兔子喝醉了。它随机地跳了很长时间。这期间,它可能走向低处,也可能踏入平地。但是,它渐渐清醒了并朝最低的方向跳去。这就是模拟退火。
TSP-SA方法
TSP(旅行商问题):一个商品推销员要去若干个城市推销商品,该推销员从一个城市出发,需要经过所有城市后,回到出发地。应如何选择行进路线,以使总的行程最短。从图论的角度来看,该问题实质是在一个带权完全无向图中,找一个权值最小的Hamilton回路。由于该问题的可行解是所有顶点的全排列,随着顶点数的增加,会产生组合爆炸,它是一个NP完全问题。
使用模拟退火算法求解TSP:
class Cities:
"""
storage the information:
- the location dataframe of cities
- the number of cities
- the distance matrix of cities
- the total distance of solution
"""
def __init__(self, coordinates):
self.coordinates = coordinates.copy()
self.city_number = coordinates.shape[0]
self.getDistance()
self.getSolutionDistance()
def getDistance(self):
"""
get the distance matrix of cities
"""
self.distances = np.zeros((self.city_number, self.city_number))
for i in range(self.city_number):
for j in range(i, self.city_number):
self.distances[i][j] = self.distances[j][i] = np.linalg.norm(
self.coordinates.iloc[i] - self.coordinates.iloc[j])
def getSolutionDistance(self):
"""
get the total distance of the array of cities by order
"""
self.solution_distance = 0
for i in range(self.city_number):
self.solution_distance += self.distances[i][(i + 1) % self.city_number]
return self.solution_distance
def getNewSolution(self):
"""
get the new sequence of cities array.
calculate the distance matrix and solution distance
"""
while True: # exchange the city index randomly
index_1 = np.random.randint(self.city_number - 1)
index_2 = np.random.randint(self.city_number - 1)
if index_1 != index_2:
if index_1 > index_2:
index_1, index_2 = index_2, index_1
break
city_index_1 = self.coordinates[index_1: index_1 + 1]
city_index_2 = self.coordinates[index_2: index_2 + 1]
above = self.coordinates[: index_1]
mid = self.coordinates[index_1 + 1: index_2]
below = self.coordinates[index_2 + 1:]
self.coordinates = above.append(city_index_2).append(mid).append(city_index_1).append(below)
self.city_number = self.coordinates.shape[0]
self.getDistance()
self.getSolutionDistance()
def SA(temperature, IN_Loop, temperature_min, best_path, t_alpha, result):
new_path = copy.deepcopy(best_path) # new solution
cur_path = copy.deepcopy(best_path) # current solution
while temperature > temperature_min:
for i in range(IN_Loop): # inner loop times
new_path.getNewSolution()
delta_distance = new_path.solution_distance - cur_path.solution_distance
if delta_distance < 0: # the better path
cur_path = copy.deepcopy(new_path)
else: # replace with random probability
if np.random.rand() < np.exp(- delta_distance / temperature):
cur_path = copy.deepcopy(new_path)
if best_path.solution_distance > cur_path.solution_distance:
# update the best solution
best_path = copy.deepcopy(cur_path)
result.append(best_path.solution_distance)
temperature *= t_alpha
return result
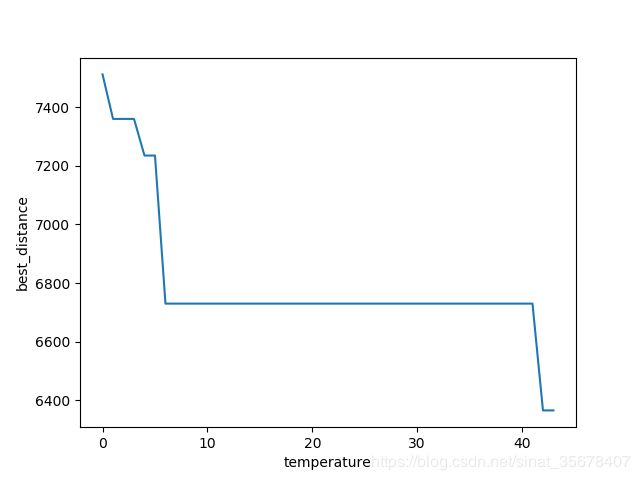
由于考虑到时间和运算,测试使用了15个城市,数据如下:
cities_location = [[565.0, 575.0], [25.0, 185.0], [345.0, 750.0], [945.0, 685.0], [845.0, 655.0],
[880.0, 660.0], [25.0, 230.0], [525.0, 1000.0], [580.0, 1175.0], [650.0, 1130.0],
[1605.0, 620.0], [1220.0, 580.0], [1465.0, 200.0], [1530.0, 5.0], [845.0, 680.0]]
cities = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O']
b = pd.DataFrame(cities_location, columns=['x', 'y'], index=cities)
city_path = Cities(b)
temperature = 100
IN_Loop = 1000
temperature_min = 1
alpha = 0.9
result = list()
result = pd.Series(SA(temperature, IN_Loop, temperature_min, city_path, alpha, result))
plt.plot(result)
plt.ylabel("best_distance")
plt.xlabel("iterators")
plt.show()
参考资料
- 算法大全
- 模拟退火算法 - ranjiewen
- Simulated annealing - Wikipedia