Auto-Machine-Learning初探
前言
最近在看AutoML,业界在 automl 上的进展还是很不错的,个人比较看好这个方向,所以做了一些了解:
- Google: Cloud AutoML, Google’s Prediction API
- Microsoft: Custom Vision, Azure Machine Learning
- Amazon: Amazon Machine Learning
- BaiDu:EasyE
- Alibaba Group:PAI
- others: BigML.com, Wise.io, SkyTree.com, RapidMiner.com, Dato.com, Prediction.io, DataRobot.com,H2O.AI
github上的开源项目也是有不少的,我所看到的包括:
- tpot
- 多项式特征组合
- 无监督特征筛选
- 集成分类
- auto_ml
- 集成分类
- 可选深度模型前置
- auto_sklearn
- 特征清洗
- 特征筛选
- 元学习前置
- 超参数自动学习
- 自动集成分类
auto_sklearn
上述开源项目中,我主要看了auto_sklearn,对他的架构设计,算法设计还是很感兴趣的,论文在这边Efficient and Robust Automated Machine Learning:
-
meta-learning
-
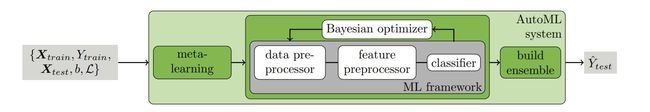
常规 ML framework 如下图灰色部分:导入数据-数据清洗-特征工程-分类器-输出预测值
- 这边都是常规操作,我扩充了他里面的各种方法,总结在数据预处理
-
Bayesian optimizer
- 这个等下细讲,是这个论文中最有价值的地方之一
-
build-ensemble
- 模型集成
Bayesian optimizer
通常我们在参数尝试的时候都是依赖如下:
- 暴力法
- Grid Search 网格搜索/穷举搜索
- Random Search 随机搜索
- Bayesian Optimization
- 能利用先验知识高效地调节超参数,通过减少计算任务而加速寻找最优参数的进程。不依赖人为猜测所需的样本量为多少,优化技术基于随机性,概率分布
- Neural Network
- 用深度神经网络代替常规配置,通过线性+非线性变化拟合任何曲线
Bayesian optimizer在实际被应用的过程中使用的较多,是实现自动参数选择的核心,让我们来仔细看下,伪代码:
- 构建超参数与优化函数的关系(代理函数):比如gbdt中的树数量与output的AUC之间的函数f,这一般都是模型,黑盒的
- 随机初始化原始数据集合
- 通过高斯过程/随机森林等对代理函数进行建模
- 设计acquisition function,(EI,UCB,TS等),获取最大acquisition function对于假设数据集作为新增数据集
- 把新增数据集扩充到2中的数据集中重复更新整个过程
上述代码实现,非常简单,完整代码自取GP_Bayes_Optimizaion
init:
init_xs = np.random.uniform(bound_dict.get("x", [0, 0])[0],bound_dict.get("x", [1, 1])[1],size=self.init_point_number)
init_ys = np.random.uniform(bound_dict.get("y", [0, 0])[0], bound_dict.get("y", [1, 1])[1],size=self.init_point_number)
init_points = zip(init_xs, init_ys)
init_labels = map(self.target_loss_function, init_xs)
train_features = np.asarray(list(init_points))
train_negative_loss = np.asarray(list(init_labels))
current_max_negative_loss = max(train_negative_loss)
Acquision function computes the max value
x_tries = np.random.uniform(bounds[:, 0], bounds[:, 1], size=(100000, bounds.shape[0]))
mean, std = gp.predict(x_tries, return_std=True)
acquisition_fucntion_values = self.Acquision_function(mean, std)
x_max = x_tries[np.argmax(acquisition_fucntion_values)]
max_acquision_fucntion_value = max(acquisition_fucntion_values)
x_max = np.clip(x_max, bounds[:, 0], bounds[:, 1])
因为我写的是简单的高斯过程这种形式,很多人对高斯过程为什么能拟合出方差均值不清楚,我手写了一些推导过程高斯过程回归。
Bayesian optimizer来解决这类问题,有很多的优点的:
- 利用先验知识高效地调节超参数,每个试验不独立,有点boost味道
- 通过高效的猜测而加速寻找最优参数的进程
- 数据要求低,在目标函数未知且计算复杂度高的情况下极其强大
- 泛化性/鲁棒性好,不易陷入局部最优
其他优秀资料
- Efficient and Robust Automated Machine Learning
- User Modeling and Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
- Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms
- Initializing Bayesian Hyperparameter Optimization via Meta-Learning
- A Conceptual Explanation of Bayesian Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning
- Automated Machine Learning Hyperparameter Tuning in Python
auto-sklearn快速体验
>>> import autosklearn.classification
>>> import sklearn.model_selection
>>> import sklearn.datasets
>>> import sklearn.metrics
>>> X, y = sklearn.datasets.load_digits(return_X_y=True)
>>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=1)
>>> automl = autosklearn.classification.AutoSklearnClassifier()
>>> automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
>>> y_hat = automl.predict(X_test)
>>> print("Accuracy score", sklearn.metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_hat))
欢迎大家关注我的个人bolg,知乎,更多代码内容欢迎follow我的个人Github,如果有任何算法、代码疑问都欢迎通过邮箱发消息给我。