Django个人博客搭建教程---haystack+whoosh+jieba中文分词搜索实践
写在最前面:
舔狗要耐得住寂寞
一个博客网站怎么可以没有全文检索呢?之前由于时间紧,一直心心念念做个完整的搜索没有实现,只用了数据库简单查询做了一下标题的搜索,今天记录下完整的实现过程。
首先安装包:
pip install django-haystack
pip install jieba
pip install whoosh注意,不要去
pip install haystack不然到时候新建索引的时候一定会报错如下:
from haystack import connections
ImportError: cannot import name connections然后是在settings.py中加入:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
、、、
'haystack', #注册 haystack
、、、
]HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'haystack.backends.whoosh_cn_backend.WhooshEngine',
'PATH': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'whoosh_index'),
}
} # 每页显示搜索结果数目为10
HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE = 10
# 自动生成索引
HAYSTACK_SIGNAL_PROCESSOR = 'haystack.signals.RealtimeSignalProcessor'在主urls中加入:
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$', views.blog_index),
url(r'^baidu_verify_iYpMqoGJf4.html/$', views.baiduyz),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('Blog/', include('Blog.urls',namespace="Blog")),
path('JiaBlog/', include('JiaBlog.urls', namespace="JiaBlog")),
path('mdeditor/', include('mdeditor.urls')),
url(r'', include('social_django.urls', namespace='social')),
url(r'^search/', include('haystack.urls')),# 加入这个,剩下的是我别的地方用的
#path(r'^media/(?P.*)$', serve, {"document_root": MEDIA_ROOT}),
]+static(settings.MEDIA_URL,document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT) 在你的子应用中加入search_indexes.py这个文件
from haystack import indexes
# 修改此处,为你自己的model
from JiaBlog.models import Articles
# 修改此处,类名为模型类的名称+Index,比如模型类为Articles,则这里类名为ArticlesIndex
class ArticlesIndex(indexes.SearchIndex, indexes.Indexable):
text = indexes.CharField(document=True, use_template=True)
def get_model(self):
# 修改此处,为你自己的model
return Articles
def index_queryset(self, using=None):
return self.get_model().objects.all()找到你python环境下的安装包haystack所在的位置,打开backend文件夹,复制whoosh_backend.py文件,复制一份,名为whoosh_cn_backend.py,然后打开此文件,把下面代码全部复制进行替换:
# encoding: utf-8
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import json
import os
import re
import shutil
import threading
import warnings
from django.conf import settings
from django.core.exceptions import ImproperlyConfigured
from django.utils import six
from django.utils.datetime_safe import datetime
from django.utils.encoding import force_text
from haystack.backends import BaseEngine, BaseSearchBackend, BaseSearchQuery, EmptyResults, log_query
from haystack.constants import DJANGO_CT, DJANGO_ID, ID
from haystack.exceptions import MissingDependency, SearchBackendError, SkipDocument
from haystack.inputs import Clean, Exact, PythonData, Raw
from haystack.models import SearchResult
from haystack.utils import log as logging
from haystack.utils import get_identifier, get_model_ct
from haystack.utils.app_loading import haystack_get_model
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
try:
import whoosh
except ImportError:
raise MissingDependency("The 'whoosh' backend requires the installation of 'Whoosh'. Please refer to the documentation.")
# Handle minimum requirement.
if not hasattr(whoosh, '__version__') or whoosh.__version__ < (2, 5, 0):
raise MissingDependency("The 'whoosh' backend requires version 2.5.0 or greater.")
# Bubble up the correct error.
from whoosh import index
from whoosh.analysis import StemmingAnalyzer
from whoosh.fields import ID as WHOOSH_ID
from whoosh.fields import BOOLEAN, DATETIME, IDLIST, KEYWORD, NGRAM, NGRAMWORDS, NUMERIC, Schema, TEXT
from whoosh.filedb.filestore import FileStorage, RamStorage
from whoosh.highlight import highlight as whoosh_highlight
from whoosh.highlight import ContextFragmenter, HtmlFormatter
from whoosh.qparser import QueryParser
from whoosh.searching import ResultsPage
from whoosh.writing import AsyncWriter
DATETIME_REGEX = re.compile('^(?P\d{4})-(?P\d{2})-(?P\d{2})T(?P\d{2}):(?P\d{2}):(?P\d{2})(\.\d{3,6}Z?)?$')
LOCALS = threading.local()
LOCALS.RAM_STORE = None
class WhooshHtmlFormatter(HtmlFormatter):
"""
This is a HtmlFormatter simpler than the whoosh.HtmlFormatter.
We use it to have consistent results across backends. Specifically,
Solr, Xapian and Elasticsearch are using this formatting.
"""
template = '<%(tag)s>%(t)s'
class WhooshSearchBackend(BaseSearchBackend):
# Word reserved by Whoosh for special use.
RESERVED_WORDS = (
'AND',
'NOT',
'OR',
'TO',
)
# Characters reserved by Whoosh for special use.
# The '\\' must come first, so as not to overwrite the other slash replacements.
RESERVED_CHARACTERS = (
'\\', '+', '-', '&&', '||', '!', '(', ')', '{', '}',
'[', ']', '^', '"', '~', '*', '?', ':', '.',
)
def __init__(self, connection_alias, **connection_options):
super(WhooshSearchBackend, self).__init__(connection_alias, **connection_options)
self.setup_complete = False
self.use_file_storage = True
self.post_limit = getattr(connection_options, 'POST_LIMIT', 128 * 1024 * 1024)
self.path = connection_options.get('PATH')
if connection_options.get('STORAGE', 'file') != 'file':
self.use_file_storage = False
if self.use_file_storage and not self.path:
raise ImproperlyConfigured("You must specify a 'PATH' in your settings for connection '%s'." % connection_alias)
self.log = logging.getLogger('haystack')
def setup(self):
"""
Defers loading until needed.
"""
from haystack import connections
new_index = False
# Make sure the index is there.
if self.use_file_storage and not os.path.exists(self.path):
os.makedirs(self.path)
new_index = True
if self.use_file_storage and not os.access(self.path, os.W_OK):
raise IOError("The path to your Whoosh index '%s' is not writable for the current user/group." % self.path)
if self.use_file_storage:
self.storage = FileStorage(self.path)
else:
global LOCALS
if getattr(LOCALS, 'RAM_STORE', None) is None:
LOCALS.RAM_STORE = RamStorage()
self.storage = LOCALS.RAM_STORE
self.content_field_name, self.schema = self.build_schema(connections[self.connection_alias].get_unified_index().all_searchfields())
self.parser = QueryParser(self.content_field_name, schema=self.schema)
if new_index is True:
self.index = self.storage.create_index(self.schema)
else:
try:
self.index = self.storage.open_index(schema=self.schema)
except index.EmptyIndexError:
self.index = self.storage.create_index(self.schema)
self.setup_complete = True
def build_schema(self, fields):
schema_fields = {
ID: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True, unique=True),
DJANGO_CT: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True),
DJANGO_ID: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True),
}
# Grab the number of keys that are hard-coded into Haystack.
# We'll use this to (possibly) fail slightly more gracefully later.
initial_key_count = len(schema_fields)
content_field_name = ''
for field_name, field_class in fields.items():
if field_class.is_multivalued:
if field_class.indexed is False:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = IDLIST(stored=True, field_boost=field_class.boost)
else:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = KEYWORD(stored=True, commas=True, scorable=True, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type in ['date', 'datetime']:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = DATETIME(stored=field_class.stored, sortable=True)
elif field_class.field_type == 'integer':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NUMERIC(stored=field_class.stored, numtype=int, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'float':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NUMERIC(stored=field_class.stored, numtype=float, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'boolean':
# Field boost isn't supported on BOOLEAN as of 1.8.2.
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = BOOLEAN(stored=field_class.stored)
elif field_class.field_type == 'ngram':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NGRAM(minsize=3, maxsize=15, stored=field_class.stored, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'edge_ngram':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NGRAMWORDS(minsize=2, maxsize=15, at='start', stored=field_class.stored, field_boost=field_class.boost)
else:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = TEXT(stored=True, analyzer=ChineseAnalyzer(), field_boost=field_class.boost, sortable=True)
if field_class.document is True:
content_field_name = field_class.index_fieldname
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname].spelling = True
# Fail more gracefully than relying on the backend to die if no fields
# are found.
if len(schema_fields) <= initial_key_count:
raise SearchBackendError("No fields were found in any search_indexes. Please correct this before attempting to search.")
return (content_field_name, Schema(**schema_fields))
def update(self, index, iterable, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
writer = AsyncWriter(self.index)
for obj in iterable:
try:
doc = index.full_prepare(obj)
except SkipDocument:
self.log.debug(u"Indexing for object `%s` skipped", obj)
else:
# Really make sure it's unicode, because Whoosh won't have it any
# other way.
for key in doc:
doc[key] = self._from_python(doc[key])
# Document boosts aren't supported in Whoosh 2.5.0+.
if 'boost' in doc:
del doc['boost']
try:
writer.update_document(**doc)
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
# We'll log the object identifier but won't include the actual object
# to avoid the possibility of that generating encoding errors while
# processing the log message:
self.log.error(u"%s while preparing object for update" % e.__class__.__name__,
exc_info=True, extra={"data": {"index": index,
"object": get_identifier(obj)}})
if len(iterable) > 0:
# For now, commit no matter what, as we run into locking issues otherwise.
writer.commit()
def remove(self, obj_or_string, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
whoosh_id = get_identifier(obj_or_string)
try:
self.index.delete_by_query(q=self.parser.parse(u'%s:"%s"' % (ID, whoosh_id)))
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
self.log.error("Failed to remove document '%s' from Whoosh: %s", whoosh_id, e, exc_info=True)
def clear(self, models=None, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if models is not None:
assert isinstance(models, (list, tuple))
try:
if models is None:
self.delete_index()
else:
models_to_delete = []
for model in models:
models_to_delete.append(u"%s:%s" % (DJANGO_CT, get_model_ct(model)))
self.index.delete_by_query(q=self.parser.parse(u" OR ".join(models_to_delete)))
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
if models is not None:
self.log.error("Failed to clear Whoosh index of models '%s': %s", ','.join(models_to_delete),
e, exc_info=True)
else:
self.log.error("Failed to clear Whoosh index: %s", e, exc_info=True)
def delete_index(self):
# Per the Whoosh mailing list, if wiping out everything from the index,
# it's much more efficient to simply delete the index files.
if self.use_file_storage and os.path.exists(self.path):
shutil.rmtree(self.path)
elif not self.use_file_storage:
self.storage.clean()
# Recreate everything.
self.setup()
def optimize(self):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
self.index.optimize()
def calculate_page(self, start_offset=0, end_offset=None):
# Prevent against Whoosh throwing an error. Requires an end_offset
# greater than 0.
if end_offset is not None and end_offset <= 0:
end_offset = 1
# Determine the page.
page_num = 0
if end_offset is None:
end_offset = 1000000
if start_offset is None:
start_offset = 0
page_length = end_offset - start_offset
if page_length and page_length > 0:
page_num = int(start_offset / page_length)
# Increment because Whoosh uses 1-based page numbers.
page_num += 1
return page_num, page_length
@log_query
def search(self, query_string, sort_by=None, start_offset=0, end_offset=None,
fields='', highlight=False, facets=None, date_facets=None, query_facets=None,
narrow_queries=None, spelling_query=None, within=None,
dwithin=None, distance_point=None, models=None,
limit_to_registered_models=None, result_class=None, **kwargs):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
# A zero length query should return no results.
if len(query_string) == 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
query_string = force_text(query_string)
# A one-character query (non-wildcard) gets nabbed by a stopwords
# filter and should yield zero results.
if len(query_string) <= 1 and query_string != u'*':
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
reverse = False
if sort_by is not None:
# Determine if we need to reverse the results and if Whoosh can
# handle what it's being asked to sort by. Reversing is an
# all-or-nothing action, unfortunately.
sort_by_list = []
reverse_counter = 0
for order_by in sort_by:
if order_by.startswith('-'):
reverse_counter += 1
if reverse_counter and reverse_counter != len(sort_by):
raise SearchBackendError("Whoosh requires all order_by fields"
" to use the same sort direction")
for order_by in sort_by:
if order_by.startswith('-'):
sort_by_list.append(order_by[1:])
if len(sort_by_list) == 1:
reverse = True
else:
sort_by_list.append(order_by)
if len(sort_by_list) == 1:
reverse = False
sort_by = sort_by_list
if facets is not None:
warnings.warn("Whoosh does not handle faceting.", Warning, stacklevel=2)
if date_facets is not None:
warnings.warn("Whoosh does not handle date faceting.", Warning, stacklevel=2)
if query_facets is not None:
warnings.warn("Whoosh does not handle query faceting.", Warning, stacklevel=2)
narrowed_results = None
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if limit_to_registered_models is None:
limit_to_registered_models = getattr(settings, 'HAYSTACK_LIMIT_TO_REGISTERED_MODELS', True)
if models and len(models):
model_choices = sorted(get_model_ct(model) for model in models)
elif limit_to_registered_models:
# Using narrow queries, limit the results to only models handled
# with the current routers.
model_choices = self.build_models_list()
else:
model_choices = []
if len(model_choices) > 0:
if narrow_queries is None:
narrow_queries = set()
narrow_queries.add(' OR '.join(['%s:%s' % (DJANGO_CT, rm) for rm in model_choices]))
narrow_searcher = None
if narrow_queries is not None:
# Potentially expensive? I don't see another way to do it in Whoosh...
narrow_searcher = self.index.searcher()
for nq in narrow_queries:
recent_narrowed_results = narrow_searcher.search(self.parser.parse(force_text(nq)),
limit=None)
if len(recent_narrowed_results) <= 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
if narrowed_results:
narrowed_results.filter(recent_narrowed_results)
else:
narrowed_results = recent_narrowed_results
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if self.index.doc_count():
searcher = self.index.searcher()
parsed_query = self.parser.parse(query_string)
# In the event of an invalid/stopworded query, recover gracefully.
if parsed_query is None:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
page_num, page_length = self.calculate_page(start_offset, end_offset)
search_kwargs = {
'pagelen': page_length,
'sortedby': sort_by,
'reverse': reverse,
}
# Handle the case where the results have been narrowed.
if narrowed_results is not None:
search_kwargs['filter'] = narrowed_results
try:
raw_page = searcher.search_page(
parsed_query,
page_num,
**search_kwargs
)
except ValueError:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
# Because as of Whoosh 2.5.1, it will return the wrong page of
# results if you request something too high. :(
if raw_page.pagenum < page_num:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
results = self._process_results(raw_page, highlight=highlight, query_string=query_string, spelling_query=spelling_query, result_class=result_class)
searcher.close()
if hasattr(narrow_searcher, 'close'):
narrow_searcher.close()
return results
else:
if self.include_spelling:
if spelling_query:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(spelling_query)
else:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(query_string)
else:
spelling_suggestion = None
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': spelling_suggestion,
}
def more_like_this(self, model_instance, additional_query_string=None,
start_offset=0, end_offset=None, models=None,
limit_to_registered_models=None, result_class=None, **kwargs):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
field_name = self.content_field_name
narrow_queries = set()
narrowed_results = None
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if limit_to_registered_models is None:
limit_to_registered_models = getattr(settings, 'HAYSTACK_LIMIT_TO_REGISTERED_MODELS', True)
if models and len(models):
model_choices = sorted(get_model_ct(model) for model in models)
elif limit_to_registered_models:
# Using narrow queries, limit the results to only models handled
# with the current routers.
model_choices = self.build_models_list()
else:
model_choices = []
if len(model_choices) > 0:
if narrow_queries is None:
narrow_queries = set()
narrow_queries.add(' OR '.join(['%s:%s' % (DJANGO_CT, rm) for rm in model_choices]))
if additional_query_string and additional_query_string != '*':
narrow_queries.add(additional_query_string)
narrow_searcher = None
if narrow_queries is not None:
# Potentially expensive? I don't see another way to do it in Whoosh...
narrow_searcher = self.index.searcher()
for nq in narrow_queries:
recent_narrowed_results = narrow_searcher.search(self.parser.parse(force_text(nq)),
limit=None)
if len(recent_narrowed_results) <= 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
if narrowed_results:
narrowed_results.filter(recent_narrowed_results)
else:
narrowed_results = recent_narrowed_results
page_num, page_length = self.calculate_page(start_offset, end_offset)
self.index = self.index.refresh()
raw_results = EmptyResults()
searcher = None
if self.index.doc_count():
query = "%s:%s" % (ID, get_identifier(model_instance))
searcher = self.index.searcher()
parsed_query = self.parser.parse(query)
results = searcher.search(parsed_query)
if len(results):
raw_results = results[0].more_like_this(field_name, top=end_offset)
# Handle the case where the results have been narrowed.
if narrowed_results is not None and hasattr(raw_results, 'filter'):
raw_results.filter(narrowed_results)
try:
raw_page = ResultsPage(raw_results, page_num, page_length)
except ValueError:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
# Because as of Whoosh 2.5.1, it will return the wrong page of
# results if you request something too high. :(
if raw_page.pagenum < page_num:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
results = self._process_results(raw_page, result_class=result_class)
if searcher:
searcher.close()
if hasattr(narrow_searcher, 'close'):
narrow_searcher.close()
return results
def _process_results(self, raw_page, highlight=False, query_string='', spelling_query=None, result_class=None):
from haystack import connections
results = []
# It's important to grab the hits first before slicing. Otherwise, this
# can cause pagination failures.
hits = len(raw_page)
if result_class is None:
result_class = SearchResult
facets = {}
spelling_suggestion = None
unified_index = connections[self.connection_alias].get_unified_index()
indexed_models = unified_index.get_indexed_models()
for doc_offset, raw_result in enumerate(raw_page):
score = raw_page.score(doc_offset) or 0
app_label, model_name = raw_result[DJANGO_CT].split('.')
additional_fields = {}
model = haystack_get_model(app_label, model_name)
if model and model in indexed_models:
for key, value in raw_result.items():
index = unified_index.get_index(model)
string_key = str(key)
if string_key in index.fields and hasattr(index.fields[string_key], 'convert'):
# Special-cased due to the nature of KEYWORD fields.
if index.fields[string_key].is_multivalued:
if value is None or len(value) is 0:
additional_fields[string_key] = []
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = value.split(',')
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = index.fields[string_key].convert(value)
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = self._to_python(value)
del(additional_fields[DJANGO_CT])
del(additional_fields[DJANGO_ID])
if highlight:
sa = StemmingAnalyzer()
formatter = WhooshHtmlFormatter('em')
terms = [token.text for token in sa(query_string)]
whoosh_result = whoosh_highlight(
additional_fields.get(self.content_field_name),
terms,
sa,
ContextFragmenter(),
formatter
)
additional_fields['highlighted'] = {
self.content_field_name: [whoosh_result],
}
result = result_class(app_label, model_name, raw_result[DJANGO_ID], score, **additional_fields)
results.append(result)
else:
hits -= 1
if self.include_spelling:
if spelling_query:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(spelling_query)
else:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(query_string)
return {
'results': results,
'hits': hits,
'facets': facets,
'spelling_suggestion': spelling_suggestion,
}
def create_spelling_suggestion(self, query_string):
spelling_suggestion = None
reader = self.index.reader()
corrector = reader.corrector(self.content_field_name)
cleaned_query = force_text(query_string)
if not query_string:
return spelling_suggestion
# Clean the string.
for rev_word in self.RESERVED_WORDS:
cleaned_query = cleaned_query.replace(rev_word, '')
for rev_char in self.RESERVED_CHARACTERS:
cleaned_query = cleaned_query.replace(rev_char, '')
# Break it down.
query_words = cleaned_query.split()
suggested_words = []
for word in query_words:
suggestions = corrector.suggest(word, limit=1)
if len(suggestions) > 0:
suggested_words.append(suggestions[0])
spelling_suggestion = ' '.join(suggested_words)
return spelling_suggestion
def _from_python(self, value):
"""
Converts Python values to a string for Whoosh.
Code courtesy of pysolr.
"""
if hasattr(value, 'strftime'):
if not hasattr(value, 'hour'):
value = datetime(value.year, value.month, value.day, 0, 0, 0)
elif isinstance(value, bool):
if value:
value = 'true'
else:
value = 'false'
elif isinstance(value, (list, tuple)):
value = u','.join([force_text(v) for v in value])
elif isinstance(value, (six.integer_types, float)):
# Leave it alone.
pass
else:
value = force_text(value)
return value
def _to_python(self, value):
"""
Converts values from Whoosh to native Python values.
A port of the same method in pysolr, as they deal with data the same way.
"""
if value == 'true':
return True
elif value == 'false':
return False
if value and isinstance(value, six.string_types):
possible_datetime = DATETIME_REGEX.search(value)
if possible_datetime:
date_values = possible_datetime.groupdict()
for dk, dv in date_values.items():
date_values[dk] = int(dv)
return datetime(date_values['year'], date_values['month'], date_values['day'], date_values['hour'], date_values['minute'], date_values['second'])
try:
# Attempt to use json to load the values.
converted_value = json.loads(value)
# Try to handle most built-in types.
if isinstance(converted_value, (list, tuple, set, dict, six.integer_types, float, complex)):
return converted_value
except:
# If it fails (SyntaxError or its ilk) or we don't trust it,
# continue on.
pass
return value
class WhooshSearchQuery(BaseSearchQuery):
def _convert_datetime(self, date):
if hasattr(date, 'hour'):
return force_text(date.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S'))
else:
return force_text(date.strftime('%Y%m%d000000'))
def clean(self, query_fragment):
"""
Provides a mechanism for sanitizing user input before presenting the
value to the backend.
Whoosh 1.X differs here in that you can no longer use a backslash
to escape reserved characters. Instead, the whole word should be
quoted.
"""
words = query_fragment.split()
cleaned_words = []
for word in words:
if word in self.backend.RESERVED_WORDS:
word = word.replace(word, word.lower())
for char in self.backend.RESERVED_CHARACTERS:
if char in word:
word = "'%s'" % word
break
cleaned_words.append(word)
return ' '.join(cleaned_words)
def build_query_fragment(self, field, filter_type, value):
from haystack import connections
query_frag = ''
is_datetime = False
if not hasattr(value, 'input_type_name'):
# Handle when we've got a ``ValuesListQuerySet``...
if hasattr(value, 'values_list'):
value = list(value)
if hasattr(value, 'strftime'):
is_datetime = True
if isinstance(value, six.string_types) and value != ' ':
# It's not an ``InputType``. Assume ``Clean``.
value = Clean(value)
else:
value = PythonData(value)
# Prepare the query using the InputType.
prepared_value = value.prepare(self)
if not isinstance(prepared_value, (set, list, tuple)):
# Then convert whatever we get back to what pysolr wants if needed.
prepared_value = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value)
# 'content' is a special reserved word, much like 'pk' in
# Django's ORM layer. It indicates 'no special field'.
if field == 'content':
index_fieldname = ''
else:
index_fieldname = u'%s:' % connections[self._using].get_unified_index().get_index_fieldname(field)
filter_types = {
'content': '%s',
'contains': '*%s*',
'endswith': "*%s",
'startswith': "%s*",
'exact': '%s',
'gt': "{%s to}",
'gte': "[%s to]",
'lt': "{to %s}",
'lte': "[to %s]",
'fuzzy': u'%s~',
}
if value.post_process is False:
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
if filter_type in ['content', 'contains', 'startswith', 'endswith', 'fuzzy']:
if value.input_type_name == 'exact':
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
# Iterate over terms & incorportate the converted form of each into the query.
terms = []
if isinstance(prepared_value, six.string_types):
possible_values = prepared_value.split(' ')
else:
if is_datetime is True:
prepared_value = self._convert_datetime(prepared_value)
possible_values = [prepared_value]
for possible_value in possible_values:
terms.append(filter_types[filter_type] % self.backend._from_python(possible_value))
if len(terms) == 1:
query_frag = terms[0]
else:
query_frag = u"(%s)" % " AND ".join(terms)
elif filter_type == 'in':
in_options = []
for possible_value in prepared_value:
is_datetime = False
if hasattr(possible_value, 'strftime'):
is_datetime = True
pv = self.backend._from_python(possible_value)
if is_datetime is True:
pv = self._convert_datetime(pv)
if isinstance(pv, six.string_types) and not is_datetime:
in_options.append('"%s"' % pv)
else:
in_options.append('%s' % pv)
query_frag = "(%s)" % " OR ".join(in_options)
elif filter_type == 'range':
start = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value[0])
end = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value[1])
if hasattr(prepared_value[0], 'strftime'):
start = self._convert_datetime(start)
if hasattr(prepared_value[1], 'strftime'):
end = self._convert_datetime(end)
query_frag = u"[%s to %s]" % (start, end)
elif filter_type == 'exact':
if value.input_type_name == 'exact':
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
prepared_value = Exact(prepared_value).prepare(self)
query_frag = filter_types[filter_type] % prepared_value
else:
if is_datetime is True:
prepared_value = self._convert_datetime(prepared_value)
query_frag = filter_types[filter_type] % prepared_value
if len(query_frag) and not isinstance(value, Raw):
if not query_frag.startswith('(') and not query_frag.endswith(')'):
query_frag = "(%s)" % query_frag
return u"%s%s" % (index_fieldname, query_frag)
class WhooshEngine(BaseEngine):
backend = WhooshSearchBackend
query = WhooshSearchQuery
再新建一个ChineseAnalyzer.py
import jieba
from whoosh.analysis import Tokenizer, Token
class ChineseTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __call__(self, value, positions=False, chars=False,
keeporiginal=False, removestops=True,
start_pos=0, start_char=0, mode='', **kwargs):
t = Token(positions, chars, removestops=removestops, mode=mode,
**kwargs)
seglist = jieba.cut(value, cut_all=True)
for w in seglist:
t.original = t.text = w
t.boost = 1.0
if positions:
t.pos = start_pos + value.find(w)
if chars:
t.startchar = start_char + value.find(w)
t.endchar = start_char + value.find(w) + len(w)
yield t
def ChineseAnalyzer():
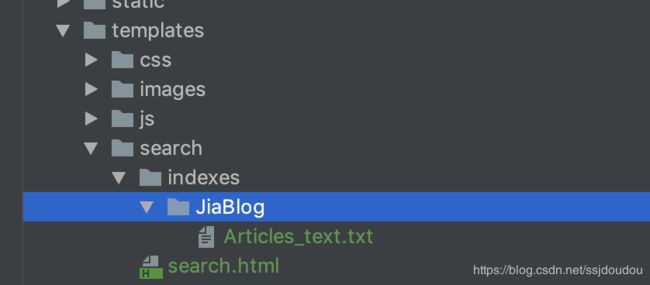
return ChineseTokenizer()在templates下面建文件夹,包含如下
这个JiaBlog是你的应用名称
txt文件如下:
{{ object.title }}
{{ object.authorname }}
{{ object.body }}title,authorname,body分别是我需要加索引的字段
search.html如下:记得自己定制一下展示的字段。
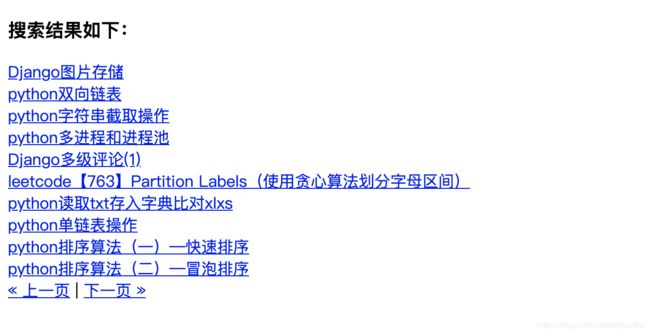
搜索结果如下:
{% for result in page.object_list %}
{{ result.object.title }}
{% empty %}
啥也没找到
{% endfor %}
{% if page.has_previous or page.has_next %}
{% if page.has_previous %}{% endif %}« 上一页{% if page.has_previous %}{% endif %}
|
{% if page.has_next %}{% endif %}下一页 »{% if page.has_next %}{% endif %}
{% endif %}
{% endif %}
接下来手动新建索引
python manage.py rebuild_index如果你完全照我的做,就可以新建索引了
如果你在linux环境下找不到python安装的第三方包的位置,可以这样:
root@iZuf647of4lcxljq1unaeeZ:/home/MyBlog# python -c "import django;print(django)"
再写一个坑吧
新建索引的时候报错:
django.template.exceptions.TemplateDoesNotExist: search/indexes/JiaBlog/articles_text.txt明明本地是ok的啊,结果是因为服务器上的文件是
Articles_text.txt,是大写,把A改成a就可以了,卧槽。。。
然后就成功了
root@iZuf647of4lcxljq1unaeeZ:/home/MyBlog# python manage.py rebuild_index
System check identified some issues:
WARNINGS:
Blog.Articles.tags: (fields.W340) null has no effect on ManyToManyField.
JiaBlog.Articles.tags: (fields.W340) null has no effect on ManyToManyField.
WARNING: This will irreparably remove EVERYTHING from your search index in connection 'default'.
Your choices after this are to restore from backups or rebuild via the `rebuild_index` command.
Are you sure you wish to continue? [y/N] y
Removing all documents from your index because you said so.
All documents removed.
Indexing 50 articless
Building prefix dict from the default dictionary ...
Dumping model to file cache /tmp/jieba.cache
Loading model cost 1.046 seconds.
Prefix dict has been built succesfully.
好了,效果如下
我们再美化一下search.html页面,用上原来的风格
注意url
http://www.guanacossj.com/search/?q=pythonhhh,大功告成!!!