深度解析InnoDB事务中的MVCC原理
文章目录
- 1. 事务相关的数据结构
- 1.1 trx_t 事务结构体
- 1.2 TrxFactory-事务工厂
- 1.3 trx_pool_t 事务缓存池
- 1.4 trx_pools_t 事务缓存池管理器
- 2. MVCC相关的数据结构
- 2.1 ReadView-事务的可见视图
- 2.2 ReadView管理器-MVCC
- 3. 事务/MVCC/ReadView的关系
- 4. 事务和MVCC相关的操作
- 4.1 开启事务并不一定需要分配trx_t对象
- 4.2 开启事务并不一定需要分配ReadView对象
- 3.3 开启事务并不一定立即开启ReadView对象
- 4.4 分配&初始化ReadView对象
- 4.5 通过ReadView判断当前版本的数据是否可见
- 4.6 事务隔离级别-读未提交的特殊处理
- 4.7 事务隔离级别-读已提交的特殊处理
- 4.8 ReadView关闭
数据和对数据的处理,贯穿着软件的生命周期。所以在了解软件的某个模块时,会从这两方面来入手。
1. 事务相关的数据结构
1.1 trx_t 事务结构体
InnoDB中用struct trx_t表示一个事务,它包含如下信息
TrxMutex mutex //互斥量,用于并发修改事务的某些状态
trx_id_t id; /*!< transaction id */ 事务id
trx_id_t no; //事务序列号
trx_state_t state; //事务当前的状态,比如说,TRX_STATE_NOT_STARTED表示未开始状态
ReadView* read_view; //事务的可见视图,用于MVCC,下面会重点介绍
UT_LIST_NODE_T(trx_t)
trx_list; //事务链表
UT_LIST_NODE_T(trx_t)
no_list; /*!< Required during view creation
to check for the view limit for
transactions that are committing */
trx_lock_t lock;//此事务中的锁结构
bool is_recovered; //是否是在崩溃恢复中的事务
hit_list_t hit_list; /*!< List of transactions to kill,
when a high priority transaction
is blocked on a lock wait. */
ulint isolation_level;/*!< TRX_ISO_REPEATABLE_READ, ... */ //事务隔离级别
/*------------------------------*/
/* MySQL has a transaction coordinator to coordinate two phase
commit between multiple storage engines and the binary log. When
an engine participates in a transaction, it's responsible for
registering itself using the trans_register_ha() API. */
bool is_registered; /* This flag is set to true after the
transaction has been registered with
the coordinator using the XA API, and
is set to false after commit or
rollback. */
bool auto_commit; /*!< true if it is an autocommit */
1.2 TrxFactory-事务工厂
TrxFactory用于生产,销毁,检测trx_t
/** Initializes a transaction object. It must be explicitly started
with trx_start_if_not_started() before using it. The default isolation
level is TRX_ISO_REPEATABLE_READ.
@param trx Transaction instance to initialise */
static void init(trx_t* trx){} //初始化一个trx_t
/** Release resources held by the transaction object.
@param trx the transaction for which to release resources */
static void destroy(trx_t* trx){} //销毁一个trx_t ,回收资源
/** Enforce any invariants here, this is called before the transaction
is added to the pool.
@return true if all OK */
static bool debug(const trx_t* trx){} //确定一个trx_t是可用的,在交付一个trx_t之前必须调用。
1.3 trx_pool_t 事务缓存池
事务缓存池中缓存了一些已经创建好了的事务体,用于事务操作时,分配给客户端线程,或者内部线程。
typedef Pool trx_pool_t;
Pool是一个模版结构体,如下
template
struct Pool {
}
其中第一个模版参数为事务的结构体,第二个参数是事务工厂的结构体,第三个是事务缓存池的锁策略。如下
/** The lock strategy for TrxPool */
struct TrxPoolLock {
TrxPoolLock() { }
/** Create the mutex */
void create()
{
mutex_create(LATCH_ID_TRX_POOL, &m_mutex);
}
/** Acquire the mutex */
void enter() { mutex_enter(&m_mutex); }
/** Release the mutex */
void exit() { mutex_exit(&m_mutex); }
/** Free the mutex */
void destroy() { mutex_free(&m_mutex); }
/** Mutex to use */
ib_mutex_t m_mutex;
};
1.4 trx_pools_t 事务缓存池管理器
PoolManager 用来管理所有的事务缓存池,它也是一个模版结构体,如下
typedef PoolManager trx_pools_t;
PoolManager提供了分配事务的功能如下
value_type* get()
{
size_t index = 0;
size_t delay = 1;
value_type* ptr = NULL;
do {
m_lock_strategy.enter();
ut_ad(!m_pools.empty());
size_t n_pools = m_pools.size();
PoolType* pool = m_pools[index % n_pools];
m_lock_strategy.exit();
ptr = pool->get();
if (ptr == 0 && (index / n_pools) > 2) {
if (!add_pool(n_pools)) {
ib::error() << "Failed to allocate"
" memory for a pool of size "
<< m_size << " bytes. Will"
" wait for " << delay
<< " seconds for a thread to"
" free a resource";
/* There is nothing much we can do
except crash and burn, however lets
be a little optimistic and wait for
a resource to be freed. */
os_thread_sleep(delay * 1000000);
if (delay < 32) {
delay <<= 1;
}
} else {
delay = 1;
}
}
++index;
} while (ptr == NULL);
return(ptr);
}
2. MVCC相关的数据结构
2.1 ReadView-事务的可见视图
在每一个事务体中,都有一个ReadView实例,用来管理此事务对于其他事务操作的可见性。
ReadView主要包含如下信息
class ReadView
{
class ids_t {} //存放当前活跃事务id的容器,基于std::vector的进一步封装处理
trx_id_t m_low_limit_id; //此事务最小不可见的事务id,任何大于等于此id的事务,对于当前事务来说都是不可见的。
trx_id_t m_up_limit_id; //此事务可见的任何小于此事务id的更改
trx_id_t m_creator_trx_id; //当前事务id,只读事务为0,ReadView关闭后会设置为TRX_ID_MAX
ids_t m_ids;//开启ReadView时获取到的当前事务系统中的所有活跃事务id
/** The view does not need to see the undo logs for transactions
whose transaction number is strictly smaller (<) than this value:
they can be removed in purge if not needed by other views */
trx_id_t m_low_limit_no; //
/** AC-NL-RO transaction view that has been "closed". */
bool m_closed;
typedef UT_LIST_NODE_T(ReadView) node_t;
/** List of read views in trx_sys */
byte pad1[64 - sizeof(node_t)];
node_t m_view_list;
}
2.2 ReadView管理器-MVCC
class MVCC主要用于管理readview,比如分配,打开,关闭等操作。如下
//用户线程在分配到事务之后,并没有立刻初始化readview,直到用户进行查询操作的时候才会进行初始化
MVCC::view_open(ReadView*& view, trx_t* trx)
如果是START TRANSACTION WITH consistent snapshot,则立即开启ReadView。逻辑在trans_begin函数中:
/* ha_start_consistent_snapshot() relies on OPTION_BEGIN flag set. */
if (flags & MYSQL_START_TRANS_OPT_WITH_CONS_SNAPSHOT)
{
if (tst)
tst->add_trx_state(thd, TX_WITH_SNAPSHOT);
res= ha_start_consistent_snapshot(thd);
}
void view_close(ReadView*& view, bool own_mutex);
3. 事务/MVCC/ReadView的关系
- 事务和全局事务系统是多对1
- 事务系统和MVCC之间是1对1
- 事务和ReadView是1对1
事务被全局事务系统所管理,事务系统中存在一个MVCC对象,事务对于ReadView的操作通过MVCC来完成。
4. 事务和MVCC相关的操作
4.1 开启事务并不一定需要分配trx_t对象
一个客户端线程可能进行多次事务操作,为了节省时间,trx_t在THD对象的生命周期内,是可以复用的(特殊情况?)。
4.2 开启事务并不一定需要分配ReadView对象
并不是每一次客户端线程开启事务操作时,都重新分配一次ReadView对象,很显然它是可以复用的,直到trx_t对象生命周期的结束。也就是说只有在第一次进行多版本读取时,才会去申请一个ReadView。
3.3 开启事务并不一定立即开启ReadView对象
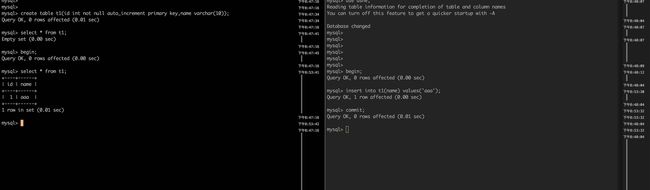
开启事务并不一定立即分配ReadView对象,举个例子:
如上图所示:虽然开启了事务,但依然查询到了后开启事务的写入成功的内容。也就是说,begin/start transaction操作,并没有确定当前事务的可见性。
这也是START TRANSACTION WITH consistent snapshot;特殊的地方,在开启事务后就已经开启了ReadView,可见范围已经确定,也因此可以用来获取一致性备份。

4.4 分配&初始化ReadView对象
用户在执行非当前读操作时,会为THD::trx分配并开启ReadView对象,确定事务可见范围.
函数调用过程如下:
ha_innobase::index_read(unsigned char*, unsigned char const*, unsigned int, ha_rkey_function)
row_search_mvcc(unsigned char*, page_cur_mode_t, row_prebuilt_t*, unsigned long, unsigned long)
trx_assign_read_view(trx_t*)
MVCC::view_open(ReadView*&, trx_t*)
mutex_enter(&trx_sys->mutex); //获取事务系统mutex
MVCC::get_view()//从m_free队列头取出一个ReadView对象,并且从队列中移除;高并发下,可能出现m_free队列为空的情况,需要临时初始化一个ReadView,这是一个我们不愿意看到的情况。m_free大小默认为1024
ReadView::prepare(unsigned long long) //开启ReadView,确定m_low_limit_id,m_low_limit_no,m_ids
ReadView::complete() //完成ReadView分配,确定m_up_limit_id,设置标记m_closed = false;
trx_sys_mutex_exit();//解锁
4.5 通过ReadView判断当前版本的数据是否可见
通过ReadView来判断数据版本可见行的逻辑在函数ReadView::changes_visible(unsigned long long, table_name_t const&)中,代码如下:
/** Check whether the changes by id are visible.
@param[in] id transaction id to check against the view
@param[in] name table name
@return whether the view sees the modifications of id. */
bool changes_visible(
trx_id_t id,
const table_name_t& name) const
MY_ATTRIBUTE((warn_unused_result))
{
ut_ad(id > 0);
if (id < m_up_limit_id || id == m_creator_trx_id) {
return(true);
}
check_trx_id_sanity(id, name);
if (id >= m_low_limit_id) {
return(false);
} else if (m_ids.empty()) {
return(true);
}
const ids_t::value_type* p = m_ids.data();
return(!std::binary_search(p, p + m_ids.size(), id));
}
逻辑整理下就是
- 如果对应索引项上记录的trx_id小于m_up_limit_id,则当前版本的数据对此事务是可见的。
- 如果对应索引记录上的trx_id等于m_creator_trx_id,则大部分情况下可以说明是此事务内的修改(有其他可能吗?),依然可见
- 如果对应索引记录上的trx_id >= m_low_limit_id,则不可见,否则判断是否在m_ids中,如果在的话,说明开启ReadView时,事务活跃,则不可见,如果不在其中,则可见。代码中先进行判空算是一种优化处理吧。
row_search_mvcc(unsigned char*, page_cur_mode_t, row_prebuilt_t*, unsigned long, unsigned long)
{
else if (prebuilt->select_lock_type == LOCK_NONE) {
/* This is a consistent read */
/* Assign a read view for the query */
if (!srv_read_only_mode) {
trx_assign_read_view(trx);
}
}
/********************************************************************//**
Assigns a read view for a consistent read query. All the consistent reads
within the same transaction will get the same read view, which is created
when this function is first called for a new started transaction.
@return consistent read view */
ReadView*
trx_assign_read_view(
/*=================*/
trx_t* trx) /*!< in/out: active transaction */
{
ut_ad(trx->state == TRX_STATE_ACTIVE);
if (srv_read_only_mode) {
ut_ad(trx->read_view == NULL);
return(NULL);
} else if (!MVCC::is_view_active(trx->read_view)) {
trx_sys->mvcc->view_open(trx->read_view, trx);
}
return(trx->read_view);
}
MVCC::view_open会分配并且初始化ReadView对象,
4.6 事务隔离级别-读未提交的特殊处理
读未提交,不考虑ReadView的可见性,直接读取最新的版本。
在函数row_search_mvcc(unsigned char*, page_cur_mode_t, row_prebuilt_t*, unsigned long, unsigned long)中,检测到当前事务隔离级别为TRX_ISO_READ_UNCOMMITTED时,则不进行ReadView可见性的判断,直接返回
/* This is a non-locking consistent read: if necessary, fetch
a previous version of the record */
if (trx->isolation_level == TRX_ISO_READ_UNCOMMITTED) {
/* Do nothing: we let a non-locking SELECT read the
latest version of the record */
} else if (index == clust_index) {
所以这里有个疑问:既然在读未提交隔离级别下,数据检索不考虑ReadView的可见性,那么对于ReadView的维护是否可以省略?
4.7 事务隔离级别-读已提交的特殊处理
读已提交意味着每一次读取读取操作前都需要重新打开ReadView,处理ReadView的可见范围。
参照函数trx_assign_read_view。如下 :
ReadView*
trx_assign_read_view(
/*=================*/
trx_t* trx) /*!< in/out: active transaction */
{
ut_ad(trx->state == TRX_STATE_ACTIVE);
if (srv_read_only_mode) {
ut_ad(trx->read_view == NULL);
return(NULL);
} else if (!MVCC::is_view_active(trx->read_view)) { //判断当前ReadView是否处于active状态
trx_sys->mvcc->view_open(trx->read_view, trx);//开启ReadView,并调用ReadView::prepare(unsigned long long),确定可见范围
}
return(trx->read_view);
}
通过上面的描述可以推测出,在读已提交事务隔离级别下,每次读取结束后,都要关闭一次ReadView对象。调试结果验证了这点:
这里就补贴代码了,直接看调试过程

4.8 ReadView关闭
ReadView的关闭通过函数MVCC::view_close(ReadView*&, bool)来完成,过程如下:
void
MVCC::view_close(ReadView*& view, bool own_mutex)
{
uintptr_t p = reinterpret_cast(view);
/* Note: The assumption here is that AC-NL-RO transactions will
call this function with own_mutex == false. */
if (!own_mutex) {
/* Sanitise the pointer first. */
ReadView* ptr = reinterpret_cast(p & ~1);
/* Note this can be called for a read view that
was already closed. */
ptr->m_closed = true;
/* Set the view as closed. */
view = reinterpret_cast(p | 0x1);
} else {
view = reinterpret_cast(p & ~1);
view->close();
UT_LIST_REMOVE(m_views, view);
UT_LIST_ADD_LAST(m_free, view);
ut_ad(validate());
view = NULL;
}
}
代码解释:ReadView的关闭分为两种处理策略,第一种是缺乏锁保护下的假关闭,后续操作可以继续使用。 第二种是在全局的事务系统mutex保护下进行,可以认为是真的关闭掉,并且从m_views中移除,返还给m_free,下次需要重新分配。