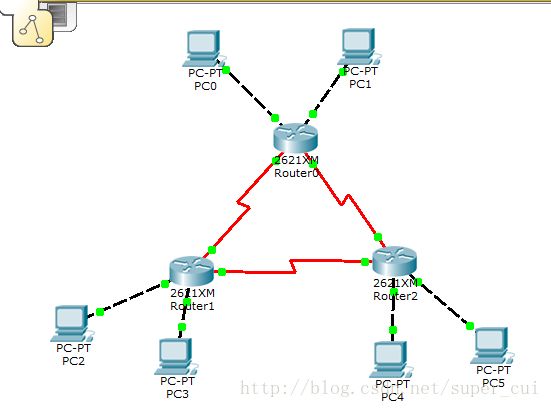
实验 10 点到点链路 OSPF 配置
一.实验目的:
掌握点到点链路 OSPF 的配置方法。
二.实验要点:
配置点到点链路上的 OSPF,对运行中的 OSPF 进行诊断。
三.实验设备:
路由器 Cisco 2621 三台,带有网卡的工作站 PC 六台,控制台电缆一条,交叉双绞线若干。
四、实验环境
步骤中的实验情况
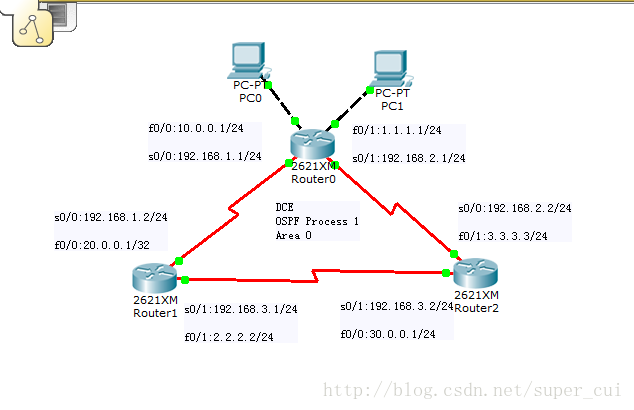
纠正一下,Router1的f0/0端口的地址为:20.0.0.1/24
五. 实验步骤
Router1的配置
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface Serial0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface Serial0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
Router2的配置
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface Serial0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
This command applies only to DCE interfaces
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface Serial0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
This command applies only to DCE interfaces
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
Router0的配置
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface Serial0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
This command applies only to DCE interfaces
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface Serial0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/1, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#router ospf 1
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#exit
Router(config)#exit
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#ping 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
Router#ping 192.168.3.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Router#ping 192.168.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/7 ms
Router#ping 192.168.3.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
当只在Router0上配置了OSPF,Router0无法ping通Router1的s0/1端口,Router0无法ping通Router2的s0/1端口。
当在Router1、 Router2的串行接口的端口配置了OSPF之后,Router0、Router1、Router2的各个串行接口的端口之间就可以相互ping通了。
Router1
Router>en
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router ospf 1
Router(config-router)#net 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#net 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#exit
Router2
Router>en
Router#
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router ospf 1
Router(config-router)#net 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#net 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config)#exit
Router0
Router>en
Router#ping 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/5/11 ms
Router#ping 192.168.3.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/7 ms
Router#ping 192.168.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/5/12 ms
Router#ping 192.168.3.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/6/8 ms
Router0上面续加的配置,只有这样才能使连接路由器Router0的两个以太网端口的主机能够ping通这个OSPF域Area 0 的所有端口,其他的路由器连接的主机同理。
Router0上面续加的配置
Router#
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int f0/0
Router(config-if)#ip ad 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#int f0/1
Router(config-if)#ip ad 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#router ospf 1
Router(config-router)#net 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#net 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router(config-router)#exit
PC0上面的ping的情况
Packet Tracer PC Command Line 1.0
PC>ping 192.168.1.1
Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
PC>ping 192.168.1.2
Pinging 192.168.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=6ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 6ms, Average = 3ms
PC>ping 192.168.3.1
Pinging 192.168.3.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=254
Ping statistics for 192.168.3.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 3ms, Average = 2ms
PC>ping 192.168.2.1
Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
PC>ping 192.168.2.2
Pinging 192.168.2.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=8ms TTL=254
Ping statistics for 192.168.2.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 8ms, Average = 2ms
PC>ping 192.168.3.2
Pinging 192.168.3.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=254
Ping statistics for 192.168.3.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 4ms
PC>ping 1.1.1.2
Pinging 1.1.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Reply from 1.1.1.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
Reply from 1.1.1.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
Reply from 1.1.1.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
Ping statistics for 1.1.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
查看Route0中命令对 OSPF 的运行进行诊断,观察诊断输出
Route0
Router>en
Router#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/1
O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/128] via 192.168.1.2, 00:23:22, Serial0/0
[110/128] via 192.168.2.2, 00:23:22, Serial0/1
Router#show ip protocol
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.2.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.2.1 110 00:13:30
192.168.3.1 110 00:23:54
192.168.3.2 110 00:23:54
Distance: (default is 110)
Router#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
192.168.3.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:34 192.168.1.2 Serial0/0
192.168.3.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:30 192.168.2.2 Serial0/1
具体步骤
(1)按 上图所示 连接各路由器。
(2)按 上图所示 配置各路由器的各个接口 IP 地址等参数。
(3)配置路由器 Router0 、Router1 和 Router2 上的 OSPF 协议(假设三个路由器都处于区域 0,
除了各路由器的 loopback0 接口所在网络外,其他网络均要求可路由)。
在 Router0 上的配置如下:
Router0(config)#router ospf 1
Router0(config-router)#net 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router0(config-router)#net 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
(4)测试各网络之间的连通性。
在路由器 0 上是否能 ping 通路由器 1、路由器 2 的各个接口。
(5)利用下面的命令对 OSPF 的运行进行诊断,观察诊断输出。
1.log-adjacency-changes
2.show ip protocol
3.show ip route
4.show ip ospf neighbor
5.show ip ospf neighbor detail
6.show ip ospf database
7.show ip ospf interface
8.show ip ospf flood-list
9.show ip ospf process-id
10.debug ip ospf hello
11.debug ip ospf adj
12.debug ip ospf events
13.debug ip ospf flood
14.debug ip ospf packet
15.debug ip ospf spf