超级账本hyperledger fabric第七集:智能合约
智能合约
- 执行环境:以太坊虚拟智能合约执行环境EVM,fabric执行环境是docker
- 链码
- 是应用层和区块链底层的中间点
- 每一个链码执行环境是一个独立的docker
- 使用GRPC协议与背书节点通信,只有背书节点才能运行智能合约
- 链码的生命周期
- 打包,智能合约的编写和编译
- 安装,将打包好的文件,上传到背书节点
- 实例化,实际的安装了,执行Init方法,只执行一次,构造函数
- 升级,升级和修复链码
- 交互,自己定义的方法的调用
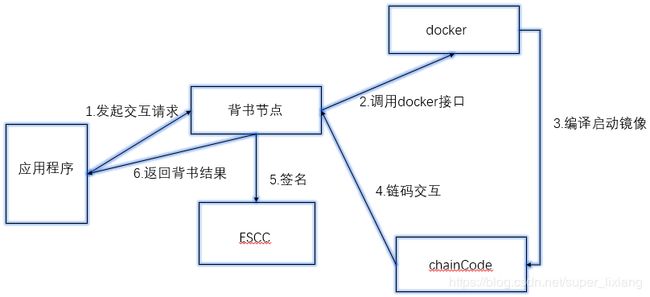
- 链码的交互流程
- 系统链码(了解)
- LSCC:管理链码的生命周期
- CSCC:配置管理链码,管理链的配置
- QSCC:查询账本存储,是一个区块索引的外部服务
- ESCC:交易背书的链码,交易执行后的链码进行封装签名,给客户端返回背书交易结果
- VSCC:交易验证的链码
- 链码编程的接口
- Init():链码初始化,只执行一次
- Invoke():链码的业务逻辑的编写
- 上面2个方法参数一样,参数是SDK的接口
- 链码SDK的接口:写代码再看
- 一些注意点:
- 分布式多机多节点执行,链码会执行很多次
- 不写随机函数,交易会无效,多次执行不一样
- 系统时间不写,多机时间不一定一样
网络搭建配置的实现
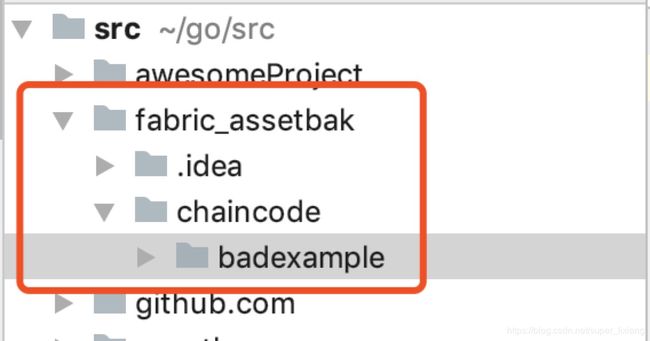
- 创建fabric_asset工程,在里面创建chaincode文件夹。
- 在badexample.go中
package main
import (
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
"bytes"
"strconv"
"math/rand"
"time"
"fmt"
)
type BadExampleCC struct {
}
//每一个链码必须实现2个方法
//链码的初始化
func (c *BadExampleCC) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
//直接返回成功
return shim.Success(nil)
}
//链码交互的入口
func (c *BadExampleCC) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
//直接返回一个随机数结果
return shim.Success(bytes.NewBufferString(strconv.Itoa(int(rand.Int63n(time.Now().Unix())))).Bytes())
}
func main() {
err := shim.Start(new(BadExampleCC))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error starting Simple chaincode: %s", err)
}
}
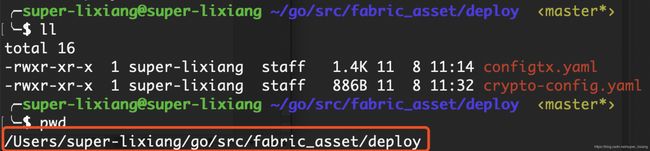
- crypto-config.yaml:用于配置组织节点的个数,参考first-network去编写
- 编写好后,传到linux对应目录
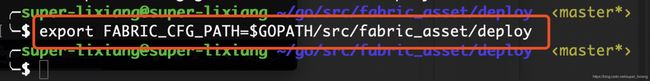
- 进入deploy目录,设置工作目录为当前目录
- 指定按照yaml文件生成配置
- configtx.yaml:用于区块联盟中的组织信息,配置名字和证书等的位置,参考firstnetwork去编写
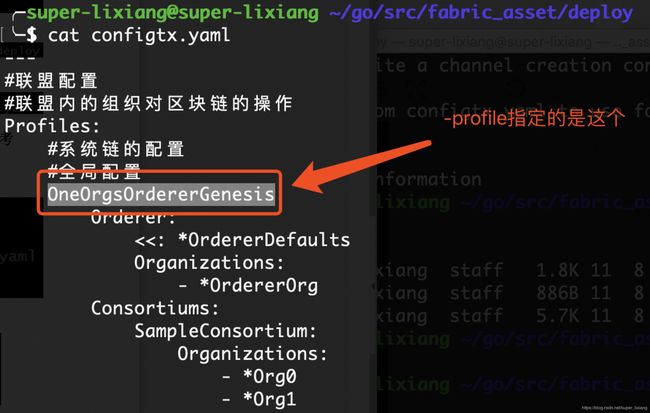
---
#联盟配置
#联盟内的组织对区块链的操作
Profiles:
#系统链的配置
#全局配置
OneOrgsOrdererGenesis:
Orderer:
<<: *OrdererDefaults
Organizations:
- *OrdererOrg
Consortiums:
SampleConsortium:
Organizations:
- *Org0
- *Org1
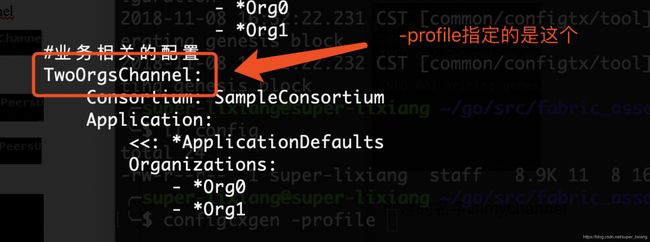
#业务相关的配置
TwoOrgsChannel:
Consortium: SampleConsortium
Application:
<<: *ApplicationDefaults
Organizations:
- *Org0
- *Org1
Organizations:
#组织内的配置
- &OrdererOrg
#组织名字
Name: OrdererOrg
#组织ID
ID: OrdererMSP
#组织证书的位置
MSPDir: crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/msp
- &Org0
Name: Org0MSP
ID: Org0MSP
MSPDir: crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org0.example.com/msp
#锚节点的配置
AnchorPeers:
- Host: peer0.org0.example.com
Port: 7051
- &Org1
Name: Org1MSP
ID: Org1MSP
MSPDir: crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/msp
#锚节点
AnchorPeers:
- Host: peer0.org1.example.com
Port: 7051
#orderer配置
Orderer: &OrdererDefaults
#配置共识机制
OrdererType: solo
Addresses:
- orderer.example.com:7050
#出块的时间间隔
BatchTimeout: 2s
#每个块的大小信息
BatchSize:
MaxMessageCount: 10
AbsoluteMaxBytes: 99 MB
PreferredMaxBytes: 512 KB
#kafka的配置
Kafka:
Brokers:
- 127.0.0.1:9092
Organizations:
Application: &ApplicationDefaults
Organizations:
- 编写好后,传到linux对应目录
- 创建用于存放配置的目录
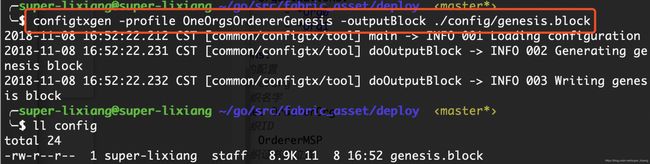
- 生成系统链的创世区块:-profile指定联盟配置,outputBlock指定存放的位置
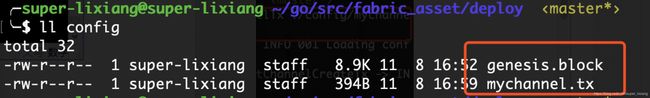
- 生成通道的创世交易:profile指定业务联盟,outputCreateChannelTx存放的路径,创建的名字叫mychannel
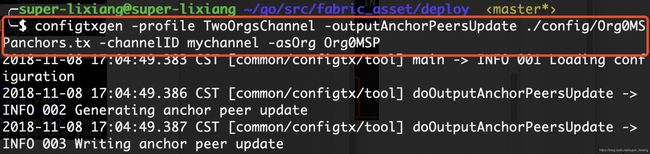
- 生成两个组织锚节点的交易信息
- 将docker-compose.yaml拖进deploy目录
version: '2'
services:
#1.系统一些环境变量的配置
#2.端口的映射关系
#3.文件的映射关系
orderer.example.com:
container_name: orderer.example.com
#指定使用镜像名称
image: hyperledger/fabric-orderer:x86_64-1.0.0
#环境变量的配置
environment:
#设置日志级别
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOGLEVEL=debug
#服务暴露的地址
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0
#下面2个是注入创世区块
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISMETHOD=file
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISFILE=/etc/hyperledger/config/genesis.block
#下面2个是证书相关的配置
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPID=OrdererMSP
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPDIR=/etc/hyperledger/orderer/msp
working_dir: /home/go_work/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/orderer
command: orderer
ports:
#前面是本机的,端口映射
- 7050:7050
volumes:
- ./config/genesis.block:/etc/hyperledger/config/genesis.block
- ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/:/etc/hyperledger/orderer
#peer的基础设置
peer.base:
image: hyperledger/fabric-peer:x86_64-1.0.0
environment:
#peer节点可能对chaincode做一些操作
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
#日志级别
- CORE_LOGGING_PEER=debug
#开启开发者模式
#- CORE_CHAINCODE_MODE=dev
#关于链码的日志级别
- CORE_CHAINCODE_LOGGING_LEVEL=DEBUG
#msp证书
- CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/etc/hyperledger/peer/msp
#状态数据库的存储引擎,这里配置使用levledb
- CORE_LEDGER_STATE_STATEDATABASE=goleveldb
#配置chaincode与peer节点使用的网络,同一个网络
- CORE_VM_DOCKER_HOSTCONFIG_NETWORKMODE=deploy_default
working_dir: /home/go_work/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
command: peer node start
#开启开发者模式
#command: peer node start --peer-chaincodedev=true
peer0.org0.example.com:
extends:
service: peer.base
container_name: peer0.org0.example.com
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer0.org0.example.com
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org0MSP
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
ports:
#grpc的端口
- 7051:7051
#事件监听的端口
- 7053:7053
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org0.example.com/peers/peer0.org0.example.com:/etc/hyperledger/peer
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
peer1.org0.example.com:
extends:
service: peer.base
container_name: peer1.org0.example.com
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer1.org0.example.com
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org0MSP
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org0.example.com:7051
ports:
#别与上面peer0的端口冲突就可以
- 17051:7051
- 17053:7053
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org0.example.com/peers/peer1.org0.example.com:/etc/hyperledger/peer
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
peer0.org1.example.com:
extends:
service: peer.base
container_name: peer0.org1.example.com
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer0.org1.example.com
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
ports:
#注意端口不冲突就可以
- 27051:7051
- 27053:7053
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com:/etc/hyperledger/peer
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
peer1.org1.example.com:
extends:
service: peer.base
container_name: peer1.org1.example.com
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer1.org1.example.com
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org1.example.com:7051
ports:
#注意端口不冲突就可以
- 37051:7051
- 37053:7053
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer1.org1.example.com:/etc/hyperledger/peer
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
peer2.org1.example.com:
extends:
service: peer.base
container_name: peer2.org1.example.com
environment:
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer2.org1.example.com
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer2.org1.example.com:7051
ports:
- 47051:7051
- 47053:7053
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer2.org1.example.com:/etc/hyperledger/peer
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
#peer节点客户端配置
cli:
container_name: cli
image: hyperledger/fabric-tools
tty: true
environment:
- GOPATH=/home/go_work
- CORE_LOGGING_LEVEL=DEBUG
- CORE_PEER_ID=cli
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:7051
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/etc/hyperledger/peer/users/[email protected]/msp
working_dir: /home/go_work/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/
command: /bin/bash
volumes:
#链码路径的注入
#本地中的相对路径,映射的容器中的绝对路径
- ./../chaincode:/home/go_work/src/github.com/chaincode
- ./config:/etc/hyperledger/config
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/:/etc/hyperledger/peer启动网络
- 启动docker,后台运行
- 查看orderer节点的运行日志
- 与客户端交互操作
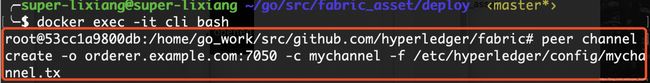
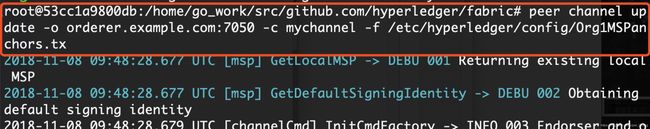
- 创建通道:-o指定与哪个orderer节点通信,-c指定创建的通道名称,-f指定使用的文件
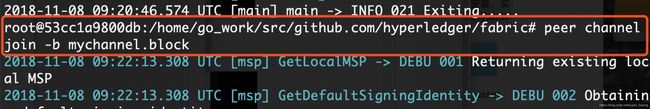
- 加入通道
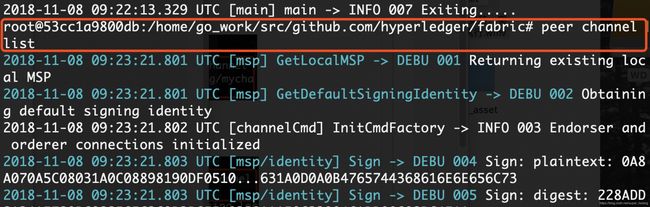
- 查看peer加入的通道列表
- 指定主节点
------------------------------------------------------------------基础网络搞定了----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
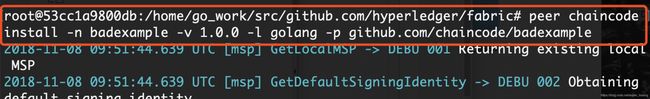
- 安装链码:-n是安装的名字,-v是version,-l是使用语言
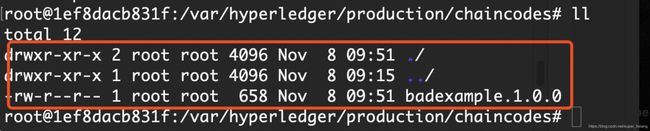
- 克隆一个会话,交互执行peer0,查看安装的链码
- 链码实例化
- 链码交互执行
- 多次执行查询,得到的结果不用,因为invoke()中使用了随机数,不要这么做
package main
import (
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
"bytes"
"strconv"
"math/rand"
"time"
"fmt"
)
type BadExampleCC struct {
}
//每一个链码必须实现2个方法
//链码的初始化
func (c *BadExampleCC) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
//直接返回成功
return shim.Success(nil)
}
//链码交互的入口
func (c *BadExampleCC) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
//直接返回一个随机数结果
return shim.Success(bytes.NewBufferString(strconv.Itoa(int(rand.Int63n(time.Now().Unix())))).Bytes())
}
func main() {
err := shim.Start(new(BadExampleCC))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error starting Simple chaincode: %s", err)
}
}