解决python3 UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode 或者decode等问题
解决python3 UnicodeEncodeError: ‘gbk’ codec can’t encode 或者decode等问题
反反复复总是出现decode或者encode 的问题,经过我尝试了n多次后莫名其妙地就可以运行了,所以说努力就能成功哈哈哈哈~
废话少数,开始我的表演~~~
环境:win10
编辑工具:sublime text2
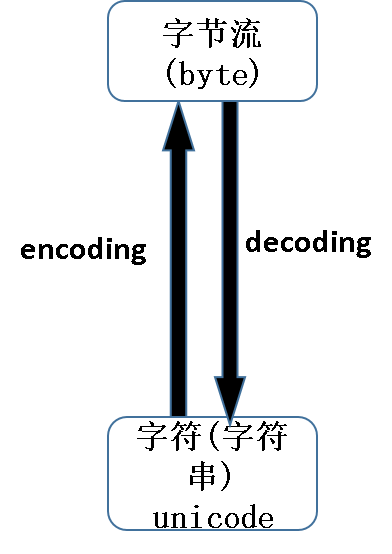
在python3里,有几点关于编码的常识:
测试代码1:
# coding:utf-8
import sys
import io
#创建并打开一个文件对其进行写操作
write_file=open("text1.txt",'w',encoding='utf-8')
#里面是一片化学文献
local_url="C:\\Users\\cheng\\Desktop\\para\\output.html"
#打开一个文件对其进行读操作
read_file= open(local_url,"r",encoding='utf-8')
#在print的显示过程中还会对内容进行先编码再解码显示unicode字符
print(read_file.read())
有以下几点是我个人经过一番测试后的结论,如果不对,欢迎批评指正~
- 上面代码中的write_file和read_file都是_io.TextIOWrapper类型,这种类型只能通过read()或者write()函数进行读写。
- 先说read()函数:read_file里面的内容如果是字符串即class=”str”,那么经过read()之后返回的也是字符串,只是这个字符串需要经过read_file中编码器的编码以及解码过程。
- print()函数在我看来和read_file一样,都是带有编码器的。如果输出字节流,就直接输出了,如果输出字符串,也需要先编码再解码。
- 所以说文件的编码方式以及print函数的编码方式就会显得比较重要,有时候需要改变一下其默认的编码方式
接下来举几个例子:
首先要明白一件事情python的默认编码是“gbk”,而且在windows里面,新文件的默认打开方式也是”gbk”。print()函数并不能识别所有的unicode字符。如下例子所示:
print('\u00bb')
结果报错!所以是print()函数自身有限制,不能完全打印所有的unicode字符。
其实print()函数的局限就是Python默认编码的局限,python的默认编码不是’utf-8’,改一下python的默认编码成’utf-8’就行了
只需要增加几行:
import io
import sys
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf8') #改变标准输出的默认编码 这样就解决了print()函数编码器的问题。
改变了标准输出的默认编码之后,程序如下:
import sys
import io
local_url="C:\\Users\\cheng\\Desktop\\para\\output.html"
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf-8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
#打开一个文件对其进行读操作
read_file= open(local_url,"r")
print(read_file.read()) 运行后结果显示如下:
UnicodeDecodeError: 'gbk' codec can't decode byte 0x93 in position 524原因:在windows下面。新文件的默认编码方式是”gbk”,read_file文件里面的内容是经过解码之后的unicode编码,也就是字符串,两者不能对应,自然就会出错。
改正后的代码:
import sys
import io
local_url="C:\\Users\\cheng\\Desktop\\para\\output.html"
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf-8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
#打开一个文件对其进行读操作
read_file= open(local_url,"r",encoding="utf-8")
print(read_file.read())没有问题了。
read()函数读取文件就是把里面的内容完全不改变得都出来,如果是字节流,就都出来字节流,如果是字符串就都出来字符串,只是在读取字符串的时候需要先编码成为字节流,再解码成为字符串。如果说原来的字符串是用”utf-8”解码的,后来还要用”utf-8”编码,我是这么理解的。
还有write()函数只能写进去str而不是byte
接着再来几个小练习测试一下刚才的猜想:
# coding:utf-8
import sys
import io
#创建并打开一个文件对其进行写操作
write_file=open("text1.txt",'w',encoding="utf-8")
#print(type(write_file))
#里面是一片化学文献
local_url="C:\\Users\\cheng\\Desktop\\para\\output.html"
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf-8') #改变标准输出的默认编码
#打开一个文件对其进行读操作
read_file= open(local_url,"r",encoding="utf-8")
#print(type(read_file))
#在print的显示过程中还会对内容进行解码显示unicode字符
#print(read_file.read())
a=open("text1.txt",'r',encoding="utf-8")
write_file.write(read_file.read())
print(a.read())bingo!