Android自定义View实现流式布局(热门标签效果)
来源:http://www.jianshu.com/p/0e12a1214e62
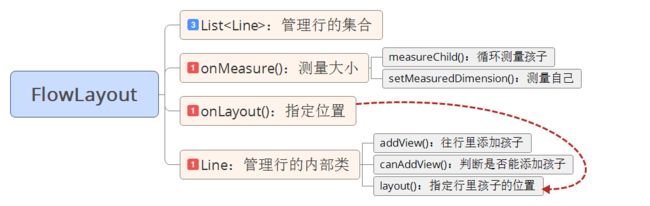
一、流式布局的实现
实现原理:采用面向对象思想将整个布局分为很多行的对象,每个行对象管理自己行内的孩子,这里通过集合来管理。
1.内部类Line的实现
1.1 定义行的基本属性
- List:管理行中的孩子
- maxWidth:行的最大宽度
- usedWidth:使用的宽度
- height:行的高度
space:孩子之间的间距
构造初始化maxWidth和space
public Line(int maxWidth, int horizontalSpace) {
this.maxWidth = maxWidth;
this.space = horizontalSpace;
}1.2 addView(View view)方法实现
- 往行的集合里添加View,更新行的使用宽度和高度
/**
* 往集合里添加孩子
*/
public void addView(View view) {
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
// 更新行的使用宽度和高度
if (views.size() == 0) {
// 集合里没有孩子的时候
if (childWidth > maxWidth) {
usedWidth = maxWidth;
height = childHeight;
} else {
usedWidth = childWidth;
height = childHeight;
}
} else {
usedWidth += childWidth + space;
height = childHeight > height ? childHeight : height;
}
// 添加孩子到集合
views.add(view);
}1.3 canAddView(View view)方法实现
- 判断是否能往行里添加孩子,如果孩子的宽度大于剩余宽度就不能
/**
* 判断当前的行是否能添加孩子
*
* @return
*/
public boolean canAddView(View view) {
// 集合里没有数据可以添加
if (views.size() == 0) {
return true;
}
// 最后一个孩子的宽度大于剩余宽度就不添加
if (view.getMeasuredWidth() > (maxWidth - usedWidth - space)) {
return false;
}
// 默认可以添加
return true;
}2.对容器进行测量(onMeasure方法的实现)
2.1 获取宽度,计算maxWidth,构造传入Line
- 总宽度减去左右边距就是行的最大宽度
// 获取总宽度
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
// 计算最大的宽度
mMaxWidth = width - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();2.2 循环获取孩子进行测量
- 获取孩子总数,遍历获取每一个孩子,然后进行测量,测量完之后还需要将孩子添加到行集合里,然后将行添加到管理行的集合里
// ******************** 测量孩子 ********************
// 遍历获取孩子
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
// 测量孩子
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 测量完需要将孩子添加到管理行的孩子的集合中,将行添加到管理行的集合中
if (mCurrentLine == null) {
// 初次添加第一个孩子的时候
mCurrentLine = new Line(mMaxWidth, HORIZONTAL_SPACE);
// 添加孩子
mCurrentLine.addView(childView);
// 添加行
mLines.add(mCurrentLine);
} else {
// 行中有孩子的时候,判断时候能添加
if (mCurrentLine.canAddView(childView)) {
// 继续往该行里添加
mCurrentLine.addView(childView);
} else {
// 添加到下一行
mCurrentLine = new Line(mMaxWidth, HORIZONTAL_SPACE);
mCurrentLine.addView(childView);
mLines.add(mCurrentLine);
}
}
}2.3 测量自己
由于宽度肯定是填充整个屏幕,这里只需要处理行的高度,累加所有的行高和竖直边距算出高度
// ******************** 测量自己 *********************
// 测量自己只需要计算高度,宽度肯定会被填充满的
int height = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
// 所有行的高度
height += mLines.get(i).height;
}
// 所有竖直的间距
height += (mLines.size() - 1) * VERTICAL_SPACE;
// 测量
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);3.指定孩子的显示位置(onLayout方法的实现)
实现思路:指定孩子的位置,孩子给了行管理,所以这里具体孩子的位置应该交给行去指定。容器只需要指定行的位置就可以。
遍历获取所有的行,让行去指定孩子的位置,指定行的高度
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 这里只负责高度的位置,具体的宽度和子孩子的位置让具体的行去管理
l = getPaddingLeft();
t = getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
// 获取行
Line line = mLines.get(i);
// 管理
line.layout(t, l);
// 更新高度
t += line.height;
if (i != mLines.size() - 1) {
// 不是最后一条就添加间距
t += VERTICAL_SPACE;
}
}
}4.Line中layout方法的实现(指定孩子的位置)
遍历获取每一个孩子,获取孩子的宽度和高度,计算上下左右的大小,指定孩子的位置,之后还需要更新孩子左边的大小
// 循环指定孩子位置
for (View view : views) {
// 获取宽高
int measuredWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int measuredHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
// 重新测量
view.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(measuredWidth + avg, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(measuredHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
// 重新获取宽度值
measuredWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int top = t;
int left = l;
int right = measuredWidth + left;
int bottom = measuredHeight + top;
// 指定位置
view.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
// 更新数据
l += measuredWidth + space;
}5.细节处理
第一次测量之后,行管理器中就有了行的对象,之后每次测量都会去创建下一行,这样就会出现很多空行出来,所以需要在测量之前将集合清空。
mLines.clear();
mCurrentLine = null;每一行的最后一个孩子放不下就放到下一行,这样每一行就都会有空格,这里将这些空格平分给行里的每一个孩子,重新指定其宽度。
// 平分剩下的空间
int avg = (maxWidth - usedWidth) / views.size();
// 重新测量
view.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(measuredWidth + avg, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(measuredHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));
// 重新获取宽度值
measuredWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();6.使用自定义属性,将水平间距和竖直间距做成属性,在布局中指定,增强扩展性
- attrs文件指定属性名
<declare-styleable name="FlowLayout">
<attr name="width_space" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="height_space" format="dimension"/>
declare-styleable> - 构造中获取属性
// 获取自定义属性
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FlowLayout);
horizontal_space = array.getDimension(R.styleable.FlowLayout_width_space,0);
vertical_space = array.getDimension(R.styleable.FlowLayout_height_space,0);
array.recycle();- 布局中使用属性
app:width_space="10dp"
app:height_space="10dp"经过以上步骤之后,FlowLayout基本就已经实现了,接下来就是使用了。
二、流式布局的使用
- 布局中申明
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:fillViewport="true"
tools:context="com.pinger.sample.MainActivity">
<com.pinger.library.FlowLayout
app:width_space="10dp"
app:height_space="10dp"
android:id="@+id/flow_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="5dp"/>
代码中使用
其实就是循环遍历数据的长度,不断的创建TextView,然后设置TextView的属性和背景,包括五彩背景等,最后将TextView添加到FlowLayout中就可以。
具体代码请查看Demo