Linux:线程概念及基本操作
Linux学习目录
- 1、 线程的概念
- 1.1、线程和进程的区别
- 1.2、线程共享的资源
- 1.3、线程独立的资源
- 1.4、线程控制
- 1.4.1、线程创建
- 1:POSIX线程库
- 2:函数格式
- 1、创建线程
- 2、获取线程id
- 3、终止线程
- 4、线程等待
- 5、查看线程
- 1.4.1、线程创建
- 1.5、分离线程
1、 线程的概念
- 1、线程是进程内部的一个执行分支,线程量级很小。(所谓的内部就是在进程的地址空间内运行)
- 2、一切进程至少都有一个线程
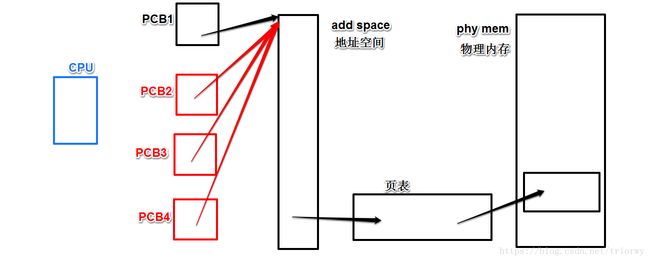
PCB1相当于主线程,新线程PCB2、PCB3、PCB4相当于用vfork创建出来的,它们指向同一块地址空间,它们隶属于同一个进程,但是他们有着自己的线程ID
1.1、线程和进程的区别
- 1、进程是资源竞争的基本单位
- 2、linux下没有真正意义的线程,因为linux下没有给线程设计专有的结构体,它的线程是用进程模拟的,而它是由多个进程共享一块地址空间而模拟得到的。
- 3、创建一个线程的资源成本小,工作效率高
- 4、Linux下cpu所看到的所以进程都可以看成轻量级的进程
- 5、进程是承担分配系统资源的基本实体,进程具有独立性(但进程间通信打破了独立性)
- 6、线程是cpu或操作系统调度的基本单位,线程具有共享性
1.2、线程共享的资源
- 同一块地址空间
- 文件描述符表()
- 每种信号的处理方式(如:SIG_DFL,SIG_IGN或者自定义的信号优先级)
- 当前工作目录
- 用户id和组id
1.3、线程独立的资源
- 线程会产生临时变量,临时变量保存再栈上,所以每个线程都有自己的私有栈结构
- 每个线程都有私有的上下文信息。
- 线程ID
- 一组寄存器的值
- errno变量
- 信号屏蔽字以及调度优先级
1.4、线程控制
1.4.1、线程创建
1:POSIX线程库
- 与线程有关的函数构成了一个完整的系列,绝大多数函数的名字都是以“pthread_”打头的
- 要使用这些函数库,要通过引入头文件
#include- 链接这些线程函数库时要使用编译器命令的“-lpthread”选项
2:函数格式
1、创建线程
功能:创建一个新的线程
原型
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*star
t_routine)(void*), void *arg);
参数
thread:返回线程ID
attr:设置线程的属性,attr为NULL表⽰示使⽤用默认属性
start_routine:是个函数地址,线程启动后要执⾏的函数
arg:传给线程启动函数的参数
返回值:成功返回0;失败返回错误码2、获取线程id
函数1:syscall(int number,...)//获取内核线程id
函数2:pthread_self()//获取用户态线程id了解内核线性和用户态线程可参考这里:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangye3017/article/details/80396745
3、终止线程
- return返回
- pthread_exit(void *val)
功能:线程终止 原型
void pthread_exit(void *value_ptr);
参数
value_ptr:value_ptr
返回值:无返回值,跟进程一样,线程结束的时候无法返回到它的调用者(自身)
- pthread_canel()取消线程,返回-1
功能:杀死一个执行中的线程
原型
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
参数
thread:线程ID
返回值:成功返回0;失败返回错误码一个线程可以自己把自己杀死,也可以被别人杀死
eg1:
#include.h>
#include.h>
#include.h>
void *thread_run(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
printf("new thread,thread is :%u,pid:%d\n",pthread_self(),getpid());
sleep(1);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_run,NULL);
while(1)
{//pthread_self()是获取线程id
printf("main thread,thread is :%u,pid:%d\n",pthread_self(),getpid()) ;
sleep(3);
pthread_cancel(pthread_self());//杀死自己
}
return 0;
} 主线程和新线程那个先运行完全由调度器决定,这里主线程先打印一句后,时间片轮转到新线程,新线程打印后遇pthread_exit(NULL)退出,主线程再睡3秒,遇到 pthread_cancel(pthread_self())退出。
使用pthread_cancel()函数需要注意:
pthread_cancel()函数并不是立即退出的,直到遇到cancel点它才会退出,而系统调用都是cancel点(如printf函数)。
如果没有cancel点就需要人为手动加cancel点
手动添加cancel点函数
pthread_testcancel(void)4、线程等待
为什么要线程等待呢?
- 1、就像子进程死亡,需要父进程等待并回收一样,新线程死亡,其空间没有被释放,需要主线程等待回收
- 2、如果再创建新的线程不会复用刚才退出线程的地址空间
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread,void **retval)
thread:线程ID
value_ptr:它指向一个指针,后者指向线程的返回值
返回值:成功返回0;失败返回错误码作用:
- 主线程等待新线程退出,否则就会导致进程的内存泄漏
- 回收新线程的退出结果
eg2:
#include5、查看线程
1.5、分离线程
为什么要分离线程?
- 如果新线程创建后,不用pthread_join()等待回收新线程,那么就会造成内存泄漏,但是当等待新线程时,主线程就会一直阻塞,影响主线程处理其他链接要求,这时候就需要一种办法让新线程退出后,自己释放所有资源,因此产生了线程分离
1:线程自己退出后释放自己资源
int pthread_detach(pthread_self())2:线程组内其他线程对目标线程进行分离
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread)返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误码
#include