TestNG使用教程
一.前言
JUnit 4和TestNG都是Java中非常受欢迎的单元测试框架。两种框架在功能上看起来非常相似。 哪一个更好? 在Java项目中应该使用哪个单元测试框架?下面表中概括了JUnit 4和TestNG之间的功能比较。如下图所示
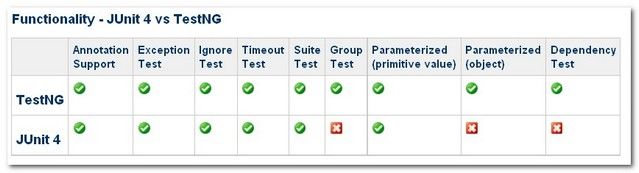
二.TestNg与JUnit4的比较
| 特点 | JUnit 4 | TestNG |
|---|---|---|
| 测试注释 | @Test | @Test |
| 在套件中的所有测试运行之前运行 | - | @BeforeSuite |
| 在套件中的所有测试运行之后运行 | - | @AfterSuite |
| 测试之前运行 | - | @BeforeTest |
| 测试之后运行 | - | @AfterTest |
| 在调用属于任何这些组的第一个测试方法之前运行 | - | @BeforeGroups |
| 在调用属于任何这些组的第一个测试方法之后运行 | - | @AfterGroups |
| 在调用当前类的第一个测试方法之前运行 | @BeforeClass | @BeforeClass |
| 在调用当前类的第一个测试方法之后运行 | @AfterClass | @AfterClass |
| 在每个测试方法之前运行 | @Before | @BeforeMethod |
| 在每个测试方法之后运行 | @After | @AfterMethod |
| 忽略测试 | @ignore | @Test(enbale=false) |
| 预期的异常 | @Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class) | @Test(expectedExceptions = ArithmeticException.class) |
| 超时测试 | @Test(timeout = 1000) | @Test(timeout = 1000) |
三.使用实例
在poml.xml加入包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>6.10</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
1.单测试类
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
2.套件组合测试
1.新建 Test1.java
public class Test1 {
//对于套件测试,在此套件中的所有测试运行之前运行。
@BeforeSuite()
public void beforeSuite() {
System.out.println("Test1-->@BeforeSuite");
}
// 对于套件测试,在此套件中的所有测试运行之后运行
@AfterSuite()
public void afterSuite() {
System.out.println("Test1-->@AfterSuite");
}
//对于套件测试,在运行属于标签内的类的任何测试方法之前运行
@BeforeTest()
public void beforeTest() {
System.out.println("Test1-->@BeforeTest");
}
//对于套件测试,在运行属于标签内的类的所有测试方法都已运行之后运行。
@AfterTest()
public void afterTest() {
System.out.println("Test1-->@AfterTest");
}
}
2.新建 Test2.java
public class Test2 {
@Test
public void runOtherTest1() {
System.out.println("@Test2 - runOtherTest1");
}
@Test
public void runOtherTest2() {
System.out.println("@Test2 - runOtherTest2");
}
}
3.新建 tsetng.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="TestAll">
<test name="case1">
<classes>
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.kit.Test2" />
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.kit.Test1" />
</classes>
</test>
<test name="case2">
<classes>
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.kit.Test2" />
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.kit.Test1" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
4.运行testng.xm 结果
Test1-->@BeforeSuite
Test1-->@BeforeTest
@Test2 - runOtherTest1
@Test2 - runOtherTest2
Test1-->@AfterTest
Test1-->@BeforeTest
@Test2 - runOtherTest1
@Test2 - runOtherTest2
Test1-->@AfterTest
Test1-->@AfterSuite
===============================================
TestAll
Total tests run: 4, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
3.预期异常测试
1.运行时异常
创建 TestRuntime.java
public class TestRuntime {
@Test(expectedExceptions = ArithmeticException.class)
public void divisionWithException() {
int a = 1 / 0;
System.out.println("结果:"+ a);
}
}
运行上面代码,得到以下结果
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
2.检查异常
新建文件 TestCheckedException.java
public class TestCheckedException {
@Test(expectedExceptions = UserSaveException.class)
public void throwIfUserIsNull() throws UserSaveException {
saveUser(null);
}
public TResult saveUser(User user){
if (user == null) {
throw new UserSaveException("user is empty!");
}
return null;
}
}
新建 UserSaveException.java
public class UserSaveException extends RuntimeException {
public UserSaveException(){
}
public UserSaveException(String msg){
super(msg);
System.out.println("异常信息:"+msg);
}
}
运行测试如下:
异常信息:user is empty!
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
4.忽略测试
如果使用@Test(enabled = false)注释在测试方法上,则会绕过这个未准备好测试的测试用例
新建测试类 TestIgnore.java.代码如下:
public class TestIgnore {
@Test // default enable=true
public void test1() {
System.out.println("test1");
Assert.assertEquals(true, true);
}
@Test(enabled = true)
public void test2() {
System.out.println("test2");
Assert.assertEquals(true, true);
}
@Test(enabled = false)
public void test3() {
System.out.println("test3");
Assert.assertEquals(true, true);
}
}
测试结果:
test1
test2
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
5.超时测试
“超时”表示如果单元测试花费的时间超过指定的毫秒数, 那么TestNG将会中止它并将其标记为失败。“超时”也可用于性能测试,以确保方法在合理的时间内返回。
新建测试类 TestTimeout.java,代码如下:
public class TestTimeout {
/**
* @Description 超时设置
**/
@Test(timeOut = 5000) // time in mulliseconds
public void testThisShouldPass() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("当前时间:"+new Date());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("超时4秒收执行,时间:"+new Date());
}
/**
* @Description 超时设置
**/
@Test(timeOut = 5000) // time in mulliseconds
public void testThisPass() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("当前时间:"+new Date());
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("超时4秒收执行,时间:"+new Date());
}
@Test(timeOut = 1000)
public void testThisShouldFail() {
while (true){
// do nothing
System.out.println("哈哈哈..."+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
测试 testThisShouldPass 结果如下:
当前时间:Fri Dec 28 10:28:30 CST 2018
超时4秒收执行,时间:Fri Dec 28 10:28:34 CST 2018
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
测试 testThisPass 结果如下:
当前时间:Fri Dec 28 10:29:15 CST 2018
org.testng.internal.thread.ThreadTimeoutException: Method com.example.springbootTest.testNg.timeout.TestTimeout.testThisPass() didn't finish within the time-out 5000
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 1, Skips: 0
===============================================
6.分组测试
分组测试是TestNG中的一个新的创新功能,它在JUnit框架中是不存在的。 它允许您将方法调度到适当的部分,并执行复杂的测试方法分组。 您不仅可以声明属于某个分组的方法,还可以指定包含其他组的组。 然后调用TestNG,并要求其包含一组特定的组(或正则表达式),同时排除另一个分组。 组测试提供了如何分区测试的最大灵活性,如果您想要背靠背运行两组不同的测试,则不需要重新编译任何内容。使用标记在testng.xml文件中指定分组。 它可以在或标签下找到。 标签中指定分组适用于其下的所有标签。
1.在方法上的分组
新建测试实例 TestGroup.java,代码如下:
public class TestGroup {
@BeforeGroups("groups1")
public void setupDB() {
System.out.println("setupDB()");
}
@AfterGroups("groups2")
public void cleanDB() {
System.out.println("cleanDB()");
}
@Test(groups = "groups1")
public void runSelenium() {
System.out.println("groups1()");
}
@Test(groups = "groups2")
public void testConnectMsSQL() {
System.out.println("groups2");
}
@Test(dependsOnGroups = { "groups1", "groups2" })
public void runFinal() {
System.out.println("runFinal");
}
}
测试结果如下:
setupDB()
groups1()
groups2
cleanDB()
runFinal
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
2.在类上的分组
新建测试类 TestGroup2.java 代码如下:
@Test(groups = "groups2")
public class TestGroup2 {
public void test1() {
System.out.println("TestGroup2==>test1");
}
public void test2() {
System.out.println("TestGroup2==>test2");
}
}
新建testng.xml 代码如下:
<suite name="TestAll">
<test name="test1">
<classes>
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.group.TestGroup2" />
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.group.TestGroup" />
</classes>
</test>
<test name="test2">
<!-- 指定运行分组-->
<groups>
<run>
<include name="groups2" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.group.TestGroup2" />
<class name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.group.TestGroup" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
测试运行testng.xml 结果如下:
TestGroup2==>test1
TestGroup2==>test2
setupDB()
groups1()
groups2
cleanDB()
runFinal
TestGroup2==>test1
TestGroup2==>test2
groups2
===============================================
TestAll
Total tests run: 8, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
7.套件测试
测试套件是用于测试软件程序的行为或一组行为的测试用例的集合。 在TestNG中,我们无法在测试源代码中定义一个套件,但它可以由一个XML文件表示,因为套件是执行的功能。 它还允许灵活配置要运行的测试。 套件可以包含一个或多个测试,并由标记定义。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| name | 套件的名称,这是一个强制属性。 |
| verbose | 运行的级别或详细程度。 |
| parallel | TestNG是否运行不同的线程来运行这个套件。 |
| thread-count | 如果启用并行模式(忽略其他方式),则要使用的线程数。 |
| annotations | 在测试中使用的注释类型。 |
| time-out | 在本测试中的所有测试方法上使用的默认超时。 |
8.依赖测试
有时,我们可能需要以特定顺序调用测试用例中的方法,或者可能希望在方法之间共享一些数据和状态。 TestNG支持这种依赖关系,因为它支持在测试方法之间显式依赖的声明。
1.dependOnMethods示例
public class dependTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("This is test1");
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = { "test1" })
public void test2() {
System.out.println("This is test2");
}
}
测试结果如下:
This is test1
This is test2
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
1.2. 如果test1()失败,则将跳过test2()
测试用例
public class dependTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("This is test1");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = { "test1" })
public void test2() {
System.out.println("This is test2");
}
}
测试结果如下:
This is test1
java.lang.RuntimeException
at com.example.springbootTest.testNg.depend.dependTest.test1(dependTest.java:14)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.testng.internal.MethodInvocationHelper.invokeMethod(MethodInvocationHelper.java:104)
at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeMethod(Invoker.java:645)
at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeTestMethod(Invoker.java:851)
at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeTestMethods(Invoker.java:1177)
at org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.invokeTestMethods(TestMethodWorker.java:129)
at org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.run(TestMethodWorker.java:112)
at org.testng.TestRunner.privateRun(TestRunner.java:756)
at org.testng.TestRunner.run(TestRunner.java:610)
at org.testng.SuiteRunner.runTest(SuiteRunner.java:387)
at org.testng.SuiteRunner.runSequentially(SuiteRunner.java:382)
at org.testng.SuiteRunner.privateRun(SuiteRunner.java:340)
at org.testng.SuiteRunner.run(SuiteRunner.java:289)
at org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.runSuite(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:52)
at org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.run(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:86)
at org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesSequentially(TestNG.java:1293)
at org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesLocally(TestNG.java:1218)
at org.testng.TestNG.runSuites(TestNG.java:1133)
at org.testng.TestNG.run(TestNG.java:1104)
at org.testng.IDEARemoteTestNG.run(IDEARemoteTestNG.java:72)
at org.testng.RemoteTestNGStarter.main(RemoteTestNGStarter.java:123)
Test ignored.
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 1, Skips: 1
===============================================
2.dependsOnGroups测试
新建Test1.java ,代码如下:
public class Test1 {
@Test(dependsOnGroups={"test2_method1"})
public void method1() {
System.out.println("Test1==>This is method 1");
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = { "method1" })
public void method2() {
System.out.println("Test1==>This is method 2");
}
}
新建Test2.java ,代码如下:
public class Test2 {
@Test(groups="test2_method1")
public void method1() {
System.out.println("Test2==>This is method 1");
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = { "method1" })
public void method2() {
System.out.println("Test2==>This is method 2");
}
}
新建Testng.xml ,代码如下:
<suite name="TestDependency">
<test name="TestCase1">
<classes>
<class
name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.depend.dependsOnGroups.Test1">
</class>
<class
name="com.example.springbootTest.testNg.depend.dependsOnGroups.Test2">
</class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
运行testng.xml ,测试结果如下:
Test2==>This is method 1
Test1==>This is method 1
Test2==>This is method 2
Test1==>This is method 2
===============================================
TestDependency
Total tests run: 4, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
9.参数化测试
TestNG中的另一个有趣的功能是参数化测试。 在大多数情况下,您会遇到业务逻辑需要大量测试的场景。 参数化测试允许开发人员使用不同的值一次又一次地运行相同的测试。
新建测试用例 TestParameterDataProvider.java 代码如下:
public class TestParameterDataProvider {
@Test(dataProvider = "num")
public void test(int x, int y) {
System.out.println("结果:"+(x+y));
}
@DataProvider(name = "num")
public Object[][] provideData() {
return new Object[][] { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 4, 5 } };
}
//传递对象参数
@Test(dataProvider = "map")
public void testConnection(Map<String, String> map) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("[Key] : " + entry.getKey() + " [Value] : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
@DataProvider(name = "map")
public Object[][] provideDbConfig() {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("username","user");
map.put("password","pass");
return new Object[][] { { map } };
}
}
测试结果:
结果:3
结果:5
结果:9
[Key] : password [Value] : pass
[Key] : username [Value] : user
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 4, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
10.负载测试
1.invocationCount标识测试的次数
public class TestRepeatThis {
//确定TestNG应该运行这个测试方法的次数
@Test(invocationCount = 3)
public void test() {
System.out.println("hello world " );
}
}
结果:
hello world
hello world
hello world
===============================================
Default Suite
Total tests run: 3, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
2.threadPoolSize
threadPoolSize属性告诉TestNG创建一个线程池以通过多个线程运行测试方法。 使用线程池,会大大降低测试方法的运行时间
public class testThreadPools {
@Test(invocationCount = 10, threadPoolSize = 2)
public void testThreadPools() {
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}