Framwork源码解析(1)_Zygote进程启动流程
Android系统启动流程
先看一张图,从Android系统设备开机到Zygote进程启动,经历了一下几个过程。

- init进程
init进程是linux的根进程,android系统是基于linux系统的,因此可以算作是整个android操作系统的第一个进程;Linux中的所有进程都是有init进程创建并运行的。首先Linux内核启动,然后在用户空间中启动init进程,再启动其他系统进程。在系统启动完成完成后,init将变为守护进程监视系统其他进程。
具体启动流程文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/wjky2014/article/details/103143700
https://www.jianshu.com/p/657336b545bd
什么是Zygote进程
Zygote(孵化)进程是所有android进程的父进程,包括SystemServer和各种应用进程都是通过Zygote进程fork出来的。Zygote进程相当于是android系统的根进程,后面所有的进程都是通过这个进程fork出来的,创建Zygote进程的时候主要做了下面几件事:
- 创建JVM
- 启动SystemServer进程
- 孵化应用进程
由于Zygote进程在启动时会创建JVM,因此通过fock而创建的应用程序进程和SystemServer进程可以在内部获取一个JVM的实例拷贝。
Zygote启动流程
一、init进程加载init.rc,引入zygote.rc
1、Zygote进程是由init进程孵化出来的,init进程启动的时候会去加载init.rc配置文件,文件地址是:/system/core/rootdir/init.rc。配置文件中又加载了zygote.rc,源码如下:
import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc
zygote,rc文件又分为32位和64位的配置,如下所示:
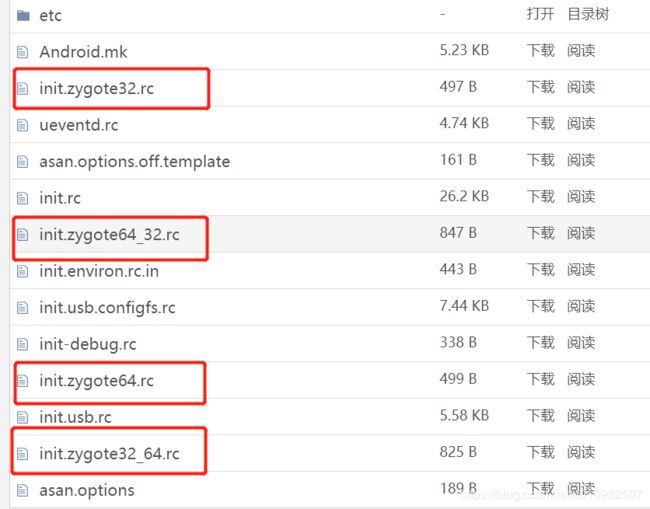
这代表了Andorid系统支持4种运行模式:
-
纯32位模式:属性ro.zygote的值为zygote32
-
混32位模式(即32位为主,64位为辅)模式:属性ro.zygote的值为zygote32_64
-
纯64位模式:属性ro.zygote的值为zygote64
-
混64位模式(即 64位为主,32位为辅)模式:属性ro.zygote值为zygote64_32
init进程会根据设备的不同来加载不同的zygote配置文件。zygote.rc配置文件如下所示:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
使用的是Android init配置脚本的语法,重点关注第一行内容:service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
zygote是启动service的名称/system/bin/app_process64是编译完成后的可执行文件路径--zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote是启动参数
zygote进程是通过fork创建的,然后执行execve()函数来启动进程,execve()函数需要传入一个可执行文件路径和创建参数,传入的就是这个地方配置的。execve()函数叫做执行程序函数,可以来执行shell脚本,单独的shell命令,或者是调用其他的程序。
2、 init.cpp分析
init.cpp程序是init进程启动程序,文件路径是/system/core/init/init.cpp。在main入口函数中,主要做了以下几件事:
- ueventd和watchdogd守护进程
- 创建目录,挂载分区
- 解析启动脚本
- 启动服务
- 守护服务
3、 fork zygote进程
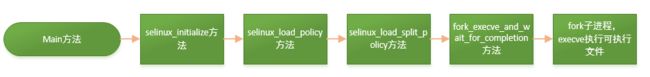
- 在main函数中调用
selinux_initialize初始化方法 - 在
selinux_initialize方法中调用selinux_load_policy方法 - 在
selinux_load_policy方法中调用selinux_load_split_policy方法 - 调用
fork_execve_and_wait_for_completion方法 - 在
fork_execve_and_wait_for_completion方法中fork子进程,当fork完进程时,如果返回0表示是子进程,如果返回子进程pid则是父进程。zygote进程就在这里被创建。 - 最后通过
execve函数来执行编译好的可执行文件,来启动zygote进程。,exec将用一个新的可执行文件的内容替换当前进程的代码段、数据段、堆和栈段。Fork加exec 是Linux启动应用的标准做法,init进程也是这样来启动的各种服务的。 - Zygote初始化时会创建创建虚拟机,同时把需要的系统类库和资源文件加载到内存里面。Zygote fork出子进程后,这个子进程也继承了能正常工作的虚拟机和各类系统资源,接下来子进程只需要装载APK文件的字节码文件就可以运行了。
二、app_main.cpp类中调用
app_main.cpp类文件路径在:/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
1、 在类中,下面代码 判断参数是不是--zygote,这个参数就是解析的zygote.rc配置文件中的参数
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
2、 如果是zygote,则通过AppRuntime来调用ZygoteInit类
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
3、 AppRuntime类的实现在app_main.cpp类中
通过对main()函数的分析,可以看出main()主要根据传入的参数初始化启动参数,具体的启动过程是由AppRuntime完成的。AppRuntime的声明和实现都在app_main.cpp中,它继承自AndroidRuntime,start是AndroidRuntime中的方法。
start函数主要作用是:
- 启动Android运行时环境,
- 启动虚拟机
- 调用className参数所指定的类的main()方法(即:Java中的main方法)。传的是
com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit,所以调用的是ZygoteInit.java类的main方法
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
// 代码省略。。。。
// 1、启动Java虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
// 2、注册Android JNI函数
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
// 3、调用ZygoteInit类中的main()方法
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
三、ZygoteInit类分析
1、加载此类首先要执行main方法
ZygoteInit类路径是:/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
// 1、创建ZygoteServer
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
BootTimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new BootTimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
// 2、设置DDMS可用
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// 3、声明变量,startSystemServer状态 socket名称 abi
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
// 4、注册socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// 5、预加载资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
// Set seccomp policy
Seccomp.setPolicy();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// 6、启动System Server
if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// 7、运行socket循环,来等待客户端的socket连接
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
从main函数代码中,主要做了以下几件事:
- 创建ZygoteServer
- 设置DDMS可用,在创建zygote进程之前就已经可用DDMS了
- 通过循环判断是否需要启动System Server 、获取socket的名称、获取abi列表
- 注册socket,通过registerZygoteSocket函数来创建一个Server端的Socket,这个name为”zygote”的Socket用来等待ActivityManagerService来请求Zygote来创建新的应用程序进程。
- 预加载资源
- 启动System Server,这样系统的关键服务也会由SystemServer进程启动起来。
- runSelectLoop函数监听socket来等待客户端连接和请求。
2、zygote的socket是如何创建的
通过调用registerServerSocket(socketName)方法来创建,
找到ZygoteServer.java类文件,路径是:/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
具体代码如下,通过 new LocalServerSocket(fd)创建服务端socket,等待ActivityManagerService来请求Zygote来创建新的应用程序进程。
void registerServerSocket(String socketName) {
if (mServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;
try {
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
// 创建本地服务socket
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}
3、preload预加载资源
预加载资源主要做了以下几件事:
- 加载所需的各种class文件
- 加载资源
- 加载OpenGL
- 加载Libraries
- 加载文字资源
- 初始化webview,要求webview的初始化必须在zygote进程,为了内存共享
static void preload(BootTimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog) {
Log.d(TAG, "begin preload");
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("BeginIcuCachePinning");
beginIcuCachePinning();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // BeginIcuCachePinning
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadClasses");
// 加载所需的各种class文件
preloadClasses();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadClasses
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadResources");
// 加载资源
preloadResources();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadResources
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadOpenGL");
// 加载OpenGL
preloadOpenGL();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
// 加载Libraries
preloadSharedLibraries();
// 加载文字资源
preloadTextResources();
// Ask the WebViewFactory to do any initialization that must run in the zygote process,
// for memory sharing purposes.
// 要求webview的初始化必须在zygote进程,为了内存共享
WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
endIcuCachePinning();
warmUpJcaProviders();
Log.d(TAG, "end preload");
sPreloadComplete = true;
}
4、启动System Server进程
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM
);
/* Containers run without this capability, so avoid setting it in that case */
if (!SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_RUNNING_IN_CONTAINER, false)) {
capabilities |= posixCapabilitiesAsBits(OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND);
}
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
// 1、配置参数
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
// 2.args数组封装成Arguments对象
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
// 3、通过zygote来孵化System Server进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
// pid为0表示是子进程,即System Server进程
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}
- 创建args数组,这个数组用来保存SystemServer的启动参数,其中可以看出SystemServer进程的用户id和用户组id被设置为1000;并且拥有用户组1001到1010,1018、1021、1032、3001~3010的权限;进程名为system_server;启动的类名为com.android.server.SystemServer。
- 将args数组封装成Arguments对象并供forkSystemServer函数调用。
- 用Zygote的forkSystemServer,主要通过fork函数在当前进程创建一个子进程(也就是SystemServer进程),如果返回的pid 为0,也就是表示在新创建的子进程中执行的,则执行注释4处的handleSystemServerProcess,反射调用SystemServer的main()函数,来启动SystemServer进程。
5、runSelectLoop
void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
// 1、将ServerSocket获取的文件描述符添加到集合中
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
// 2、遍历将fds存储的信息转移到pollFds数组中
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
// 3 遍历pollFds
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
// 4、i==0则说明服务端Socket与客户端连接上
if (i == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
// 5、i的值大于0,则说明ActivityManagerService向Zygote进程发送了一个创建应用进程的请求
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
- mServerSocket就是在registerZygoteSocket函数中创建的服务端Socket,调用sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor()用来获得该Socket的fd字段的值并添加到fd列表fds中。接下来无限循环用来等待ActivityManagerService请求Zygote进程创建新的应用程序进程。
- 通过遍历将fds存储的信息转移到pollFds数组中。
- 遍历pollFds
- 如果i==0则说明服务端Socket与客户端连接上,也就是当前Zygote进程与ActivityManagerService建立了连接,则通过acceptCommandPeer函数得到ZygoteConnection类并添加到Socket连接列表peers中,接着将该ZygoteConnection的fd添加到fd列表fds中,以便可以接收到ActivityManagerService发送过来的请求。
- 如果i的值大于0,则说明ActivityManagerService向Zygote进程发送了一个创建应用进程的请求,则调用ZygoteConnection的runOnce函数来创建一个新的应用程序进程。并在成功创建后将这个连接从Socket连接列表peers和fd列表fds中清除。
5、runOnce函数
ZygoteConnection.java类路径在:/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
boolean runOnce(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
// 1、读取参数列表
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
closeSocket();
return true;
}
// 省略......
// 2、fork子进程
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.instructionSet,
parsedArgs.appDataDir);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
}
// 省略......
try {
// 3、在子进程运行程序handleChildProc
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
}
- 读取参数列表
- fork子进程,其中会调用Zygote类的forkAndSpecialize函数
- 在子进程运行程序handleChildProc
问题与思考
1、孵化应用进程为什么不给SystemServer来做,而专门设计一个Zygote?
我们知道,应用在启动的时候需要做很多准备工作,包括启动虚拟机,加载各类系统资源等等,这些都是非常耗时的,如果能在zygote里就给这些必要的初始化工作做好,子进程在fork的时候就能直接共享,那么这样的话效率就会非常高。这个就是zygote存在的价值,这一点呢SystemServer是替代不了的,主要是因为SystemServer里跑了一堆系统服务,这些是不能继承到应用进程的。而且我们应用进程在启动的时候,内存空间除了必要的资源外,最好是干干净净的,不要继承一堆乱七八糟的东西。所以呢,不如给SystemServer和应用进程里都要用到的资源抽出来单独放在一个进程里,也就是这的zygote进程,然后zygote进程再分别孵化出SystemServer进程和应用进程。孵化出来之后,SystemServer进程和应用进程就可以各干各的事了。
2、Zygote的IPC通信机制为什么不采用binder?如果采用binder的话会有什么问题?
第一个原因,我们可以设想一下采用binder调用的话该怎么做,首先zygote要启用binder机制,需要打开binder驱动,获得一个描述符,再通过mmap进行内存映射,还要注册binder线程,这还不够,还要创建一个binder对象注册到serviceManager,另外AMS要向zygote发起创建应用进程请求的话,要先从serviceManager查询zygote的binder对象,然后再发起binder调用,这来来回回好几趟非常繁琐,相比之下,zygote和SystemServer进程本来就是父子关系,对于简单的消息通信,用管道或者socket非常方便省事。第二个原因,如果zygote启用binder机制,再fork出SystemServer,那么SystemServer就会继承了zygote的描述符以及映射的内存,这两个进程在binder驱动层就会共用一套数据结构,这显然是不行的,所以还得先给原来的旧的描述符关掉,再重新启用一遍binder机制,这个就是自找麻烦了。
学习参考资料
Framework学习系列文章:https://blog.csdn.net/huaxun66/article/details/78135556
Android之初学framework开发的理解:https://www.jianshu.com/p/e005a1ca35e1
Android 8.0系统源码分析–Zygote启动过程分析:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_22657459/article/details/78946921
Android启动流程简析:https://www.jianshu.com/p/657336b545bd
视频教程:https://ke.qq.com/webcourse/index.html#cid=477966&term_id=100572538&taid=4291033106434830&vid=5285890797273915599
android 学习之 zygote作用:https://www.cnblogs.com/pcmpcm/p/11928124.html
zygote启动过程:https://blog.csdn.net/u011578734/article/details/99440961
Zygote进程【1】——Zygote的诞生:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34037977/article/details/85844588