linux inotify 监控文件系统事件
1. Inotify 机制概述
1.1. Inotify 介绍
在日常的运维过程中,经常需要备份某些文件,或者对系统的某些文件进行监控,比如重要的配置文件等。如果需要作到实时同步或者监控,就需要使用内核的inotify机制
Inotify 是基于inode级别的文件系统监控技术,是一种强大的、细粒度的、异步的机制,它满足各种各样的文件监控需要,不仅限于安全和性能
- Inotify 不需要对被监视的目标打开文件描述符,而且如果被监视目标在可移动介质上,那么在 umount 该介质上的文件系统后,被监视目标对应的 watch 将被自动删除,并且会产生一个 umount 事件。
- Inotify 既可以监视文件,也可以监视目录。
- Inotify 使用系统调用而非 SIGIO 来通知文件系统事件。
- Inotify 使用文件描述符作为接口,因而可以使用通常的文件 I/O 操作select 和 poll 来监视文件系统的变化。
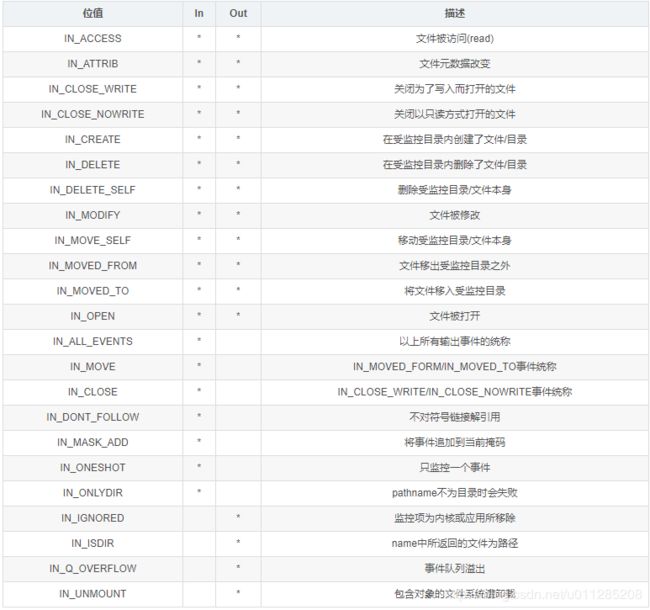
1.2. Inotify 可监视的文件系统事件
- IN_ACCESS : 即文件被访问
- IN_MODIFY : 文件被 write
- IN_ATTRIB : 文件属性被修改,如 chmod、chown、touch 等
- IN_CLOSE_WRITE : 可写文件被 close
- IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE : 不可写文件被 close
- IN_OPEN : 文件被open
- IN_MOVED_FROM : 文件被移走,如 mv
- IN_MOVED_TO : 文件被移来,如 mv、cp
- IN_CREATE : 创建新文件
- IN_DELETE : 文件被删除,如 rm
- IN_DELETE_SELF : 自删除,即一个可执行文件在执行时删除自己
- IN_MOVE_SELF : 自移动,即一个可执行文件在执行时移动自己
- IN_UNMOUNT : 宿主文件系统被 umount
- IN_CLOSE : 文件被关闭,等同于(IN_CLOSE_WRITE | IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE)
- IN_MOVE : 文件被移动,等同于(IN_MOVED_FROM | IN_MOVED_TO)
注:上面所说的文件也包括目录
1.3. Inotify内核版本支持
- 从kernel 2.6.13开始,Inotify正式并入内核,RHEL5已经支持.
- 看看是否有 /proc/sys/fs/inotify/目录,以确定内核是否支持inotify
[root@RHEL5 Rsync]# ls -l /proc/sys/fs/inotify/ total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Oct 9 09:36 max_queued_events -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Oct 9 09:36 max_user_instances -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Oct 9 09:36 max_user_watches
1.4. inotify 的默认内核参数
- /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events默认值: 16384 该文件中的值为调用inotify_init时分配给inotify instance中可排队的event的数目的最大值,超出这个值得事件被丢弃,但会触发IN_Q_OVERFLOW事件
- /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances默认值: 128 指定了每一个real user ID可创建的inotify instatnces的数量上限
- /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches默认值: 8192 指定了每个inotify instance相关联的watches的上限
注意: max_queued_events 是 Inotify 管理的队列的最大长度,文件系统变化越频繁,这个值就应该越大
如果你在日志中看到Event Queue Overflow,说明max_queued_events太小需要调整参数后再次使用.
2. Inotify 在系统中使用
2.1. linux shell 下使用inotify
- 下载安装 inotify-tools源码 rhel5/centos5 RPM包
- inotifywait 仅执行阻塞,等待 inotify 事件。您可以监控任何一组文件和目录,或监控整个目录树(目录、子目录、子目录的子目录等等)
在 shell 脚本中使用 inotifywait。 - inotifywatch 收集关于被监视的文件系统的统计数据,包括每个 inotify 事件发生多少次。
- inotifywait 仅执行阻塞,等待 inotify 事件。您可以监控任何一组文件和目录,或监控整个目录树(目录、子目录、子目录的子目录等等)
- shell脚本示例
[root@localhost ]# cat /tmp/test.sh #!/bin/bash inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f %e' --event modify,delete,create,attrib /home/admin | while read date time file event do case $event in MODIFY|CREATE|MOVE|MODIFY,ISDIR|CREATE,ISDIR|MODIFY,ISDIR) echo $event'-'$file ;; MOVED_FROM|MOVED_FROM,ISDIR|DELETE|DELETE,ISDIR) echo $event'-'$file ;; esac done - 执行脚本,结果输出(这里测试删除了一个目录 rm -fr cronolog-1.6.2.bak)
[root@localhost]# /tmp/test.sh DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/COPYING DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/cronolog.info DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/cronolog.texi DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/Makefile.am DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/Makefile.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/texinfo.tex DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/cronosplit.1m DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/Makefile DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc/cronolog.1m DELETE,ISDIR-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/doc DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/TODO DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronotest.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronolog.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronoutils.h DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronoutils.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/Makefile.am DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/Makefile.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronosplit.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/Makefile DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/cronosplit DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src/config.h DELETE,ISDIR-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/src DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/getopt1.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/getopt.h DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/Makefile.am DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/Makefile.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/localtime_r.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/getopt.c DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/Makefile DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib/strptime.c DELETE,ISDIR-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/lib DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/config.cache DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/install-sh DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/Makefile.am DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/README DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/AUTHORS DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/Makefile.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/testsuite/Makefile.am DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/testsuite/README DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/testsuite/Makefile.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/testsuite/Makefile DELETE,ISDIR-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/testsuite DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/cronolog.spec DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/NEWS DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/configure DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/ChangeLog DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/missing DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/config.log DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/aclocal.m4 DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/Makefile DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/INSTALL DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/config.status DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/configure.in DELETE-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak/mkinstalldirs DELETE,ISDIR-/home/admin/cronolog-1.6.2.bak
详细请参考 man inotify , man inotifywait
2.2. 使用incron实现重要配置文件监控
Incron是inotify的cron系统,与os本身的cron一样,包含一个后台守护进程(incrond)和一个事件编辑器(incrontab
与os本身的cron不同的仅仅是触发时间的是os对某个文件(夹)的操作而不是时间,由系统事件触发的机制,对于应用系统来说,几乎可以做到实时性。
- 安装Incron Incron Rpm包
[root@localhost]# yum install Incron
- 查看 incron 支持的事件类型 incrontab -t ,编辑配置文件使用 incrontab -e
- 配置文件格式说明(默认配置在/var/spool/incron/ 目录下)
选项说明:
:欲监控的文件或者目录
:os对监控对象发生的事件
:command可以是系统命令,也可以是脚本,不能是用系统的重定向,除非重定向写在脚本中。 中还可以使用下面的这些变量:
$@:代表,即监控对象
$#:发生系统事件的对象(例如监控了某个文件夹,其下的某个文件发生了变化,那么$#就代表了该文件名)
$%:代表,即发生的事件
- 配置举例:
- /home/admin/a.txt IN_MODIFY echo "$@ $#" 表示文件abc一旦被修改,就执行 echo "$@ $#"
- /home/admin/ IN_ALL_EVENTS echo "$@ $# $%" 表示目录下的文件任何事件触发,就执行 echo "$@ $#"
- 启动incrond (/etc/init.d/incrond start),然后在 /home/admin目录删除 ssss 文件,查看日志 tail /var/log/cron ,有如下输出
Mar 23 14:05:19 localhost incrond[6857]: (root) CMD (echo "/home/admin = = IN_OPEN,IN_ISDIR") Mar 23 14:05:19 localhost incrond[6857]: (root) CMD (echo "/home/admin = = IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE,IN_ISDIR") Mar 23 14:05:20 localhost incrond[6857]: (root) CMD (echo "/home/admin = = IN_OPEN,IN_ISDIR") Mar 23 14:05:20 localhost incrond[6857]: (root) CMD (echo "/home/admin = = IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE,IN_ISDIR") Mar 23 14:05:20 localhost incrond[6857]: (root) CMD (echo "/home/admin = ssss = IN_DELETE")
总体来说,在文件和目录实时监控还是很有效的,可以结合其他工具来作统一化的解决方案,比如使用syslog-ng作统一化收集,当然最重要还是要有场景.
2.3 linux API
使用inotify API有以下关键步骤:
使用inotify_init()创建一个inotify实例,返回的文件描述符用于后续操作中指代该实例。
使用inotify_add_watch向inotify实例的监控列表添加条目,即添加应用感兴趣的文件或目录。每个监控项包含一个路径名及相关的位掩码,位掩码指明所要监控的事件。inotify_add_watch将返回一个监控描述符,用于后续操作指代该监控项(inotify_rm_watch移除监控项)。
应用需要对inotify文件描述符执行read()操作以获取事件通知,read()调用会返回一个或多个inotify_event结构,记录了所发生的事件。
应用结束时关闭inotify描述符,这会自动清除与inotify实例相关的所有监控项。
inotify可用于监控文件或目录。监控目录时,与路径自身及其所含文件相关的事件都会通知应用程序。
inofity为非递归的,若想监控目录下整个目录树,需要对目录树下每个目录发起inotify_add_watch调用。
2.3.1、API
#include
int inotify_init(void);
int inotify_add_watch(int fd, const char *pathname, uint32_t mask);
int inotify_rm _watch(int fd, uint32_t wd);
2.3.2、inotify事件
使用inotify_add_watch添加、修改监控项时,位掩码参数mask标识了针对 给定路径名要监控的事件。下表中“in”列列出了可以mask中定义的事件位。
2.3.3、读取inotify事件
在监控列表中添加监控项后,应用程序可用read从inotify文件描述符中读取事件,以判定发生了哪些事件。若读取时还没有事件发生,read将阻塞直到事件发生(除非设置O_NONBLOCK标志)。
事件发生后,每次调用read会返回一个缓冲区,包含一个或多个如下类型的结构:
struct inotify_event {
int wd; //Watch descriptor on which event occurred
uint32_t mask; //Bits describing event that occurred
uint32_t cookie; //Cookie for related events(for rename())
uint32_t len; //Size of 'name' field
char name[]; //Optional null-terminated filename
}
![]()
#include
#include
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void /* Display information from inotify_event structure */
displayInotifyEvent(struct inotify_event *i)
{
printf(" wd =%2d; ", i->wd);
if (i->cookie > 0)
printf("cookie =%4d; ", i->cookie);
printf("mask = ");
if (i->mask & IN_ACCESS) printf("IN_ACCESS ");
if (i->mask & IN_ATTRIB) printf("IN_ATTRIB ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_WRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_WRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CREATE) printf("IN_CREATE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE) printf("IN_DELETE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE_SELF) printf("IN_DELETE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_IGNORED) printf("IN_IGNORED ");
if (i->mask & IN_ISDIR) printf("IN_ISDIR ");
if (i->mask & IN_MODIFY) printf("IN_MODIFY ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVE_SELF) printf("IN_MOVE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_FROM) printf("IN_MOVED_FROM ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_TO) printf("IN_MOVED_TO ");
if (i->mask & IN_OPEN) printf("IN_OPEN ");
if (i->mask & IN_Q_OVERFLOW) printf("IN_Q_OVERFLOW ");
if (i->mask & IN_UNMOUNT) printf("IN_UNMOUNT ");
printf("\n");
if (i->len > 0)
printf(" name = %s\n", i->name);
}
#define BUF_LEN (10 * (sizeof(struct inotify_event) + NAME_MAX + 1))
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int inotifyFd, wd, j;
char buf[BUF_LEN] __attribute__ ((aligned(8)));
ssize_t numRead;
char *p;
struct inotify_event *event;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s pathname...\n", argv[0]);
inotifyFd = inotify_init(); /* Create inotify instance */
if (inotifyFd == -1)
errExit("inotify_init");
/* For each command-line argument, add a watch for all events */
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) {
wd = inotify_add_watch(inotifyFd, argv[j], IN_ALL_EVENTS);
if (wd == -1)
errExit("inotify_add_watch");
printf("Watching %s using wd %d\n", argv[j], wd);
}
for (;;) { /* Read events forever */
numRead = read(inotifyFd, buf, BUF_LEN);
if (numRead == 0)
fatal("read() from inotify fd returned 0!");
if (numRead == -1)
errExit("read");
printf("Read %ld bytes from inotify fd\n", (long) numRead);
/* Process all of the events in buffer returned by read() */
for (p = buf; p < buf + numRead; ) {
event = (struct inotify_event *) p;
displayInotifyEvent(event);
p += sizeof(struct inotify_event) + event->len; //event->len 变动的文件名长度。
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}