小白mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(2)| getMapper与sqlSession.selectList区别
mybatis源码分析系列:
- mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(1)| 前言
- mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(2)| getMapper
- mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(3)| Configuration及解析配置文件
- mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(4)| SqlSession.select调用分析
- mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(5)| 与springboot整合
上一章我们后面留下了一个问题就是 getMapper获取的UserDao操作和直接sqlSession.selectList的区别?
下面我们就从这里展开mybatis源码的面纱
UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);这句操作究竟做了些什么?
首先第一步DefaultSqlSession.getMapper:
这里调用Configuration.getMapper:
然后接着调用MapperRegistry.getMapper:
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
} knownMappers是一个map,Map
MapperProxyFactory.newInstance:
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
} 接着newInstance(mapperProxy):
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} 这里我们可以看到通过代理创建一个代理对象,也就是UserDao拿到的是一个代理对象,而InvocationHandler就是我们前面new 出来的MapperProxy,也就是说那么我们在调用UserDao.select()执行sql时,其实是调用代理对象的invoke方法,好那我们回头看下这个MapperProxy:
它实现了InvocationHandler接口,我们来看下invoke:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
} private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
} 这里从Map
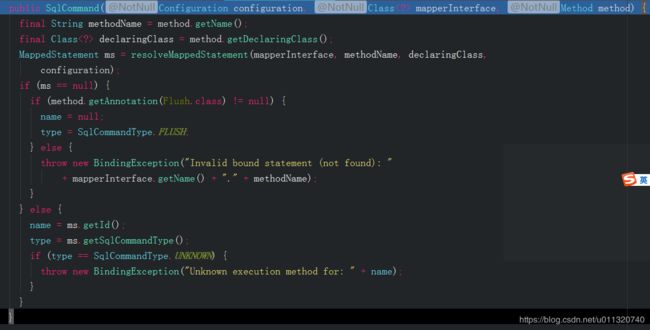
public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}MapperMethod有个内部类SqlCommand,看看这里到底做了些什么:
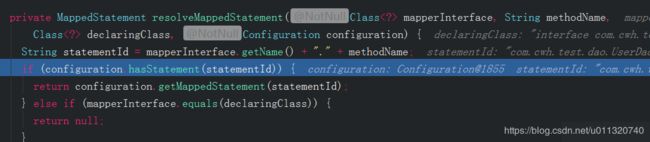
调用resolveMappedStatement获取MappedStatement:
configuration.hasStatement(statementId)判断Configuration里的Map
有则返回:
那么这个mappedStatements的Map数据是哪儿来的?这个后续再分析 ,参考 mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(3)
拿到MappedStatement将id和type赋值给SqlCommand的id和type;初始化完SqlCommand后也算拿到MapperMethod接着执行mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args):
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}这里有各个数据库操作类型,通过前面SqlCommand初始化的数据,判断type,我们直接关注我们的select:
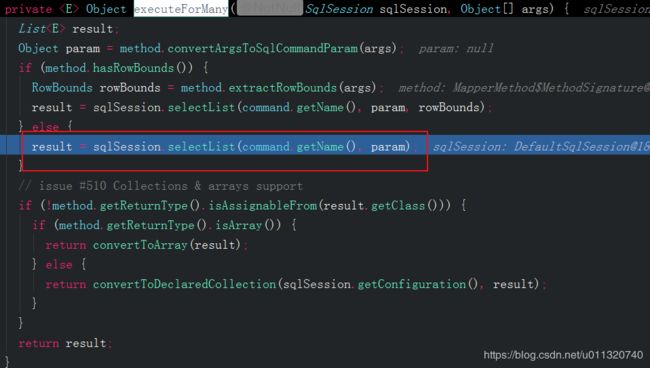
调用MapperMethod.executeForMany:
看到上面圈红的地方没有,是不是很熟悉,这里是不是也是sqlSession.selectList,也就是说两者其实并无区别,只不过UserDao利用代理对象操作sqlSession.selectList();
到这里我们也搞明白上一章最后留下的疑问,那么是否还有其他疑问呢?
小朋友你是不是有很多问号,为什么?sqlSession.selectList这一步究竟做了啥,这和jdbc又有什么关系?
具体查看mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(4)
前面的knownMappers获取MapperProxyFactory又是哪里来?Configuration做了些什么?
具体查看mybatis源码看这一遍就够了(3)
不急,下一章我们继续分析