Mybatis中select、insert、update、delete用法总结
一、select用法示例
<!-- 查询学生,根据id -->
<select id="getStudent" parameterType="String" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.CLASS_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID}
</select>
这条语句就叫做‘getStudent,有一个String参数,并返回一个StudentEntity类型的对象。
注意参数的标识是:#{studentID}。
二、insert示例
<!-- 插入学生 -->
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
INSERT INTO STUDENT_TBL (STUDENT_ID, STUDENT_NAME,STUDENT_SEX,STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
CLASS_ID)
VALUES
(#{studentID}, #{studentName}, #{studentSex}, #{studentBirthday},
#{classEntity.classID})
</insert>
insert可以使用数据库支持的自动生成主键策略,设置useGeneratedKeys=”true”,然后把keyProperty 设成对应的列,就搞定了。比如说上面的StudentEntity 使用auto-generated 为id 列生成主键.
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="studentID">
推荐使用这种用法。
另外,还可以使用selectKey元素。下面例子,使用mysql数据库nextval(‘student’)为自定义函数,用来生成一个key。
<!-- 插入学生 自动主键-->
<insert id="insertStudentAutoKey" parameterType="StudentEntity">
<selectKey keyProperty="studentID" resultType="String" order="BEFORE">
select nextval('student')
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO STUDENT_TBL (STUDENT_ID, STUDENT_NAME, STUDENT_SEX,STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
CLASS_ID)
VALUES
(#{studentID},#{studentName}, #{studentSex},#{studentBirthday},
#{classEntity.classID})
</insert>
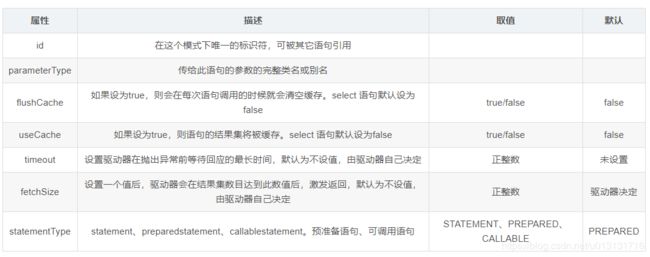
insert语句属性配置细节:
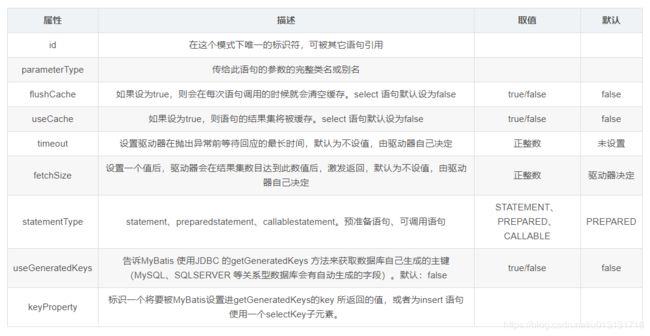
selectKey语句属性配置细节:
批量插入(说明两种方式)
方法一:
<insert id="add" parameterType="EStudent">
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=";">
INSERT INTO TStudent(name,age) VALUES(#{item.name}, #{item.age})
</foreach>
</insert>
上述方式相当语句逐条INSERT语句执行,将出现如下问题:
注意:
1)mapper接口的add方法返回值将是最一条INSERT语句的操作成功的记录数目(就是0或1),而不是所有INSERT语句的操作成功的总记录数目
2)当其中一条不成功时,不会进行整体回滚。
方法二:
<insert id="insertStudentAutoKey" parameterType="java.util.List">
INSERT INTO STUDENT_TBL (STUDENT_NAME,STUDENT_SEX,STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,CLASS_ID)
VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
( #{item.studentName},#{item.studentSex},#{item.studentBirthday},
#{item.classEntity.classID})
</foreach>
</insert>
三、update使用示例
一个简单的update:
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
SET STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},
STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};
</update>
批量更新
情景一:更新多条记录为多个字段为不同的值
方法一:
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="" close="" separator=";">
update course
<set>
name=${item.name}
</set>
where id = ${item.id}
</foreach>
</update>
比较普通的写法,是通过循环,依次执行update语句。
方法二:
UPDATE TStudent SET Name = R.name, Age = R.age
from (
SELECT 'Mary' as name, 12 as age, 42 as id
union all
select 'John' as name , 16 as age, 43 as id
) as r
where ID = R.id
情景二:更新多条记录的同一个字段为同一个值
<update id="updateOrders" parameterType="java.util.List">
update orders set state = '0' where no in
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</update>
四、delete使用示例
一个简单的delete:
<!-- 删除学生 -->
<delete id="deleteStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
DELETE FROM STUDENT_TBL WHERE STUDENT_ID = #{studentID}
</delete>
批量删除:
<delete id="batchRemoveUserByPks" parameterType="java.util.List">
DELETE FROM LD_USER WHERE ID in
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</delete>
五、sql使用示例
Sql元素用来定义一个可以复用的SQL 语句段,供其它语句调用。比如:
<sql id="selectStudentAll">
SELECT ST.STUDENT_ID,
ST.STUDENT_NAME,
ST.STUDENT_SEX,
ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
ST.CLASS_ID
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
</sql>
这样,在select的语句中就可以直接引用使用了,将上面select语句改成:
<!-- 查询学生,根据id -->
<select id="getStudent" parameterType="String" resultMap="studentResultMap">
<include refid="selectStudentAll"/>
WHERE ST.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID}
</select>
六、parameters使用示例
上面很多地方已经用到了参数,比如查询、修改、删除的条件,插入,修改的数据等,MyBatis可以使用Java的基本数据类型和Java的复杂数据类型。如:基本数据类型,String,int,date等。但是使用基本数据类型,只能提供一个参数,所以需要使用Java实体类,或Map类型做参数类型。通过#{}可以直接得到其属性。
1)基本类型参数
根据入学时间,检索学生列表:
<!-- 查询学生list,根据入学时间 -->
<select id="getStudentListByDate" parameterType="Date" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT_TBL ST LEFT JOIN CLASS_TBL CT ON ST.CLASS_ID = CT.CLASS_ID
WHERE CT.CLASS_YEAR = #{classYear};
</select>
List<StudentEntity> studentList = studentMapper.getStudentListByClassYear(
StringUtil.parse("2007-9-1"));
for (StudentEntity entityTemp : studentList) {
System.out.println(entityTemp.toString());
}
2)Java实体类型参数
根据姓名和性别,检索学生列表。使用实体类做参数:
<select id="getStudentListWhereEntity" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
</select>
StudentEntity entity = new StudentEntity();
entity.setStudentName("李");
entity.setStudentSex("男");
List<StudentEntity> studentList = studentMapper.getStudentListWhereEntity(entity);
for (StudentEntity entityTemp : studentList) {
System.out.println(entityTemp.toString());
}
3)Map参数
根据姓名和性别,检索学生列表。使用Map做参数:
<!-- 查询学生list,=性别,参数map类型 -->
<select id="getStudentListWhereMap" parameterType="Map" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{sex}
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{sex}
</select>
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("sex", "女");
map.put("name", "李");
List<StudentEntity> studentList = studentMapper.getStudentListWhereMap(map);
for (StudentEntity entityTemp : studentList) {
System.out.println(entityTemp.toString());
}
4)多参数的实现
如果想传入多个参数,则需要在接口的参数上添加@Param注解。给出一个实例:
接口写法:
public List<StudentEntity> getStudentListWhereParam(@Param(value = "name") String name,
@Param(value = "sex") String sex, @Param(value = "birthday") Date birthdar,
@Param(value = "classEntity") ClassEntity classEntity);
sql写法:
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名、=性别、=生日、=班级,多参数方式 -->
<select id="getStudentListWhereParam" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name!='' ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{name}),'%')
</if>
<if test="sex!= null and sex!= '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="birthday!=null">
AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{birthday}
</if>
<if test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID !=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
</if>
</where>
</select>
进行查询:
List<StudentEntity> studentList = studentMapper.getStudentListWhereParam("","",StringUtil.parse("1985-05-28"), classMapper.getClassByID("20000002"));
for (StudentEntity entityTemp : studentList) {
System.out.println(entityTemp.toString());
}
七、#{}与${}的区别
网址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013131716/article/details/100761140