Android事件分发简单分析(源码分析)
想玩转自定义View,我们需要了解事件分发流程,知道具体的触摸事件怎么去处理、消费。
事件定义:当用户触摸屏幕时,会产生触摸行为。
一、常用的事件的类型(四种):
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN 手指刚接触屏幕
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE 手指在屏幕上滑动
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP 手指从屏幕松开
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL 非人为因素的取消
二、事件分发对象
- Activity:控制生命周期,处理事件
- ViewGroup:一组View的集合(包含多个子View)
- 所有UI组件的基类
三、事件分发主要方法
- dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event):用来进行事件分发
- onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev):判断是否是拦截事件(只存在于ViewGroup)
- onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event):处理触摸事件
四、Activity事件分发
第一步:调用Activity的dispatchTouchEvent
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
onUserInteraction();
}
// 调用PhoneWindow的方法
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
// 如果ViewGroup没有处理,就会执行Activity的onTouchEvent
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}
第二步:调用PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
第三步:调用DecorView的superDispatchTouchEvent
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
第四步:因为DecorView是FrameLayout的子类,因此最终会调用ViewGroup的
dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)方法。
五、ViewGroup的事件分发
所有的事件都是从一个down事件开始到up事件结束,所以我们查阅源码的时候先从down事件入手。
从ViewGroup的**dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)**开始阅读
1. 第一步、dispatchTouchEvent中找到down事件,清空target,清空target的标记
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// 重置target
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
resetTouchState();
}
深入cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev),然后走到clearTouchTargets方法,清空mFirstTouchTarget,我们可以看到源码注释,清空所有的target。
/**
* Clears all touch targets.
*/
private void clearTouchTargets() {
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
if (target != null) {
do {
TouchTarget next = target.next;
target.recycle();
target = next;
} while (target != null);
mFirstTouchTarget = null;
}
}
然后调用resetTouchState,清除所有的标记状态
/**
* Resets all touch state in preparation for a new cycle.
*/
private void resetTouchState() {
clearTouchTargets();
resetCancelNextUpFlag(this);
// FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT涉及到后面的子View请求父控件是否拦截
// 此处是清除标记
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
mNestedScrollAxes = SCROLL_AXIS_NONE;
}
2. 第二步,还是dispatchTouchEvent源码,检测ViewGroup是否需要拦截事件
// Check for interception.
// 标记ViewGroup是否去拦截事件
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
// disallowIntercept 用来禁止或者允许ViewGroup拦截除了down事件之外的所有事件,一般由子View调用
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
// If intercepted, start normal event dispatch. Also if there is already
// a view that is handling the gesture, do normal event dispatch.
if (intercepted || mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
disallowIntercept:用来禁止或者允许ViewGroup拦截除了down事件之外的所有事件,一般由子View调用requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(boolean disallowIntercept)来修改mGroupFlags。
一般调用就是view.getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent
@Override
public void requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(boolean disallowIntercept) {
if (disallowIntercept == ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0)) {
// We're already in this state, assume our ancestors are too
return;
}
if (disallowIntercept) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
} else {
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
}
// Pass it up to our parent
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(disallowIntercept);
}
}
为什么说是除了down事件之外的所有事件?
因为在第一步我们就已经讲解了,当事件开始的时候是在down事件,我们对target进行清空,并且清空了标记状态mGroupFlags。因此当事件为down事件的时候disallowIntercept是为false,因此判断之内的方法onInterceptTouchEvent一定会执行,因此FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT影响的是除了down事件以外的其他的事件。
查看onInterceptTouchEvent的返回值,默认是返回false,因此说明ViewGroup默认是不去拦截事件的。
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)
&& ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY)
&& isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
第三步、如果ViewGroup不拦截,仍然是dispatchTouchEvent()f方法,走到如下代码
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()
? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null;
// 判断是否是down事件
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for down
final int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex)
: TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;
// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they
// have become out of sync.
removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
// 判断target不为空,并且子View不为0
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);
final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);
// Find a child that can receive the event.
// Scan children from front to back.
final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList();
final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null
&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();
final View[] children = mChildren;
// 倒序检索出子view
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
// If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it
// to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a
// normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is
// safer given the timeframe.
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) {
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) {
continue;
}
childWithAccessibilityFocus = null;
i = childrenCount - 1;
}
// canReceivePointerEvents()判断是否是可见的或者是否在执行动画
// isTransformedTouchPointInView()检查当前触摸范围是否在当前View的范围内
// 下面判断表示如果是不可见或者在执行动画,或者不在View的触摸范围内,就跳转循环继续查找下一个View
if (!child.canReceivePointerEvents()
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);
if (newTouchTarget != null) {
// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.
// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
break;
}
resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);
// 如果我们找到满足条件的View,就会调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent,将子view传递进去
// 如果返回true就表示子view消耗了事件
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// Child wants to receive touch within its bounds.
mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime();
if (preorderedList != null) {
// childIndex points into presorted list, find original index
for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) {
if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) {
mLastTouchDownIndex = j;
break;
}
}
} else {
mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex;
}
mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();
mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();
// 查看后知道,将子View赋值给mFirstTouchTarget
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
// 对alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget进行赋值
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;
}
// The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear
// the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children.
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();
}
if (newTouchTarget == null && mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
// Did not find a child to receive the event.
// Assign the pointer to the least recently added target.
newTouchTarget = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (newTouchTarget.next != null) {
newTouchTarget = newTouchTarget.next;
}
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
}
}
}
第四步、查看dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()源码
/**
* Transforms a motion event into the coordinate space of a particular child view,
* filters out irrelevant pointer ids, and overrides its action if necessary.
* If child is null, assumes the MotionEvent will be sent to this ViewGroup instead.
*/
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
// 定义一个handled,用来表示是否消费事件
final boolean handled;
// Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations
// or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents.
final int oldAction = event.getAction();
if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) {
event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL);
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
// 当子view不为null的时候将事件传递给子view去处理
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
event.setAction(oldAction);
return handled;
}
// Calculate the number of pointers to deliver.
final int oldPointerIdBits = event.getPointerIdBits();
final int newPointerIdBits = oldPointerIdBits & desiredPointerIdBits;
// If for some reason we ended up in an inconsistent state where it looks like we
// might produce a motion event with no pointers in it, then drop the event.
if (newPointerIdBits == 0) {
return false;
}
// If the number of pointers is the same and we don't need to perform any fancy
// irreversible transformations, then we can reuse the motion event for this
// dispatch as long as we are careful to revert any changes we make.
// Otherwise we need to make a copy.
final MotionEvent transformedEvent;
if (newPointerIdBits == oldPointerIdBits) {
if (child == null || child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
if (child == null) {
// 当View为空的时候,就会走到View的dispatchTouchEvent
// 如果当前的View是ViewGroup的话,那么就会执行ViewGroup的onTouchEvent
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
event.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
// 当子view不为null的时候将事件传递给子view去处理
// handled表示子view是否消费事件,然后作为方法的返回值
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
event.offsetLocation(-offsetX, -offsetY);
}
return handled;
}
transformedEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event);
} else {
transformedEvent = event.split(newPointerIdBits);
}
... 省略
return handled;
}
第五步、回到第三步,我们查看addTouchTarget()方法
给mFirstTouchTarget赋值,指向子View,并且将mFirstTouchTarget插入链表中
/**
* Adds a touch target for specified child to the beginning of the list.
* Assumes the target child is not already present.
*/
private TouchTarget addTouchTarget(@NonNull View child, int pointerIdBits) {
// 根据子view去获取TouchTarget 对象
final TouchTarget target = TouchTarget.obtain(child, pointerIdBits);
target.next = mFirstTouchTarget;
mFirstTouchTarget = target;
return target;
}
第六步、经过分析,如果子view消耗事件,mFirstTouchTarget就会被赋值,我们重新回到dispatchTouchEvent()方法(第三步代码之后),继续往下查看。
// Dispatch to touch targets.
// 判断mFirstTouchTarget 是否为空
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
// 如果mFirstTouchTarget 为空,执行dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法,然后将子View传递为null,回到第四步,我们会发现最终会走supre.dispatchTouchEvent
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
// alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget在第三步的时候赋值
// 此时down事件alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget被赋值,并且target已经赋值(子view消耗了事件)
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
// 表示对down事件的处理
handled = true;
} else {
// 处理down事件之外的其他事件
final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)
|| intercepted;
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
if (cancelChild) {
if (predecessor == null) {
mFirstTouchTarget = next;
} else {
predecessor.next = next;
}
target.recycle();
target = next;
continue;
}
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
总结:
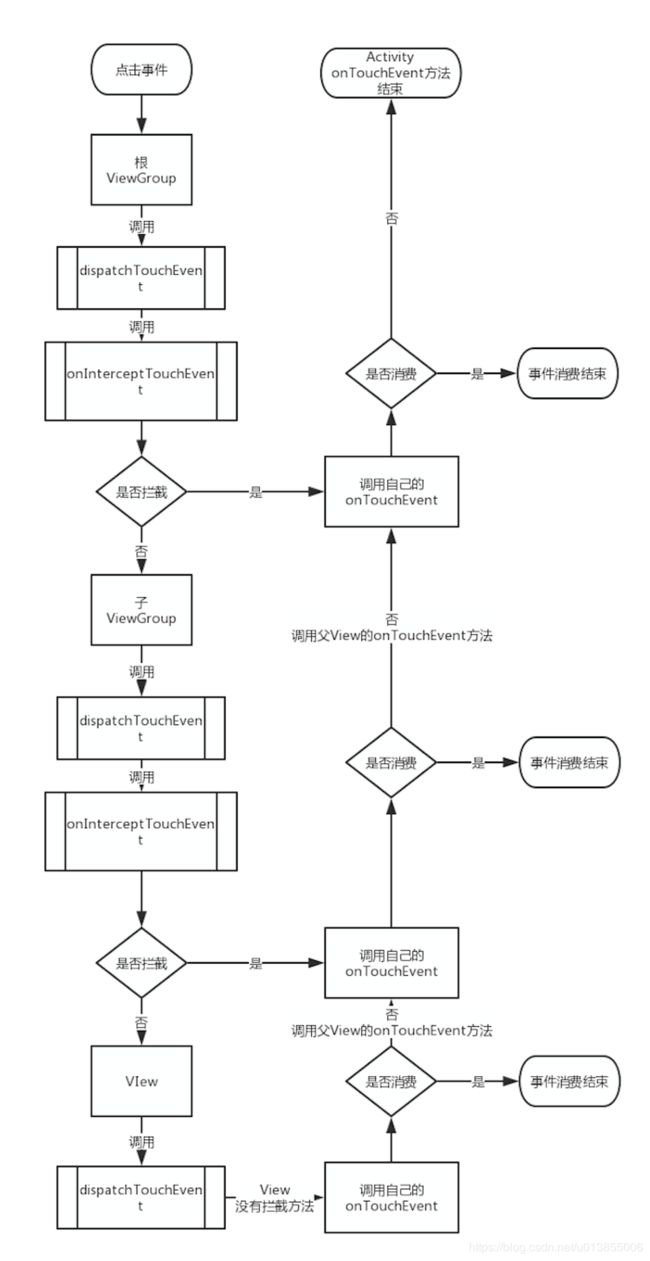
1、事件先传递到ViewGroup,然后在传递到View。ViewGroup可以通过onInterceptTouchEvent()将事件进行拦截,返回true表示拦截事件,事件将不会传递到子view,返回false表示不对事件进行拦截(默认就是返回false),最终调用子View的dispatchTouchEvent方法,将事件交给子View处理。
2、当ViewGroup中所有的子View都不消耗事件,就会走到ViewGroup的onTouchEvent方法(ViewGroup没有实现onTouchEvent方法,最终会走到View的onTouchEvent方法中)
3、ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法才是真的用来分发事件的,而View的dispatchTouchEvent仅仅是分发给自己(或者说就是交给自己处理)。
六.、View的事件分发
第一步、找到View的dispatchTouchEvent方法
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first.
if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) {
// We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event.
if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {
return false;
}
// We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch.
event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
boolean result = false;
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0);
}
// 嵌套滚动的逻辑
final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked();
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Defensive cleanup for new gesture
stopNestedScroll();
}
// 找到我们的关键代码,进行一个安全判断
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
// 判断view是否可用,并且是否可以滚动,满足条件直接返回
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
// 此处是我们的重点代码
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
// 需要满足如下所有条件,才会返回true,就是View才会去消耗事件
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
}
// 嵌套滚动的逻辑
// Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture;
// also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest
// of the gesture.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP ||
actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL ||
(actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) {
stopNestedScroll();
}
return result;
}
抽丝剥茧,我们的关键代码就是如下
// 此处是我们的重点代码
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
// 需要满足如下所有条件,才会返回true
// 通过后面的判断,我们只要设置了监听器li就肯定不为空,
// 如果在View中调用了setOntouchListener(),那么第二个条件li.mOnTouchListener肯定不为空
// 默认的View就是enabled的,所以第三个条件成立
// 最后mOnTouchListener.onTouch返回true,那么久不会走View的onTouchEvent,如果返回false,才会继续走后面的View的onTouchEvent方法
// 因此可以知道OnTouchListener的onTouch的优先级高于onTouchEvent方法
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
然后找到mListenerInfo什么时候被初始化,被赋值。最终找到getListenerInfo中被赋值。
ListenerInfo getListenerInfo() {
// 不为空直接返回mListenerInfo
if (mListenerInfo != null) {
return mListenerInfo;
}
// 当mListenerInfo为空,就初始化mListenerInfo对象
mListenerInfo = new ListenerInfo();
return mListenerInfo;
}
我们去找一个我们常用的设置点击事件
public void setOnClickListener(@Nullable OnClickListener l) {
if (!isClickable()) {
setClickable(true);
}
// 将mListenerInfo中的mOnClickListener赋值
getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener = l;
}
最后我们知道,只要我们去给View设置一些监听器getListenerInfo()就会被调用,而mListenerInfo就会被初始化。
第二步、走到onTouchEvent()方法,一块一块的拆分,放在一起实在太多了,哈哈。
// 判断View是否是可点击的
final boolean clickable = ((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE
|| (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)
|| (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE;
// 如果view是不可用的
if ((viewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {
// 判断对view的按压的状态
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
setPressed(false);
}
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
// A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch
// events, it just doesn't respond to them.
// 仍然返回clickable(消费事件),证明无论View是否可用,View都会消耗点击事件,只是不做响应。
return clickable;
}
如果当前View是可点击的,接下来就会走我们常规的四个事件。
Down,Move,Up,Cancel。
Down事件
if (event.getSource() == InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN) {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
}
// 是否处理了长按事件
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (!clickable) {
// 如果不可点击,检测是否可以长按
// 我们发现又发送了500ms的延迟
checkForLongClick(
ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout(),
x,
y,
TOUCH_GESTURE_CLASSIFIED__CLASSIFICATION__LONG_PRESS);
break;
}
if (performButtonActionOnTouchDown(event)) {
break;
}
// Walk up the hierarchy to determine if we're inside a scrolling container.
// 判断当前View是否在一个容器中
boolean isInScrollingContainer = isInScrollingContainer();
// For views inside a scrolling container, delay the pressed feedback for
// a short period in case this is a scroll.
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
// 发送一个延时任务,然后就会执行mPendingCheckForTap中checkForLongClick方法,检测长按事件
// mPendingCheckForTap是一个Runnable
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// Not inside a scrolling container, so show the feedback right away
setPressed(true, x, y);
// 如果没在容器中,就直接去检测是否是长按事件
checkForLongClick(
ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout(),
x,
y,
TOUCH_GESTURE_CLASSIFIED__CLASSIFICATION__LONG_PRESS);
}
然后查看checkForLongClick方法,查看CheckForLongPress这个类,然后在CheckForLongPress的run方法中调用了performLongClick方法,如果performLongClick返回true,就会对我们上面的长按标记mHasPerformedLongPress 赋值为true。
最终我们找到真正的执行长按的方法performLongClickInternal(float x, float y),返回true和false就影响到我们的长按事件是否继续走向点击事件,然后走向up。
我们平时开发中使用长按事件的时候,需要注意mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this)的返回值,如果我们响应了长按事件,并且长按事件返回false就会造成长按和点击事件都被响应
private boolean performLongClickInternal(float x, float y) {
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED);
boolean handled = false;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLongClickListener != null) {
// 就是我们平常使用的OnLongClickListener监听
// 将返回值直接返回
handled = li.mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this);
}
if (!handled) {
final boolean isAnchored = !Float.isNaN(x) && !Float.isNaN(y);
handled = isAnchored ? showContextMenu(x, y) : showContextMenu();
}
if ((mViewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
if (!handled) {
handled = showLongClickTooltip((int) x, (int) y);
}
}
if (handled) {
performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS);
}
return handled;
}
UP事件
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
if ((viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
handleTooltipUp();
}
// 如果不可点击,清除点击和长按回调,清除标记
if (!clickable) {
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
}
// 判断是否被点击
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
setPressed(true, x, y);
}
// mHasPerformedLongPress为false,没有响应长按事件,执行后续的点击事件逻辑
// mHasPerformedLongPress为true,后续的点击逻辑都不会执行
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
// 清除长按事件的回调,执行后面点击的逻辑
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
最终会调用performClick(),也就是我们平时设置的点击事件mOnClickListener.onClick(this)
public boolean performClick() {
// We still need to call this method to handle the cases where performClick() was called
// externally, instead of through performClickInternal()
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
// 设置点击事件
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
return result;
}
事件分发整个流程模型
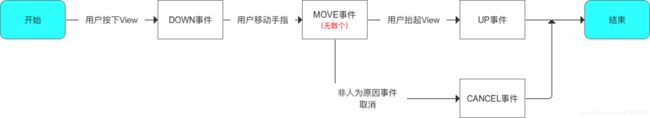
事件序列
表明一个事件从用户触摸屏幕开始(down事件),中间经历无数Move事件,到手指离开屏幕(UP事件,也就是事件的结束)。
事件分发总结
- 一个事件序列从手指接触屏幕开始,到手指离开屏幕结束,在这个过程中产生了一系列事件,以DOWN事件开始,中间包含无数的MOVE事件,到UP事件结束。
- 正常情况下,一个事件序列只能被一个View拦截并消耗
- 一个View一旦决定拦截事件,那么这个事件序列都将由它的onTouchEvent处理,并且它的onInterceptTouchEvent不会再调用。
- 一个View一旦开始处理事件,如果它不消耗ACTION_DOWN事件(onTouchEvent返回false),那么同一事件序列中其他事件都不会再交给它处理。并且重新交由它的父元素处理(父元素onTouchEvent被调用)
- 事件的传递过程是由外向内的,即事件总是先传递给父元素,然后在由父元素分发给子View,通过requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent方法可以在子View中干预父元素的事件分发过程,ACTION_DOWN事件除外。
- ViewGroup默认不拦截任何事件,即onInterceptTouchEvent默认返回false。View没有onInterceptTouchEvent,一旦事件传递给它,那么它的onTouchEvent方法就会被调用。
- View的onTouchEvent默认会消耗事件(返回true),除非它是不可点击的(clickable和longClickable同时为false)。View的longClickable默认为false,clickable需要看情况,比如Button的clickable默认就为true,而TextView的clickable默认为false。
- View的enable属性不影响onTouchEvent的默认返回值,哪怕一个View是disable状态,只要它clickable和longClickable有一个为true,那么它的onTouchEvent就返回true。
- onClick会响应的前提是当前View是可点击的,并且收到了ACTION_DOWN和ACTION_UP事件,并且受长按事件影响,当长按事件返回true是时,onClick不会响应。
- onLongClick在ACTION_DOWN判断是否进行响应,要想执行长按事件,该View必须是longClickable的,并且设置了OnLongClickListener。