撸了今年阿里、头条和美团的面试,我有一个重要发现.......>>> ![]()
第一节
现在开始springboot-web开发教程。
引入依赖,pom.xml
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-web已经包含了spring-boot-starter依赖,因此只需引入这个依赖就可以了。
新建UserController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/home")
@ResponseBody
public String home() {
return "user home";
}
}
新建App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
运行App.java,则服务器正常运行,默认端口号是8080,通过浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/user/home正常。
这样最简单的web开发就完成了。
如果要修改端口,可以再application.properties中修改:
server.port=8081这样端口号就修改成功了。
默认的请求方式是:GET,POST,PUT方式都支持。我们可以限制他的请求方式:
方法一:
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/home", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String home() {
return "user home";
}
方法二:
使用GetMapping
@GetMapping("/user/show")
@ResponseBody
public String show() {
return "user home";
}
@PostMapping("/user/create")
@ResponseBody
public String create() {
return "user home";
}GetMapping PostMapping等是spring4.3的新特性
如何传递参数
方法一:
修改UserController.java
@PostMapping("/user/create")
@ResponseBody
public String create(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password) {
return "user create, username: " + username + ", password: " + password;
}@RequestParam注解默认是参数必须提供,如果可以不提供可以使用required=false
可以提供一个默认值defaultValue=""
方法二:
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public String show(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
return "user home id: " + id;
}方法三:
注入Servlet的api
@GetMapping("/user/edit")
@ResponseBody
public String edit(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest){
return "user edit: " + httpServletRequest.getRemoteHost();
}我们发现每个方法都必须使用@ResponseBody来注释。因此可以使用RestController来简化
新建RoleController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RoleController {
@GetMapping("/role/show")
public String show(){
return "role show ";
}
}
@RestController 表明了当前controller的方法的返回值可以直接用body输出。
如何在springboot中使用jsp
新建LoginController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam(value = "password") String password) {
if (username.equals(password)) {
return "ok";
}
return "fail";
}
}
在main文件夹下面新建webapp,与java和resources文件夹并列。
修改application.properties
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp在webapp目录下新建文件夹/WEB-INF/jsp,然后新建ok.jsp和fail.jsp
springboot默认是不支持使用jsp的
在springboot中使用jsp,需要引入依赖:
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
这样就可以成功访问jsp了。
如何向jsp传参数?
@GetMapping("/loginIndex")
public String loginIndex(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username", "root");
model.addAttribute("password", "123456");
return "login";
}新建login.jsp
username; ${username}
password: ${password}
在springboot中使用jsp时,不能使用@RestController, 而要使用@Controller
如何在Jsp中使用模板?
添加pom.xml依赖:并且删除jsp的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
在application.properties中删除jsp的配置。
在springboot中使用freemarker的步骤:
1. 在pom中加入依赖,
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
2. 默认的freemaker的模板文件在classpath:/template/, 默认的文件扩展名为:ftl
新建AccountController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class AccountController {
@GetMapping("/reg")
public String reg(){
return "reg";
}
}
在resources/template下新建reg.ftl
ftl reg
可以通过访问 http://192.168.170.132:8081/reg来获取这个模板页面了
如何修改模板文件的文件路径
在application.properties中修改:
spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/ftl/ 多个用逗号隔开在resources下新建ftl文件夹,然后将reg.ftl文件移动到这个路径下,就可以访问了。
如何在模板文件中传参数
在AccountController.java
@GetMapping("/logout")
public String logout(Model model){
model.addAttribute("username", "admin");
model.addAttribute("logout", "true");
return "logout";
}在ftl目录下新建logout.ftl文件:
logout
username: ${username}
logout is ${logout}
这样就传递参数到模板中了。
最好在项目中要么选择模板,要么选择jsp,不要二者都选。
Springboot默认容器是Tomcat,如果想换成Jetty,如何做
首先需要把tomcat排除掉。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
导入jetty依赖。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jetty
其余都不需要改变,直接运行,输出:
2019-05-15 21:00:56.619 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.e.jetty.server.handler.ContextHandler : Started o.s.b.w.e.j.JettyEmbeddedWebAppContext@37d3d232{application,/,[org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.jetty.JettyServletWebServerFactory$LoaderHidingResource@30c0ccff],AVAILABLE}
2019-05-15 21:00:56.619 INFO 14692 --- [ main] org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server : Started @2652ms
2019-05-15 21:00:56.776 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
2019-05-15 21:00:57.069 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.e.j.s.h.ContextHandler.application : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-05-15 21:00:57.070 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-05-15 21:00:57.075 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 5 ms
2019-05-15 21:00:57.194 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.e.jetty.server.AbstractConnector : Started ServerConnector@614aeccc{HTTP/1.1,[http/1.1]}{0.0.0.0:8081}
2019-05-15 21:00:57.196 INFO 14692 --- [ main] o.s.b.web.embedded.jetty.JettyWebServer : Jetty started on port(s) 8081 (http/1.1) with context path '/'
2019-05-15 21:00:57.198 INFO 14692 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.App : Started App in 2.8 seconds (JVM running for 3.23)说明容器已经变成jetty了。
添加项目名称
默认是不需要有项目名称的,在application.properties文件中修改:
server.servlet.context-path=/mall在地址栏中,需要指定/mall才能访问。例如:http://192.168.170.132:8081/mall/logout
第二节
如何在springboot中访问静态资源
1. src/main/webapp 下可以直接访问
2. 默认的静态资源路径是:classpath:[/META-INF/resources/, * /resources/, /static/, /public/] 源码在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web包中
3. 可以通过spring.resources.static-locations配置项修改默认静态资源路径
方法一:
在src/main/webapp下新建user.html
Title
this is user page
可以直接在浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/user.html,说明直接将html页面放到webapp下面就可以直接访问了。
在webapp下面新建目录img,在img目录中拷贝一张图片进去my.jpg,在user.html中添加图片, 。这样可以直接在user.html中访问图片了。
。这样可以直接在user.html中访问图片了。
方法二:
在resources下新建文件夹public
在resources/public 下新建login.html,
login
this is login html page. 在public下
访问http://localhost:8080/login.html 可以访问成功。
在public下新建css文件夹,新建main.css
body {
color: red;
}在login.html中引入这个main.css文件
访问login.html页面可以成功访问,字体颜色生效。
方法三:
在application.properties中添加:
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/html/在resources中新建文件夹html
然后在resources/html/中新建index.html页面,
重启以后可以直接访问http://localhost:8080/index.html
如何在springboot中使用Servlet
新建UserServlet.java,并且继承HTTPServlet
使用Servlet3.0注解
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/user.do")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().println("user servlet");
}
}
修改App.java ,将Servlet添加到spring容器中。
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
运行,可以通过浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/user.do
如何在springboot容器中使用Servlet filter
新建LogFilter.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebFilter("/user.do")
public class LogFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("income log filter " + servletRequest.getRemoteHost());
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
这个Filter可以拦截user.do请求。运行访问http://localhost:8080/user.do时,控制台输出结果:
income log filter 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1如何在springboot中使用Listener
新建MyContextListener.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@WebListener
public class MyContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("app start up at: " + LocalDateTime.now().toString());
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
这个监听器将监听应用程序启动。启动程序时,控制台将会输出:
app start up at: 2019-05-16T15:09:23.084如何不使用上述方法,实现Servlet的API
新建包com.edu.spring.springboot.servlet,在这个包下面新建BookServlet.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BookServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().println("book servlet output");
}
}
在这个包下新建ServletConfiguration.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.servlet;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class ServletConfiguration {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean createBookServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new BookServlet(), "/book.do");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}
}
修改App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/book.do返回结果正常
使用这个方法,不用在Servlet上使用注释,也不用使用@ServletComponentScan注释。
同理,可以使用这个方法使用Filter
在Servlet这个包下新建EchoFilter.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
public class EchoFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
System.out.println("spring boot web filter " + httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
在ServletConfiguration.java中添加bean
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean createFilterRegistraionBean() {
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new EchoFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/book.do"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
浏览器上输入http://localhost:8080/book.do,控制台输出:
spring boot web filter /book.do同理,新建StartUpListener.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class StartUpListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("===========");
System.out.println("application is started");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
在ServletConfiguration.java中添加bean
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean createServletListenerRegistrationBean() {
ServletListenerRegistrationBean servletListenerRegistrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(new StartUpListener() );
return servletListenerRegistrationBean;
}
运行App.java,在应用程序运行开始,控制台输出:
===========
application is started总结
springboot 中使用Servlet的API
方法一:
1. 编写Servlet,然后加上相应的注解
2. 需要启用@ServletComponentScan注解
servlet2.5以上版本 可以使用这种方法使用
这种方法更方便一些。
方法二:
1. 编写Servlet,
2. 装配相应的bean到spring容器中
Servlet -> ServletRegistrationBean
Filter -> FilterRegistrationBean
Listener -> ServletListenerRegistrationBean
Servlet2.5及以下版本可以使用这种方法
第三节
如何在springboot中使用拦截器
新建UserController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/user/home")
public String home() {
System.out.println("----user---home");
return "user home";
}
}
新建LogHandlerInterceptor.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class LogHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=preHandle=====" + handler.getClass());
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=postHandle=====");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=afterCompletion=====");
}
}
新建WebConfiguration.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class WebConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LogHandlerInterceptor());
}
}
或者:
package cn.ac.iie.authorization.config;
import cn.ac.iie.authorization.interceptor.AuthorizationInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LogHandlerInterceptor());
}
}
这里的@Configuration注释可以替换为@SpringBootConfiguration
运行App.java,然后在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/home,正常显示user home
控制台输出:
=preHandle=====class org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod
----user---home
=postHandle=====
=afterCompletion=====总结:拦截器的使用步骤
1. 写一个拦截器,实现HandlerInterceptor接口
2. 写一个类,继承WebvcConfigurereAdapter抽象类,然后重写addInterceptors方法,并调用registry.addInterceptor把上一步的拦截器加进去
HanderInterceptor
1. preHanle: controller执行之前调用
2. postHandle: controller执行之后,且页面渲染之前调用
3. afterCompletion: 页面渲染之后调用,一半用于资源清理操作
springboot开发中的异常处理
将拦截器关闭,注释WebConfiguration.java中的@Configuration
在UserController.java中添加方法:
@GetMapping("/user/help")
public String help() {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("args is empty");
}
当页面请求/user/help的时候抛出异常,运行App.java
浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/help,浏览器显示如下:
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
Sun May 19 22:03:18 CST 2019
There was an unexpected error (type=Internal Server Error, status=500).
args is empty同时控制台输出:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: args is empty
at com.edu.spring.springboot.UserController.help(UserController.java:17) ~[classes/:na]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) ~[na:1.8.0_144]
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) ~[na:1.8.0_144]
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) ~[na:1.8.0_144]
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) ~[na:1.8.0_144]
at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:189) ~[spring-web-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
如何使用我们自己的异常页面?
方法一
默认的异常页面在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.java中定义,我们需要将这个类排除掉。
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
这时,我们如果在浏览器中输入一个不存在的网址时例如http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/help000,出现404的错误。
如果在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/help,出现500错误页面。
如何去掉springboot 默认的异常处理逻辑?
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
如何使用自己的异常逻辑页面?
在resoures下新建文件夹public,这时默认的web页面访问路径,在public文件夹下面新建404.html和500.html
Title
404 not found
Title
500 error
新建CommonErrorPageRegistry.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPage;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistrar;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistry;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CommonErrorPageRegistry implements ErrorPageRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry registry) {
ErrorPage e404 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "/404.html");
ErrorPage e500 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "/500.html");
registry.addErrorPages(e404, e500);
}
}
浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/help000和http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/help分别跳转到我们自定义的页面
总结:
使用ErrorPageRegistrar方法
写一个类,实现ErrorPageRegistrar接口,然后实现registerErrorPage方法,在该方法里面,添加具体的错误处理逻辑(类似web.xml有里面配置错误处理方法)
如果我们想单独给IllegalArgumentException异常渲染一个页面,如何做?
修改CommonErrorPageRegistry.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPage;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistrar;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistry;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CommonErrorPageRegistry implements ErrorPageRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry registry) {
ErrorPage e404 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "/404.html");
ErrorPage e500 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "/500.html");
ErrorPage args = new ErrorPage(IllegalArgumentException.class, "/args.html");
registry.addErrorPages(e404, e500, args);
}
}
这样IllegalArgumentException异常可以单独页面渲染了。
方法二:
首先将上一种方式屏蔽,将CommonErrorPageRegistry.java中的@Component注释掉
新建BookController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
@RestController
public class BookController {
@ExceptionHandler(value = FileNotFoundException.class)
public String error(Exception e) {
return "file not found exception" + e.getMessage();
}
@GetMapping("/book/error1")
public String error1() throws FileNotFoundException {
throw new FileNotFoundException("book.txt not found");
}
@GetMapping("/book/error2")
public String error2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("book.class not found");
}
}
在BookController.java中定义当前Controller中的异常,这个error方法将捕获到FileNotFoundException并返回file not found exception,捕获不到FileNotFound异常。并且这个只对当前Controller生效。对UserController中的异常并不处理。
如果要对当前Controller中的所有异常都捕获,则@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
如何对所有Controller生效?
新建GlobalExceptionHandler.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public String errorHandler(Exception e) {
return "global error " + e.getClass().getName();
}
}
这样就可以捕获所有的Controller中的异常。
全局异常处理
1. 写一个类,需要加上@ControllerAdvice注解
2. 写一个异常处理方法,方法上面需要加上@ExceptionHandler(value=Exception.class)这个注解,然后在该方法里面处理异常
第四节
springboot如何定制和优化内嵌的Tomcat
springboot默认集成了2种web容器分别是tomcat和jetty
新建UserController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/user/home")
public String home(){
return "user home";
}
}
在application.properties中修改端口号
server.port=8081运行应用程序,在浏览器中输入网址:http://127.0.0.1:8081/user/home和http://192.168.170.132:8081/user/home都可以访问成功
在application.properties中添加:
server.port=8081
server.address=192.168.170.132运行应用程序,在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8081/user/home就无法访问了,说明ip绑定成功。
可以启用tomcat日志:
server.port=8081
server.address=192.168.170.132
server.tomcat.accesslog.enabled=true
server.tomcat.accesslog.directory=F:/test如何通过代码的方式配置tomcat
注释application.properties中的内容
新建MyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.setPort(8081);
return tomcat;
}
}
同样端口号修改为8081
设置tomcat连接数和线程数:
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve;
import org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatConnectorCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.setPort(8081);
tomcat.addConnectorCustomizers(new MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer());
return tomcat;
}
class MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer implements TomcatConnectorCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
Http11NioProtocol protocol=(Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
//设置最大连接数
protocol.setMaxConnections(2000);
//设置最大线程数
protocol.setMaxThreads(500);
}
}
}
添加tomcat日志,和404错误重定向页面
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve;
import org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatConnectorCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPage;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
@Configuration
public class MyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.setPort(8081);
tomcat.addContextValves(getLogAccessLogValve());
tomcat.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND,"/404.html"));
tomcat.addInitializers(servletContext -> System.out.println("servlet start up =========="));
tomcat.addConnectorCustomizers(new MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer());
return tomcat;
}
private AccessLogValve getLogAccessLogValve(){
AccessLogValve log = new AccessLogValve();
log.setDirectory("F:/test");
log.setEnabled(true);
log.setPattern("common");
log.setPrefix("springboot--");
log.setSuffix(".txt");
return log;
}
class MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer implements TomcatConnectorCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(Connector connector) {
Http11NioProtocol protocol=(Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
//设置最大连接数
protocol.setMaxConnections(2000);
//设置最大线程数
protocol.setMaxThreads(500);
}
}
}
总结
定制和优化Tomcat,以编码的方式设置Tomcat的各个属性值,以及Tomcat的日志配置
TomcatServletWebServerFactory纳入spring容器中管理
当我们的springboot中没有自定义的web容器,那么springboot使用自己的tomcat,如果我们自定义了容器,则使用我们自定义的tomcat。 原因如下:在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded包下
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
public class EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Nested configuration if Tomcat is being used.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
public static class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration {
@Bean
public TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
Environment environment, ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer(environment, serverProperties);
}
}第五节
spring JDBC配置
引入pom.xml
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
mysql
mysql-connector-java
application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.152.45:3306/renyuanku
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456在App.java中使用数据源
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
try {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getCatalog());
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果输出数据库名。
总结:
装配DataSource的步骤
1. 加入数据库驱动
2. 配置数据源
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.152.45:3306/renyuanku spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456以上操作,springboot会自动装配好DataSource,JDBCTemplate,可以直接使用
数据库使用JDBCTemplate操作数据库
新建ProductDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class ProductDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void addProduct(String id){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
}
}
修改App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
try {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getCatalog());
connection.close();
ProductDao bean = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(ProductDao.class);
bean.addProduct("123");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
执行App.java,查询数据库,可以看到执行成功
查看Springboot用的什么数据源
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
}
}
输出结果:
class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource可以看到使用的是HikariDataSource数据源
如何使用其他数据源
在application.properties中配置
spring.datasource.type=可以指定具体使用哪种数据源,springboot默认支持一下数据源,在类中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration
@Import({ DataSourceConfiguration.Hikari.class, DataSourceConfiguration.Tomcat.class,
DataSourceConfiguration.Dbcp2.class, DataSourceConfiguration.Generic.class,
DataSourceJmxConfiguration.class })Hikari,tomcat,dbcp2,generic,放到classpath下
如何自己配置数据源
添加druid数据源依赖
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.6
新建DBConfiguration.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class DBConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public DataSource createDataSource() {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setUrl(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"));
druidDataSource.setUsername(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.username"));
druidDataSource.setPassword(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.password"));
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name"));
return druidDataSource;
}
}
application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.152.45:3306/renyuanku
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
}
}
运行输出:
class com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource说明数据源已经变为Druid了。
springboot的特点是优先使用自己的配置,然后使用spring默认配置。
同样可以使用JDBCTemplate
修改App.java
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
try {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getCatalog());
connection.close();
ProductDao bean = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(ProductDao.class);
bean.addProduct("124");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
}
}成功插入数据124
Springboot对事务也做了很好的集成
修改ProductDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
public class ProductDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void addProduct(String id){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
}
@Transactional
public void addProductBatch(String ...ids) throws FileNotFoundException {
for(String id: ids){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
if("".equals("")) {
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
}
}
}
使用事务需要在方法上添加注释@Transactional
然后在App.java启用事务,添加注释@EnableTransactionManagement
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
DataSource dataSource = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
try {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getCatalog());
connection.close();
ProductDao bean = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(ProductDao.class);
try {
bean.addProductBatch("111", "222", "333", "444", "555");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
}
}
然后执行,报异常,查询数据库发现存入了一条数据 111,说明事务没有生效。
原因是spring默认会对运行时的异常进行事务的操作,而fileNotFound不是运行时的异常,我们需要修改为RunTimeException。修改:
@Transactional
public void addProductBatch(String ...ids) throws FileNotFoundException {
for(String id: ids){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
if("".equals("")) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
}然后运行App.java,报出异常,查询数据库,没有插入数据,说明事务生效。
事务
首先要使用@EnableTransactionManagement启用对事务的支持
然后在需要使用事务的方法上面加上@Transactional
注意,默认只会对运行时异常进行事务回滚,非运行时异常不会回滚事务
如何回滚非运行时异常
使用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)可以回滚所有异常
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addProductBatch(String ...ids) throws FileNotFoundException {
for(String id: ids){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
if("".equals("")) {
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
}
}
如何不回滚某些异常
使用@Transactional(noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class)
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class)
public void addProductBatch(String ...ids) throws Exception {
for(String id: ids){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
if("".equals("")) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
}注意:@Transactional必须要标注在纳入到spring容器管理bean的公有方法,例如:
@Transactional()
public void addTest(String ...ids){
add(ids);
}
@Transactional()
private void add(String ...ids){
for(String id: ids){
String sql = "insert into test (id) values ("+ id + ")";
jdbcTemplate.execute(sql);
if("".equals("")) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
}运行App.java可以成功插入数据库,事务没有生效。
注意:直接调用的方法必须要使用@Transactional注释,否则不能回滚
第六节
SpringAOP
日志记录、权限处理、监控、异常处理
添加依赖pom.xml
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
新建包dao,在dao下面新建UserDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserDao {
public void add (String username, String password){
System.out.println("add: username:" + username + ",password:" + password);
}
}
新建LogAspect.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.edu.spring.springboot.dao..*.*(..))")
public void log() {
System.out.println("method log done" );
}
}
execution(* com.edu.spring.springboot.dao..*.*(..)) 表示织入到com.edu.spring.springboot.dao及其子包下面的所有的类的所有的方法。
执行的时机就是,前置执行。
App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
configurableApplicationContext.getBean(UserDao.class).add("admin", "123456");
configurableApplicationContext.close();
}
}
运行结果:
method log done
add: username:admin,password:123456这是一个最简单的AOP。
AOP开发流程
1. spring-boot-starter-aop加入依赖,默认开启了AOP的支持
2. 写一个Aspect,封装横切关注点(日志,监控等等),需要配置通知(前置通知,后置通知等等)和切入点(哪些包的哪些类的哪些方法等等);
3. 这个Aspect需要纳入到spring容器管理,并且需要加入@Aspect注解
在application.properties中配置:
spring.aop.auto=false表示不启用aop,默认是为true启用,运行App.java,结果如下:
add: username:admin,password:123456在application.properties中配置:
spring.aop.auto=true
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=falsespring.aop.proxy-target-class默认是true,false表示使用的是JDK的动态代理,true表示使用CGLIB的动态代理
JDK的动态代理需要一个接口
新建IUserDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
public interface IUserDao {
public void add (String username, String password);
}
然后让UserDao实现这个接口,修改App.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
System.out.println(configurableApplicationContext.getBean(UserDao.class).getClass());
configurableApplicationContext.getBean(UserDao.class).add("admin", "123456");
configurableApplicationContext.close();
}
}
运行报错:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao' available
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:343)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:335)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1123)
at com.edu.spring.springboot.App.main(App.java:12)原因是基于JDK的动态代理之后,就不能根据class来获取对象,需要根据接口来获取对象。
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
System.out.println(configurableApplicationContext.getBean(IUserDao.class).getClass());
configurableApplicationContext.getBean(IUserDao.class).add("admin", "123456");
configurableApplicationContext.close();
}
}
运行输出结果如下:
class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy55
method log done
add: username:admin,password:123456这是典型的动态代理。
将spring.aop.proxy-target-class改为true,运行结果如下:
class com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$62d64f2d
method log done
add: username:admin,password:123456总结:
aop默认是使用基于JDK的动态代理来实现AOP,默认启用
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true或者不配置,表示使用cglib的动态代理,
=false表示jdk动态代理
如果配置了false,而类没有借口,则依然使用cglib
将application.properties中的配置注释掉。
如何得到aop相关参数
修改LogAspect.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.edu.spring.springboot.dao..*.*(..))")
public void log() {
System.out.println("before method log done" );
}
@After("execution(* com.edu.spring.springboot.dao..*.*(..))")
public void logAfter(JoinPoint point) {
System.out.println("before method log done" + point.getTarget().getClass() + ", args="+ Arrays.asList(point.getArgs()) + ", method=" + point.getSignature().getName());
}
}
输出结果如下:
class com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$abbff7d9
before method log done
add: username:admin,password:123456
before method log doneclass com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao, args=[admin, 123456]虽然springboot默认支持了AOP,但是springboot依然提供了enable的注解,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
第七节 Springboot starter
新建RedisProperties.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis")
public class RedisProperties {
private String host;
private Integer port;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public Integer getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
}
新建RedisConfiguration.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Jedis.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Jedis jedis(RedisProperties redisProperties){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis(redisProperties.getHost(), redisProperties.getPort());
System.out.println("springbourse bean" + jedis);
return jedis;
}
}
这样的话spring容器在装配Jedis这个bean的时候会先从容器中获取RedisProperties这个bean,然后传到这个方法中去。
@ConditionalOnClass(Jedis.class)表示装配这个bean的时候Jedis.class这个类一定要存在。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean表示没有这个Jedis这个类的时候,我们才装配。
新建项目spring-course-redis,将上面的项目加到这个项目中去:pom.xml如下
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course-redis
1.0-SNAPSHOT
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
加入好依赖以后,在spring-course-redis项目中我们可以直接从容器中获取jedis了,App.java如下:
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
Jedis jedis = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(Jedis.class);
System.out.println("springbourseredis bean" + jedis);
jedis.set("id", "vincent");
System.out.println(jedis.get("id"));
}
}
新建application.properties,内容如下:
redis.host=192.168.152.45
redis.port=6379运行App.java输出如下:
springbourse beanredis.clients.jedis.Jedis@60bdf15d
springbourseredis beanredis.clients.jedis.Jedis@60bdf15d
vincent说明已经成功注入进去了。
但是在springboot1.X版本中是无法直接这样使用的。
解决方法有两种,
方法一:
在springbootcourse项目中,新建EnableRedis.java,需要使用@Import注解
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableRedis {
}
在springbootcourseredis项目中,添加@EnableRedis注解
@EnableRedis
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
Jedis jedis = configurableApplicationContext.getBean(Jedis.class);
System.out.println("springbourseredis bean" + jedis);
jedis.set("id", "vincent");
System.out.println(jedis.get("id"));
}
}
方法二:
使用spring.factories
在springbootcourse项目中在resources目录下,新建/META-INF文件夹,然后在这个文件夹下新建spring.factories文件,内容如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.edu.spring.springboot.RedisAutoConfiguration总结
springboot2.x 可以直接使用
springboot1.x 需要进行配置。
自己开发一个spring boot starter的步骤
1. 新建一个项目
2. 需要一个配置类,配置类里面需要装配好需要提供出去的类
3. 使用
(1)@Enable ,使用@Import导入需要装配的类
(2)/META-INF/spring.factories, 在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration配置需要装配的类
第八节 springboot日志
默认的日志输出结果如下:
2019-05-26 14:29:27.650 INFO 641 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.App : Starting App on duandingyangdeMacBook-Pro.local with PID 641 (/Users/duandingyang/git-project/springcourse/target/classes started by duandingyang in /Users/duandingyang/git-project/springcourse)
2019-05-26 14:29:27.654 INFO 641 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.App : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
2019-05-26 14:29:28.804 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
2019-05-26 14:29:28.834 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2019-05-26 14:29:28.835 INFO 641 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/9.0.17]
2019-05-26 14:29:28.931 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2019-05-26 14:29:28.931 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.s.web.context.ContextLoader : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1230 ms
2019-05-26 14:29:29.203 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
2019-05-26 14:29:29.409 INFO 641 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
2019-05-26 14:29:29.416 INFO 641 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.App : Started App in 2.638 seconds (JVM running for 3.64)
日志级别为Info ,进程ID(PID)641 , 线程名字main,所在类,日志内容。
新建dao包,然后在这个dao包下新建UserDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserDao {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDao.class);
public void log() {
logger.debug("user dao debug log");
logger.info("user dao info log");
logger.warn("user dao warn log");
logger.error("user dao error log");
}
}
App.java内容如下:
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
run.getBean(UserDao.class).log();
run.close();
}
}
运行输出结果如下:
2019-05-26 14:35:24.170 INFO 787 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao info log
2019-05-26 14:35:24.170 WARN 787 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao warn log
2019-05-26 14:35:24.170 ERROR 787 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao error log说明日志的默认级别是info。
如何调整日志级别?
方法一:
修改application.properties
logging.level.*=DEBUG可以通过logging.level.*=debug 来设置,* 可以是包,也可以是某个类。
方法二
在program arguments中设置--debug,也可以启用DEBUG,但是这种方式无法输出我们自己的DEBUG信息,只可以输出Spring的debug
新建service包,然后在这个包下新建UserService.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class UserService {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserService.class);
public void log() {
logger.debug("user service debug log");
logger.info("user service info log");
logger.warn("user service warn log");
logger.error("user service error log");
}
}
如果我们只想在service包下面使用debug,则需要修改application.properties内容:
logging.level.com.edu.spring.springboot.service=DEBUG在App.java中添加
run.getBean(UserService.class).log();输出结果如下:
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 INFO 843 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao info log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 WARN 843 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao warn log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 ERROR 843 --- [ main] com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao : user dao error log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 DEBUG 843 --- [ main] c.e.s.springboot.service.UserService : user service debug log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 INFO 843 --- [ main] c.e.s.springboot.service.UserService : user service info log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 WARN 843 --- [ main] c.e.s.springboot.service.UserService : user service warn log
2019-05-26 14:54:20.149 ERROR 843 --- [ main] c.e.s.springboot.service.UserService : user service error logservice启用了debug,dao默认的info
日志级别有:trace,debug,info,warn,error,fatal,off
日至级别off表示关闭日志
如何配置日志输出文件?
application.properties
logging.file=/Users/vincent/my.log指定日志文件路径与名字。
logging.path 也可以指定日志的路径,此时名字为spring.log
日志文件输出,文件的大小10M之后,就会分割了
如何指输出日志格式
logging.pattern.console=%-20(%d{yyy-MM-dd} [%thread]) %-5level %logger{80} - %msg%n
logging.file.console=%-20(%d{yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread]) %-5level %logger{80} - %msg%n分别为控制台的日志输出格式和文件日志输出格式
使用logback
在resources下新建logback.xml
%-20(%d{yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread]) %-5level %logger{80} - %msg%n
springboot 默认支持logback,也就是说,只需要在classpath下放一个logback.xml或者logback-spring.xml的文件,即可定制日志的输出。
如何使用log4j2
现将默认的日志排除,并且加入log4j依赖,pom.xml
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-logging
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-log4j2
在resources目录下新建log4j2.xml
运行App.java,输出结果为:
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] DEBUG com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao - user dao debug log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] INFO com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao - user dao info log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] WARN com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao - user dao warn log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] ERROR com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao - user dao error log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] DEBUG com.edu.spring.springboot.service.UserService - user service debug log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] INFO com.edu.spring.springboot.service.UserService - user service info log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] WARN com.edu.spring.springboot.service.UserService - user service warn log
2019-05-27 23:28:51.808 [main] ERROR com.edu.spring.springboot.service.UserService - user service error log说明log4j2配置成功。当然了,log4j2.xml 文件名也可以改为log4j2-spring.xml
使用其他的日志组件的步骤 1:排除掉默认的日志组件spring-boot-starter-logging 2:加入新的日志组件依赖 3:把相应的日志文件加到classpath下
springboot 的相关日志源码在org.springframework.boot.logging包下面,其中LogLevel.java定义了日志级别,LoggingSystemProperties定义了日志配置项。
第九节 springboot监控和度量
添加依赖pom.xml
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-actuator
spring boot2.x中,默认只开放了info、health两个端点,其余的需要自己通过配置management.endpoints.web.exposure.include属性来加载(有include自然就有exclude)。如果想单独操作某个端点可以使用management.endpoint.端点.enabled属性进行启用或者禁用。
Endpoints
Actuator endpoints 允许你去监控和操作你的应用。SpringBoot包含了许多内置的端点,当然你也可以添加自己的端点。比如 health 端点就提供了基本的应用健康信息。
Metrics
Spring Boot Actuator 提供 dimensional metrics 通过集成 Micrometer.
Audit
Spring Boot Actuator 有一套灵活的审计框架会发布事件到 AuditEventRepository。
springboot 2.x 默认只启动了 health 和 info 端点,可以通过 application.properties 配置修改:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info,env,metrics项目启动时可以看到暴露出来的接口信息:
2019-05-30 18:47:35.162 INFO 9888 --- [ main] o.s.b.a.e.web.EndpointLinksResolver : Exposing 4 endpoint(s) beneath base path '/actuator'浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/actuator/,结果如下:
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator",
"templated": false
},
"health-component": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}",
"templated": true
},
"health-component-instance": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health/{component}/{instance}",
"templated": true
},
"health": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health",
"templated": false
},
"env": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/env",
"templated": false
},
"env-toMatch": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/env/{toMatch}",
"templated": true
},
"info": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/info",
"templated": false
},
"metrics": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics",
"templated": false
},
"metrics-requiredMetricName": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/{requiredMetricName}",
"templated": true
}
}
}浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/system.cpu.usage,结果如下:
{
"name": "system.cpu.usage",
"description": "The \"recent cpu usage\" for the whole system",
"baseUnit": null,
"measurements": [
{
"statistic": "VALUE",
"value": 0.24420139608387495
}
],
"availableTags": []
}常用的endpoint:
| HTTP方法 | 路径 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /autoconfig | 查看自动配置的使用情况 |
| GET | /configprops | 查看配置属性,包括默认配置 |
| GET | /beans | 查看bean及其关系列表 |
| GET | /dump | 打印线程栈 |
| GET | /env | 查看所有环境变量 |
| GET | /env/{name} | 查看具体变量值 |
| GET | /health | 查看应用健康指标 |
| GET | /info | 查看应用信息 |
| GET | /mappings | 查看所有url映射 |
| GET | /metrics | 查看应用基本指标 |
| GET | /metrics/{name} | 查看具体指标 |
| POST | /shutdown | 关闭应用 |
| GET | /trace | 查看基本追踪信息 |
想要查看服务器的健康状态详细信息,需要配置application.properties
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always这样就可以查看健康状态的详细信息了,例如磁盘利用情况,数据库情况。
如何自定义健康状态检查?
新建MyHealthIndicator.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
return Health.up().withDetail("error","springboot error").build();
}
}
在浏览器中输入http://localhost:8080/actuator/health可以看到自定义的健康状态监控。
总结:
自定义健康状态监测,实现HealthIndicator接口,并纳入spring容器的管理之中。
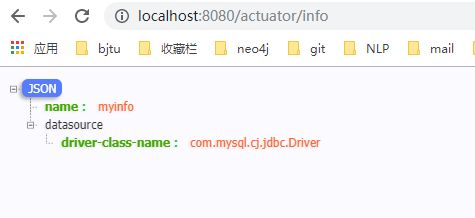
使用info,
在application.properties中使用info开头的信息都可以显示出来,例如:
info.name=myinfo
info.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver在浏览器中输入,http://localhost:8080/actuator/info 可以查看到这些配置信息。
可以对git信息进行监控。
Prometheus Grafana实现应用可视化监控
第十节 打包springboot
pom.xml文件:
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.1.4.RELEASE
com.edu.spring.springboot.App
repackage
一定要指定mainClass才可以
springboot 测试
添加pom.xml依赖
4.0.0
cn.ac.iie
spring-course
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.1.4.RELEASE
import
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.1.4.RELEASE
com.edu.spring.springboot.App
repackage
新建UserDao.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserDao {
public Integer addUser(String username) {
System.out.println("user dao adduser " + username);
if(username == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
在Intellij下Ctrl + Shift + T 新建测试类UserDaoTest.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserDaoTest {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
public void addUser() {
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), userDao.addUser("root"));
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(0), userDao.addUser(null));
}
}输出结果如下:
user dao adduser root
user dao adduser nullspringboot测试步骤,
直接在测试类上面添加下面的注解:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
Test下的包名和java下的包名应该一致。
如何测试bean?
新建User.java并且纳入到spring容器管理中去。
package com.edu.spring.springboot.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
}
新建测试类ApplicationContextTest.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.bean.User;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ApplicationContextTest {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Test
public void testNull() {
Assert.assertNotNull(applicationContext.getBean(User.class));
}
}
输出结果可以显示,输出正常。
如何在测试类中自定义一个bean?
在src/test/java/com/edu/springboot/dao下新建TestBeanConfiguration.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@TestConfiguration
public class TestBeanConfiguration {
@Bean
public Runnable createRunnable() {
return () -> {};
}
}
然后在ApplicationContextTest.java 指定classes
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.bean.User;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = TestBeanConfiguration.class)
public class ApplicationContextTest {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Test
public void testNull() {
Assert.assertNotNull(applicationContext.getBean(User.class));
Assert.assertNotNull(applicationContext.getBean(Runnable.class));
}
}
指定classes=TestBeanConfiguration.class就可以使用这个bean了。
使用@TestConfiguration可以在测试环境下指定bean。如果在App.java 中使用这个bean,那么会报错,找不到这个bean。
只有在测试环境下有效。
测试环境下,只能用@TestConfiguration,不能用@Configuration
如何环境测试
在test/java/com/edu/spring/springboot/dao下 新建EnvTest.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class EnvTest {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Test
public void testValue() {
Assert.assertEquals("myapplication", environment.getProperty("spring.application.name"));
}
}
在main/resources/application.properties内容如下:
spring.application.name=myapplication测试运行正常。
如果我们的application.properties在test/resources/下怎么办?
在test下新建文件夹resources,然后在test/resources/目录下新建application.properties,内容如下:
spring.application.name=myapplication-test然后运行EnvTest.java文件,报错:
Expected :myapplication
Actual :myapplication-test说明这里面的配置文件,优先去取test/resources中的application.properties,如果没有这个配置文件,则去main/resoures中去取。
在测试环境中,springboot会优先加载测试环境下的配置文件(application.properties)
测试环境下没有,才会加载正式环境下的配置文件。
测试环境中自定义指定配置项
(properties = {"app.version=1.0.0"}):
package com.edu.spring.springboot.dao;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"app.version=1.0.0"})
public class EnvTest {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Test
public void testValue() {
Assert.assertEquals("myapplication-test", environment.getProperty("spring.application.name"));
Assert.assertEquals("1.0.0", environment.getProperty("app.version"));
}
}
运行成功。
Mock如何测试接口?
新建mapper包,在包下新建UserMapper.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.mapper;
public interface UserMapper {
Integer createUser(String username);
}
在Test下,新建UserDaoTest.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.mapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.BDDMockito;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class UserMapperTest {
@MockBean
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test(expected = NullPointerException.class)
public void createUser() {
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser("admin")).willReturn(Integer.valueOf(1));
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser("")).willReturn(Integer.valueOf(0));
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser(null)).willThrow(NullPointerException.class);
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), userMapper.createUser("admin"));
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(0), userMapper.createUser(""));
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(0), userMapper.createUser(null));
}
}因为接口并没有实现类,因此需要做提前预测,BDDMockito.given就是这个功能。当user.createUser()的输入时admin时,返回整型1,当user.createUser()的输入是“”时,返回整型0,当user.createUser()的输入时null时,返回异常。
mock方法可以卸载init方法中,如下所示:
package com.edu.spring.springboot.mapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.BDDMockito;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class UserMapperTest {
@MockBean
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Before
public void init() {
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser("admin")).willReturn(Integer.valueOf(1));
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser("")).willReturn(Integer.valueOf(0));
BDDMockito.given(userMapper.createUser(null)).willThrow(NullPointerException.class);
}
@Test(expected = NullPointerException.class)
public void createUser() {
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), userMapper.createUser("admin"));
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(0), userMapper.createUser(""));
Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(0), userMapper.createUser(null));
}
}对Controller进行测试
方法一:
新建BookController.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class BookController {
@GetMapping("/book/home")
public String home() {
System.out.println("/book/home url is invoke");
return "book home";
}
}
新建测试类BookControllerTest.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.controller;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class BookControllerTest {
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@Test
public void home() {
String forObject = testRestTemplate.getForObject("/book/home", String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("book home", forObject);
}
}TestRestTemplate 需要在web环境中,因此需要SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT
在BookController.java中添加方法,测试有参数的Controller方法:
@GetMapping("/book/show")
public String show(@RequestParam("id") String id) {
System.out.println("/book/show url is invoke");
return "book" + id;
}在测试方法中:
@Test
public void show() {
String forObject = testRestTemplate.getForObject("/book/show?id=100", String.class);
Assert.assertEquals("book100", forObject);
}方法二:
新建测试类BookControllerTest2.java
package com.edu.spring.springboot.controller;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvcBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(controllers = BookController.class)
public class BookControllerTest2 {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void home() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/home")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/home")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("book home"));
}
}@WebMvcTest 不需要运行在web环境下,但是,需要指定controllers,表示需要测试哪些controller
修改BookController.java,使用UserDao
package com.edu.spring.springboot.controller;
import com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@GetMapping("/book/home")
public String home() {
System.out.println("/book/home url is invoke");
return "book home";
}
@GetMapping("/book/show")
public String show(@RequestParam("id") String id) {
System.out.println("/book/show url is invoke");
userDao.addUser("aaa");
return "book" + id;
}
}
报错信息如下:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to load ApplicationContext
at org.springframework.test.context.cache.DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.loadContext(DefaultCacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate.java:125) ~[spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DefaultTestContext.getApplicationContext(DefaultTestContext.java:108) ~[spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.injectDependencies(DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:118) ~[spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.support.DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.prepareTestInstance(DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:83) ~[spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.SpringBootDependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.prepareTestInstance(SpringBootDependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener.java:44) ~[spring-boot-test-autoconfigure-2.1.4.RELEASE.jar:2.1.4.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.TestContextManager.prepareTestInstance(TestContextManager.java:246) ~[spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.createTest(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:227) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner$1.runReflectiveCall(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:289) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.methodBlock(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:291) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:246) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:97) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.statements.RunBeforeTestClassCallbacks.evaluate(RunBeforeTestClassCallbacks.java:61) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.statements.RunAfterTestClassCallbacks.evaluate(RunAfterTestClassCallbacks.java:70) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.run(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.java:190) [spring-test-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137) [junit-4.12.jar:4.12]
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:68) [junit-rt.jar:na]
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:47) [junit-rt.jar:na]
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:242) [junit-rt.jar:na]
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:70) [junit-rt.jar:na]
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'bookController': Unsatisfied dependency expressed through field 'userDao'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.edu.spring.springboot.dao.UserDao' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement.inject(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:596) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata.inject(InjectionMetadata.java:90) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:374) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1411) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:592) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:515) ~[spring-beans-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar:5.1.6.RELEASE]
说没有UserDao对象。因为使用@WebMvcTest方式测试,不会加载整个spring容器,只能测试controller。Controller里面的一些依赖,需要自己去mock。
但是使用@SpringBootTest方式是可以把整个spring容器加载进来的。但不能和@WebMvcTest同时使用
如果要使用@SpringBootTest,则无法使用MockMVC,如果要是用MockMvc需要添加@AutoConfigureMockMvc,如下所示
package com.edu.spring.springboot.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class BookControllerTest3 {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void home() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/home")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/home")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("book home"));
}
@Test
public void show() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/show").param("id", "400")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book/show").param("id", "400")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("book400"));
}
}