Spring boot随机端口你都不会,怎么动态扩容?
一般情况下每个spring boot工程启动都有固定的端口,但是固定端口不利用服务的动态扩容,如果在一台服务器上需要对同一个服务进行多实例部署,很容易出现端口冲突,那么怎么解决这个问题呢?
random随机端口
在spring boot中,可以通过${random}来生成随机数字,我们可以在配置文件中,这么设置端口:
server.port=${random.int(2000,8000)}
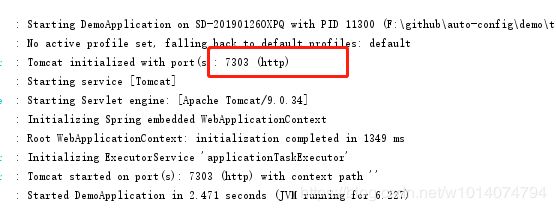
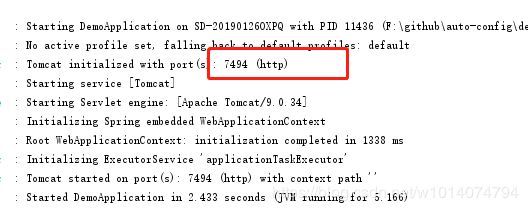
通过random.int方法,指定生成2000~8000的随机端口。这样每次启动的端口都不一样。
多次启动,发现每次的端口都不一致说明配置成功。
注意事项:
这里需要注意spring boot项目启动属性文件的加载顺序,spring boot的属性是由里向外加载,所以最外层的最后被加载,会覆盖里层的属性。
所以如果主动在启动命令中使用–server.port配置了项目的端口号,那么属性文件中配置的随机端口属性就不会生效。
注意:除Spring boot外,我还整理了最新Java架构项目实战教程+大厂面试题库,有兴趣的可以 点击此处 免费获取,没基础勿进哦
通过System.setProperty设置有效随机端口
上面的方法虽然暂时达到了想要的效果,但是有个问题:如果生成的这个随机端口已经被使用了,那么项目启动就会出现端口冲突。
那么,我们能否通过一个检测机制,让生成的随机端口一定是一个没有被占用的有效的随机端口呢?
有效端口检测原理:
通过建立socket连接,Socket socket = new Socket(Address,port);#address代表主机的IP地址,port代表端口号
如果对该主机的特定端口号能建立一个socket,则说明该主机的该端口在使用。
Socket socket = new Socket(Address,port);#address代表主机的IP地址,port代表端口号
如果对该主机的特定端口号能建立一个socket,则说明该主机的该端口在使用。
实现思路:
通过在项目启动前,获取有效的随机端口并通过System.setProperty将变量设置到系统的全局变量中,这样项目启动时就可以从全局变量中获取到server.port变量的值。
这里的system,系统指的是 JRE (runtime)system,即设置jvm运行时的全局变量。
工具类:
@Slf4j
public class NetUtils {
/**
* 测试本机端口是否被使用
* @param port
* @return
*/
public static boolean isLocalPortUsing(int port){
boolean flag = true;
try {
//如果该端口还在使用则返回true,否则返回false,127.0.0.1代表本机
flag = isPortUsing("127.0.0.1", port);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return flag;
}
/***
* 测试主机Host的port端口是否被使用
* @param host
* @param port
* @throws UnknownHostException
*/
public static boolean isPortUsing(String host,int port) {
boolean flag = false;
try {
InetAddress Address = InetAddress.getByName(host);
Socket socket = new Socket(Address,port); //建立一个Socket连接
flag = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
//log.info(e.getMessage(),e);
}
return flag;
}
//start--end是所要检测的端口范围
static int start=0;
static int end=1024;
/**
* 由于本机上安装了mysql,采用3306端口去验证
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String args[]){
int testPost =3306;
if(isLocalPortUsing(testPost)){
System.out.println("端口 "+testPost+" 已被使用");
}else{
System.out.println("端口 "+testPost+"未使用");
}
}
}
public class ServerPortUtils {
/**
* 获取可用端口
* @return
*/
public static int getAvailablePort(){
int max = 65535;
int min = 2000;
Random random = new Random();
int port = random.nextInt(max)%(max-min +1) + min;
boolean using = NetUtils.isLocalPortUsing(port);
if(using){
return getAvailablePort();
}else{
return port;
}
}
}
项目启动前设置server.port环境变量
/**
* 开始命令
*/
@Slf4j
public class StartCommand {
public StartCommand(String[] args){
Boolean isServerPort = false;
String serverPort = "";
if(args != null){
for (String arg:args){
if(StringUtils.hasText(arg) &&
arg.startsWith("--server.port")
){
isServerPort = true;
serverPort = arg;
break;
}
}
}
//没有指定端口,则随机生成一个可用的端口
if(!isServerPort){
int port = ServerPortUtils.getAvailablePort();
log.info("current server.port=" + port);
System.setProperty("server.port",String.valueOf(port));
}else{//指定了端口,则以指定的端口为准
log.info("current server.port=" + serverPort.split("=")[1]);
System.setProperty("server.port",serverPort.split("=")[1]);
}
}
}
启动类调用方法:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableUserClient
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
@Autowired
Environment environment;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new StartCommand(args);
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
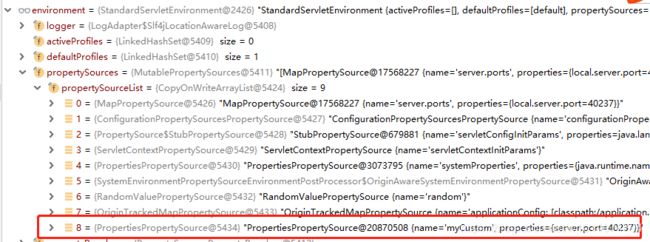
通过自定义PropertiesPropertySource属性源实现
public class MyEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
//MapPropertySource
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("server.port", ServerPortUtils.getAvailablePort());
System.out.println(properties.get("server.port"));
PropertiesPropertySource source = new PropertiesPropertySource("myCustom", properties);
environment.getPropertySources().addLast(source);
//environment.getPropertySources().addAfter();
}
}
通过配置在resources/META-INF/spring.factories文件中使用全名注册
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=com.laowan.demo.command.MyEnvironmentPostProcessor
这样在项目启动后,就会将该属性源加载到Environment中。
server.port=0随机端口 (推荐)
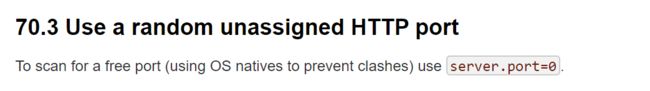
通过设置server.port=0,在spring boot项目启动时,会自动去寻找一个空闲的端口,避免端口冲突。
扩展:server.port=-1
设置为-1是为了完全关闭HTTP端点,但仍创建一个WebApplicationContext,
主要是在单元测试时使用。
验证:
执行单元测试,获取server.port属性
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Environment environment;
@Test
void getProperties() {
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("server.port"));
}
}
执行结果为:-1
注意:最后送大家十套2020最新Java架构实战教程+大厂面试题库,有兴趣的 点击此处 免费获取,没基础勿进哦
总结
1、为什么要设置随机端?主要是为了解决动态扩容时出现端口冲突的问题。
2、怎么获取一个有效的随机端口号
3、spring boot下实现随机端口的三种方式。关于方式三的自定义属性源的实现方式可以多多品味,实践一下,更好的体会属性文件的加载顺序。
4、补充通过server.port=0,设置一个有效的随机端口,推荐做法