spring知识点整理
一、概述
- spring是一站式服务站点。
- Spring 是轻量级的框架,核心特性是可以用于开发任何 Java 应用程序
- Spring 最认同的技术是控制反转的依赖注入(DI)模式。对于依赖注入,举例:我是这样理解的,将依赖注入四字拆开。依赖:类A依赖于类B。注入:类B通过反转IOC注入到类A中。
- 面向方面的程序设计(AOP):一个程序中跨越多个点的功能被称为横切关注点。
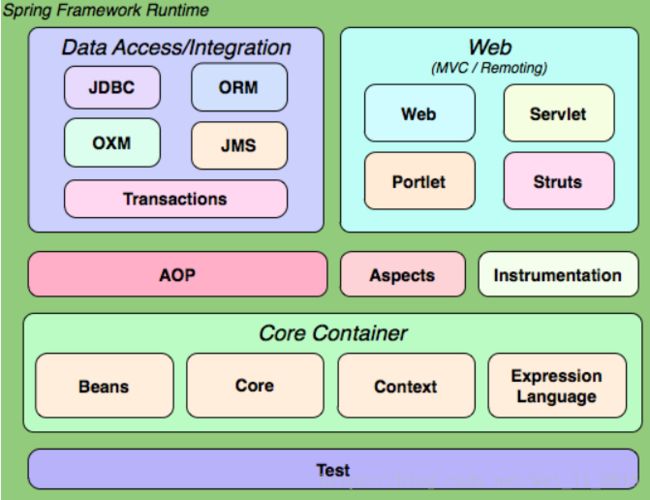
- 结构图如下:
二、HelloWorld案例
spring的jar包可以从https://blog.csdn.net/wei_li_2015/article/details/81382291下载。
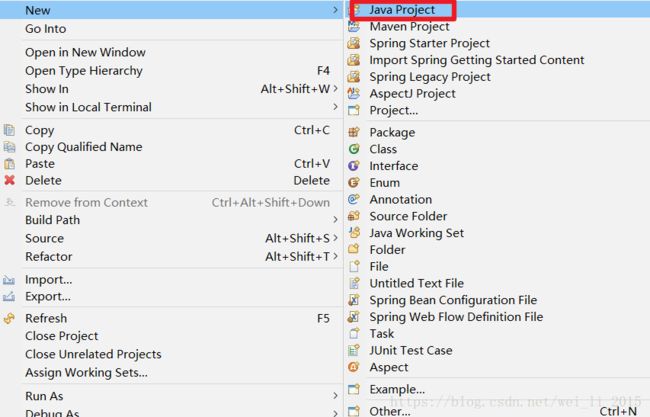
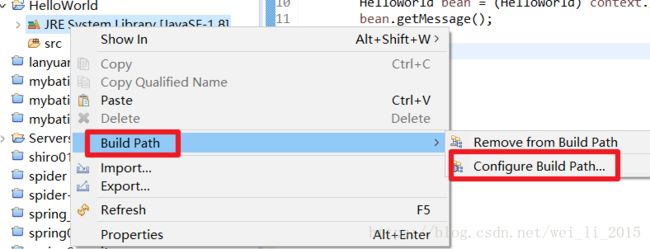
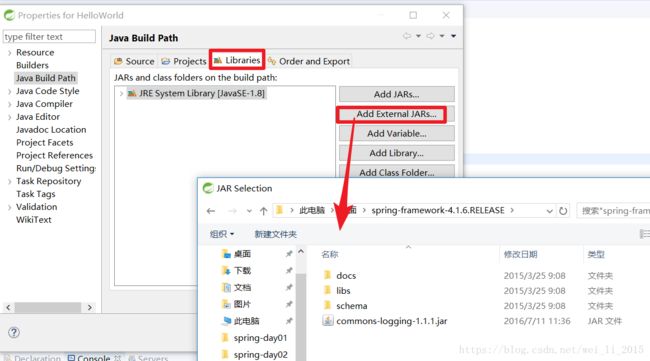
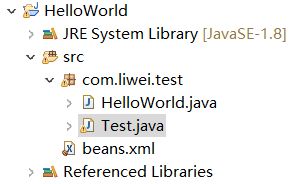
第一步:使用eclipse开发软件,创建java Project项目,导入spring的核心库和通用日志包。
项目结构如下:
相应的代码如下:
Test程序入口文件:
package com.liwei.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ac.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.getTestHelloWorld();
}
}HelloWorld文件:
package com.liwei.test;
public class HelloWorld {
private String testHelloWorld;
public String getTestHelloWorld() {
return testHelloWorld;
}
public void setTestHelloWorld(String testHelloWorld) {
System.out.println("打印信息:" + testHelloWorld);
}
}beans配置文件:
在上面的代码中,需要注意的是:
- beans.xml文件中,property属性中的name必须是HelloWorld中的属性。
- Test中的getBean中的字段属性,必须是beans.xml中的name属性名称
输出结果如下:
三、spring的相关配置
1.id和name属性
id:给Bean 起个名字, 在约束中采用 ID 的约束:唯一, 必须以字母开始,可以使用字母、数字、连字符、下划线、句话、冒号 。id不能出现特殊字符。
name:Bean 起个名 name可以出现特殊字符,如果
没有 id 的话 , name 可以当做 id 使用。
2.scope 属性
scope:控制Bean 的作用范围。
singleton :默认值,单例的。
prototype :多例的。
3.Bean 的生命周期
初始化:通过配置
标签上的 init-method 作为 Bean 的初始化的时候执行的方法
销毁:配置 destroy-method作为 Bean 的销毁的时候执行的方法。销毁方法想要执行,需要是单例创建的 Bean 而且在工厂关闭的时候,Bean 才会被销毁。
除此之外,还需要配置实体类中初始化方法。
package com.liwei.test; public class HelloWorld { private String testHelloWorld; public String getTestHelloWorld() { return testHelloWorld; } public void setTestHelloWorld(String testHelloWorld) { System.out.println("打印信息:" + testHelloWorld); } public void init() { System.out.println("我是初始化方法"); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("我是销毁方法"); } }Test.java文件:
package com.liwei.test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ac.getBean("helloWorld"); helloWorld.getTestHelloWorld(); ac.close(); } }打印:
四、spring的依赖注入
1. spring构造函数的注入
当容器调用带有一组参数的类构造函数时,基于构造函数的依赖注入(DI) 就完成了,其中每个参数代表一个对其他类的依赖。
Teacher.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
public class Teacher {
public Teacher() {
System.out.println("这是教师类的构造方法");
}
public void teaching() {
System.out.println("这是老师教的方法");
}
}Student.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
public class Student {
private Teacher teacher;
public Student(Teacher teacher) {
System.out.println("这是学生类的构造方法");
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public void teaching() {
teacher.teaching();
System.out.println("这是调用老师类中教的方法");
}
}Test.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student)ac.getBean("student");
student.teaching();
}
}beans.xml配置文件:
打印结果:
2. spring的set方式的注入
Teacher.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
public class Teacher {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("这是set方式的注入");
this.name = name;
}
public void teaching() {
System.out.println(name + "老师, 您好,非常感谢您教我们这个方法!");
}
}
Student.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
public class Student {
private Teacher teacher;
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
public void teaching() {
teacher.teaching();
}
}beans.xml文件:
Test.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student)ac.getBean("student");
student.teaching();
}
}
你应该注意定义在基于构造函数注入和基于设值函数注入中的 Beans.xml 文件的区别。唯一的区别就是
第一:在基于构造函数注入中,我们使用的是〈bean〉标签中的〈constructor-arg〉元素,而在基于设值函数的注入中,我们使用的是〈bean〉标签中的〈property〉元素。
第二个:你需要注意的点是,如果你要把一个引用传递给一个对象,那么你需要使用 标签的 ref 属性,而如果你要直接传递一个值,那么你应该使用 value 属性。
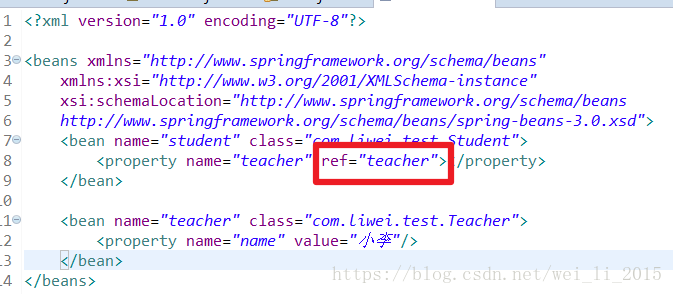
3. 对象类型的注入
对象类型的注入,其实就如上边所示中:
对teacher类文件进行引入。
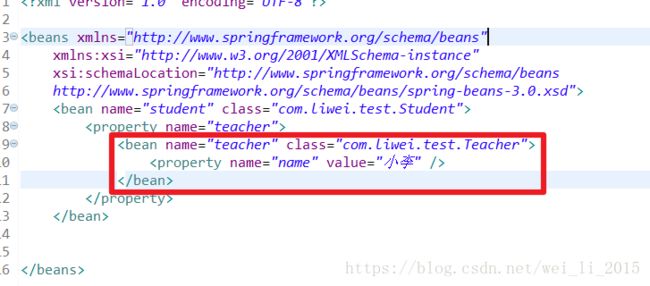
另外一种方式如下:
直接将对象放入
属性中:
以上两种其结果都是一样的。
4. 注入集合
在上面你已经看到,使用 value 属性来配置基本数据类型和在bean 配置文件中使用
标签的 ref 属性来配置对象引用。这两种情况是将值传递给一个 bean。如果想传递多个值,可以使用 Java Collection 类型 List、Set、Map 和 Properties。
元素 描述 它有助于连线,如注入一列值,允许重复。 它有助于连线一组值,但不能重复。 它可以用来注入名称-值对的集合,其中名称和值可以是任何类型。 它可以用来注入名称-值对的集合,其中名称和值都是字符串类型。 1)List的注入
Teacher.java文件:
package com.liwei.test; import java.util.List; public class Teacher { private Listname; public List getName() { return name; } public void setName(List name) { this.name = name; } public void teaching() { for (String string : name) { System.out.println(string + "老师, 您好,非常感谢您教我们这个方法!"); } } } beans.xml文件:
小李
小王
张三
王五
Student.java和Test.java文件和上面的一样。
打印结果:
2)set的注入
主要是beans.xml中的配置,其余的和上面的一样。
小李
小王
张三
王五
小李
打印结果:
3)map的注入
Teacher.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
import java.util.Map;
public class Teacher {
private Map name;
public Map getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(Map name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void teaching() {
System.out.println(name.get("one") + "老师, 您好,非常感谢您教我们这个方法!");
}
}
beans.xml文件:
Student.java和Test.java文件和上面使用的一样,没有变。
打印结果:
注意:在teacher.java文件中name.get("one")中的one,就是beans.xml文件中的one。
4)Properties的注入
Teacher.java文件:
package com.liwei.test;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Teacher {
private Properties name;
public Properties getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(Properties name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void teaching() {
System.out.println(name.get("one") + "老师, 您好,非常感谢您教我们这个方法!");
}
}
beans.xml文件:
小李
小王
张三
打印结果: