接下来学习一下ServletConfig和ServletContext的内容,简单来说ServletConfig是相对当前servlet的,ServletContext是相对整个web应用的,此外ServletContext还可以获得资源路径,下面简单整理一下。
Servlet Config
获取当前servlet对象的配置信息
Servlet Config代表当前servlet在web.xml中的配置信息对象,除了在web.xml中配置servlet的基本映射信息外,还可以配置一个或多个参数,参数和参数值可以通过Servlet config对象的api来获得,在servlet3.0中也可以在注解中配置参数,下面简单的看下。
ServletConfig对象通过getInitParameter方法可以获取参数值,通过getInitParameterNames来获取参数名。
(1)web.xml中配置参数,在servlet标签内,添加init-param标签,里面填写参数名和参数值即可。
1 2 <servlet> 3 <servlet-name>SConfigDemo01servlet-name> 4 <servlet-class>com.boe.servletconfig.SConfigDemo01servlet-class> 5 6 <init-param> 7 <param-name>nameparam-name> 8 <param-value>clyangparam-value> 9 init-param> 10 servlet> 11 <servlet-mapping> 12 <servlet-name>SConfigDemo01servlet-name> 13 <url-pattern>/SConfigDemo01url-pattern> 14 servlet-mapping>
servlet代码测试获取参数,servlet启动时,init方法只会执行一次,将web.xml中的信息加载到config对象中。如果想多次获取config对象中的参数,可以将其设置为全局变量,这样每次访问都可以得到参数值,另外下面使用init方法获取config对象。
1 package com.boe.servletconfig; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 5 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 11 /** 12 * 获取servletconfig参数 13 */ 14 //@WebServlet("/SConfigDemo01") 15 public class SConfigDemo01 extends HttpServlet { 16 17 //设置全部变量,其他方法也可以使用config 18 ServletConfig config; 19 20 /** 21 * servlet启动时,会加载web.xml信息到ServletConfig config对象,只在第一次访问时加载一次web.xml 22 * @param config 23 * @throws ServletException 24 */ 25 @Override 26 public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { 27 //重写init方法 28 //super.init(config); 29 //获取web.xml中的参数,只能获取一次 30 String parameter = config.getInitParameter("name"); 31 System.out.println("name="+parameter); 32 //初始化方法中,将config初始化 33 this.config=config; 34 } 35 36 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 37 //测试多次获取参数,OK 38 String parameter = config.getInitParameter("name"); 39 System.out.println("name="+parameter); 40 } 41 42 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 43 doPost(request, response); 44 } 45 }
多次访问后,可以重复得到结果。
(2) 在servlet3.0中也可以在注解中添加参数,即使用@WebServlet( initParams={@WebInitParam(name="参数名",value="参数值")})来添加,下面使用注解的方式测试获取参数,另外config对象可以使用this.getServletConfig方法获得,config对象本来就是给当前servlet服务的,通过它可以获取它身上的config对象。
1 package com.boe.servletconfig; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 5 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 6 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebInitParam; 7 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 9 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 10 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 11 import java.io.IOException; 12 import java.util.Enumeration; 13 //注解配置初始化参数的方式,使用initParams 14 @WebServlet(value="/SConfigDemo02",initParams = {@WebInitParam(name="name",value = "张飞")}) 15 public class SConfigDemo02 extends HttpServlet { 16 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 17 //也可以直接使用它来获取config 18 ServletConfig config = this.getServletConfig(); 19 //可以多次获取web.xml中的参数 20 String name = config.getInitParameter("name"); 21 System.out.println("name="+name); 22 //获取参数名 23 EnumerationparameterNames = config.getInitParameterNames(); 24 while(parameterNames.hasMoreElements()){ 25 String s = parameterNames.nextElement(); 26 System.out.println("初始化参数名为:"+s); 27 } 28 29 //获取全局配置信息 30 ServletContext context = config.getServletContext(); 31 String driver = context.getInitParameter("driver"); 32 System.out.println("driver="+driver); 33 } 34 35 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 36 doPost(request, response); 37 } 38 }
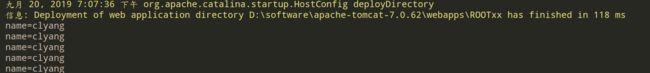
测试结果,可以看到可以正常获取config,以及它身上的参数。另外还可以获取cofig中的参数名,getInitParameterNames方法返回的是一个枚举类型。
![]()
Servlet Context
ServletContext对象可以获取全局配置信息,可以作为域对象使用,还可以获取资源路径。
获取全局配置信息
ServletContext是针对整个web应用的,它的范围是最大的,当有些信息不仅仅只局限在单个servlet内使用时,就可以将信息配置到Servlet Context中,可以在web.xml中配置,如下所示。ServletContext对象是在web应用被加载时就会被创建保存在内存中供使用,直到web应用被移除出容器或者服务器关闭它才销毁。
1 2 <context-param> 3 <param-name>driverparam-name> 4 <param-value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driverparam-value> 5 context-param>
测试servlet类,获取全局信息,有两个方法可以获取ServletContext对象,其中this.getServletContext方法底层就是调用this.getServletConfig().getServletContext()方法。
1 package com.boe.servletcontext; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 5 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 import java.util.Enumeration; 11 12 /** 13 * 获取全局配置信息 14 */ 15 @WebServlet("/SContextDemo01") 16 public class SContextDemo01 extends HttpServlet { 17 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 18 //获取servletContext对象 以下两种方法都可以 19 //ServletContext context = this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); 20 ServletContext context=this.getServletContext(); 21 22 //获取全局的配置信息 23 String driver = context.getInitParameter("driver"); 24 System.out.println("driver="+driver); 25 26 //获取参数名 27 EnumerationparameterNames = context.getInitParameterNames(); 28 while(parameterNames.hasMoreElements()){ 29 String name = parameterNames.nextElement(); 30 System.out.println("context的参数名为:"+name); 31 } 32 } 33 34 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 35 doPost(request, response); 36 } 37 }
测试结果,发现可以获取web.xml中的全局信息,另外也可以获取参数名,通过参数名可以遍历参数值。
![]()
域对象共享数据
与前面讲的ServletRequest类似,ServletContext对象也可以作为域对象使用,它也有一个可见的范围(整个web应用可见),并且通过map可以共享身上的数据,它提供的api跟其他域属性类似。下面在一个servlet中set一下域属性值,然后使用另外一个servlet获取域属性值,来测试是否可以在多个servlet之间共享数据。
保存域属性数据servlet
1 package com.boe.servletcontext; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 5 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 11 /** 12 * 当前web应用,作为域对象使用 13 */ 14 @WebServlet("/SContextDemo02") 15 public class SContextDemo02 extends HttpServlet { 16 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 17 //1 获取servletContext对象 18 ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); 19 //2 通过它共享数据,设置域属性,demo03中去获取 20 context.setAttribute("name","关羽"); 21 } 22 23 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 24 doPost(request, response); 25 } 26 }
获取域属性数据servlet
1 package com.boe.servletcontext; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 5 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 11 /** 12 * 从servletcontext域中取出域属性 13 */ 14 @WebServlet("/SContextDemo03") 15 public class SContextDemo03 extends HttpServlet { 16 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 17 //创建servletcontext对象 18 ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); 19 //获取域属性 20 String name = (String) context.getAttribute("name"); 21 System.out.println("获取域属性name="+name); 22 } 23 24 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 25 doPost(request, response); 26 } 27 }
测试先访问第一个servlet,然后访问第二个servlet,查看控制台是否输出,发现可以正常输出域属性。
![]()
获取资源路径
ServletContext可以用在获取资源路径名,这样可以实现动态获取路径名的效果,就算项目路径改了依然可以获取到想要的资源路径,参考如下代码,通过若干种方式尝试获取放置在工程src目录下的conf.properties文件目录。
1 package com.boe.servletcontext; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 5 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 9 import java.io.File; 10 import java.io.IOException; 11 12 /** 13 * servletContext获取资源路径 14 */ 15 @WebServlet("/SContextDemo04") 16 public class SContextDemo04 extends HttpServlet { 17 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 18 //相对路径 19 /*String path="conf.properties"; 20 File file=new File(path); 21 String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); 22 //这种使用相对路径获取文件,再获取绝对路径的方式不对 23 System.out.println("路径为:"+absolutePath);//路径为:D:\software\apache-tomcat-7.0.62\bin\conf.properties*/ 24 25 //绝对路径 26 /*String path="/conf.properties"; 27 File file=new File(path); 28 String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); 29 //这种使用绝对路径获取文件,再获取绝对路径的方式不对 30 System.out.println("路径为:"+absolutePath);//路径为:D:\conf.properties*/ 31 32 //静态全路径 33 /*String path="D:\\software\\apache-tomcat-7.0.62\\webapps\\day11-servletConfigContext\\WEB-INF\\classes\\conf.properties"; 34 File file=new File(path); 35 String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); 36 //这种使用静态写死路径获取文件,再获取绝对路径的方式对,但是维护不方便 37 System.out.println("路径为:"+absolutePath);//路径为:D:\conf.properties*/ 38 39 //使用servletContext 40 /*ServletContext context = this.getServletContext(); 41 //这个方法会动态在前面拼接上web应用的根目录D:\software\apache-tomcat-7.0.62\webapps\day11-servletConfigContex 42 String realPath = context.getRealPath("\\WEB-INF\\classes\\conf.properties"); 43 File file=new File(realPath); 44 String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); 45 // 46 System.out.println("路径为:"+absolutePath);*/ 47 48 //使用字节码文件获取路径 49 String realPath = SContextDemo04.class.getClassLoader().getResource("conf.properties").getPath(); 50 File file=new File(realPath); 51 String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); 52 // 53 System.out.println("路径为:"+absolutePath); 54 55 56 } 57 58 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 59 doPost(request, response); 60 } 61 }
(1)使用相对路径,会去程序启动的目录下寻找这个资源,tomcat的启动脚本在bin目录下,因此这里获得的结果就是bin目录下的结果,是不对的。
![]()
(2)使用绝对路径,会去程序启动目录的根目录下去寻找,这里tomcat在D盘,因此获得的结果就是D盘根目录下的结果,也是不对的。
![]()
(3)使用静态全路径,即将真实文件目录作为路径传入File,再输出File的路径,这样的获取资源路径的结果是对的,但是如果我将项目部署到其他的地方,或者linux中,就不是从D盘开始了,这样就需要重新改路径名非常的不方便,不可取。
![]()
(4)使用ServletContext的getRealPath方法,这方法会在传入参数路径前面动态拼接上web应用的根目录,即部署在webapp下的目录,因此就算更换了部署环境也可以动态获取到真实的路径,是推荐使用的方法。
![]()
(5)使用class文件的类加载器,这个方法也可以获取到,因为获取的资源和当前类的相对路径是确定的,更换部署环境依然可以通过两者不变的相对路径来获取到对应资源,这里注意getResource里传入的文件路径必须是相对于类加载器加载类的路径 。
![]()
实际位置:
以上是对ServletConfig和ServletContext的简单总结,后续拿来查看。