20-Joint entity and relation extraction based on a hybrid neural network(LSTM-ED+CNN),考虑长距离的实体标签之间的关
文章目录
- abstract
- 1.introduction
- 2.相关工作
- 2.1. Named entity recognition
- 2.2. Relation classification
- 2.3 联合模型
- 2.4. LSTM and CNN models On NLP
- 3.模型
- 3.1. Bidirectional LSTM encoding layer
- 3.2. Named entity recognition (NER) module:LSTM decoder
- 3.3. Relation classification (RC) module
- 3.4. Training and implementation
- 4. Experiment
- 4.1. Experimental setting
- 4.2. Results
- 5. Analysis and discussions
- 5.1. Analysis of named entity recognition module
- 5.2. Analysis of relation classification module
- 5.3. The effect of two entities’ distance
- 5.4. Error analysis
- 6. Conclusion
- 参考文献
Zheng, S., et al. (2017). “Joint entity and relation extraction based on a hybrid neural network.” Neurocomputing 257(000): 1-8.
abstract
实体和关系提取是一个结合检测实体提及和从非结构化文本识别实体的语义关系的任务。我们提出了一种混合神经网络模型来提取实体及其关系,而不需要任何手工制作的特征。混合神经网络包含用于实体提取的新型双向编码器 - 解码器L STM模块(BiL STM-ED)和用于关系分类的CNN模块。在BiLSTM-ED中获得的实体的上下文信息关键词:进一步通过CNN模块以改进关系分类。我们在公共数据集ACE05(自动内容提取程序)上进行实验神经网络,以验证我们的信息提取方法的有效性。我们提出的方法实现了实体和关系提取标记分类任务的最新结果。
- 任务:实体关系联合抽取
- 模型:
- 实体抽取:BiLSTM编码器-解码器
- 获取实体的上下文信息
- 关系分类:CNN
- 实体抽取:BiLSTM编码器-解码器
- 数据集:ACE05
1.introduction
实体和关系提取是检测实体提及并从文本中识别它们的语义关系。它是知识提取中的一个重要问题,在知识库的自动构建中起着至关重要的作用。传统系统将此任务视为两个独立任务的管道,即命名实体识别(NER)[1]和关系分类(RC)[2]。这个分离的框架使任务易于处理,每个组件都可以更灵活。但它很少关注两个子任务的相关性。联合学习框架是一种有效的方法来关联NER和RC,这也可以避免错误的级联[3]。然而,大多数现有的联合方法是基于特征的结构化系统[3-7]。它们需要复杂的特征工程,并且严重依赖于受监督的NLP工具包,这也可能导致错误传播。为了减少特征提取中的手工工作,最近,Miwa和Bansal [8]提出了一种基于神经网络的端到端实体和关系提取方法。然而,当检测到实体时,它们使用NN结构来预测实体标签,这忽略了标签之间的长关系。基于上述分析,我们提出了一种混合神经网络模型来解决这些问题,
- pipeline
- 命名实体识别
- 关系分类
- 分开处理,优点灵活,缺点没有关注两个子任务的相关性
- 联合学习框架
- 优点:避免错误的级联
- 以前:基于特征,依赖于受监督的nlp工具包,这也有错误传播
- 神经网络方法:
- Miwa和Bansal端到端的方法
- LSTM(encode)+softmax(NN-decode):实体提取
- dependency Tree LSTM:关系抽取
- NN的解码忽略了标签之间的长关系
- Miwa和Bansal端到端的方法
- LSTM-ED+CNN
- 优点:
- 联合模型:无错误传递
- 混合神经网络:不用nlp工具(依赖树)
- LSTM-decoder:可以获取标签之间的长关系依赖
- 结构
- 共享编码层:BiLSTM,获取实体的上下文信息
- 实体抽取:LSTM解码器
- decoder:也用Lstm,可以获得标签之间的长关系
- 关系分类:CNN
- 优点:
2.相关工作
- 信息抽取
- pipeline
- 命名实体识别
- 关系分类
- 分开处理,优点灵活,缺点没有关注两个子任务的相关性
- 联合学习框架
- 优点:避免错误的级联
- 以前:基于特征,依赖于受监督的nlp工具包,这也有错误传播
- 神经网络方法:
- Miwa和Bansal端到端的方法
- LSTM(encode)+softmax(NN-decode):实体提取
- dependency Tree LSTM:关系抽取
- NN的解码忽略了标签之间的长关系
- Miwa和Bansal端到端的方法
- pipeline
2.1. Named entity recognition
- 特征
- CRF[14,20] .
- HMM
- 神经网络
- 序列标注
- CNN
- Collobert et al[21]:CNN+CRF
- RNN
- Chiu and Nichols [15]:character level+word level混合特征
- decode:线性层+softmax
- BiLSTM+CRF[16,17,22]
- decode:CRF
- Miwa and Bansal [8] :
- encode:BiLSTM
- decode:NN+softmax
- Chiu and Nichols [15]:character level+word level混合特征
- CNN
- 序列标注
- decode不同
2.2. Relation classification
- 特征
- Kambhatla [23] employs Maximum Entropy model
- 结合从文本中衍生出的各种词汇,句法和语义特征
- Rink [2]设计了16种使用许多有监督的NLP工具包和资源提取的功能,包括POS,Word-Net,依赖解析等。
- 手工设计的特征不全面
- 依赖于nlp工具
- 手工特征设计需要大量工作
- Kambhatla [23] employs Maximum Entropy model
- 神经网络
- CNN
- RNN
- RecNN
- LSTM
- 其他
- 基于核的方法
- Nguyen et al. [28] :探索基于句法和语义结构的创新内核的使用
- Sun and Han [34]:提出了一种新的树内核,称为特征丰富的树内核(FTK),用于关系提取。
- 组合方法
- FCM [25]:学习了一个句子的子结构的表示。与现有的组合模型相比,FCM可以轻松处理任意类型的输入和组合的全局信息。
- 基于核的方法
2.3 联合模型
- pipeline
- 学习了一个句子的子结构的表示。与现有的组合模型相比,FCM可以轻松处理任意类型的输入和组合的全局信息。
- 联合模型
- 特征
- 基于特征的结构化系统[3,4,35-37],需要复杂的特征工程。 [35,36]提出了一个联合模型,该模型使用子任务的最佳结果并寻求全局最优解。
- Singh et al. [37]:单一图模型,它表示了子任务之间的各种依赖关系
- Li and Ji [3]:逐步预测,结构感知器,具有高效的beam搜索
- Miwa and Sasaki [4]:引入了一个表格来表示句子中的实体和关系结构,并提出了一种基于历史的波束搜索结构化学习模型。
- 神经网络:
- Miwa和Bansal [8]:LSTM+Tree-LSTM使用基于LSTM的模型来提取实体和关系,这可以减少手工工作。
- 特征
2.4. LSTM and CNN models On NLP
- CNN
- 视觉:图像特征
- 用于nlp:能够提取句子语义和关键词信息
- LSTM
- 有长期记忆
本文使用的方法基于神经网络模型:卷积神经网络(CNN)和长短期记忆(LSTM)。CNN最初是为计算机视觉而发明的[38],它总是被用来提取图像的特征[39,40]。近年来,CNN已成功应用于不同的NLP任务,并且还显示了提取感知语义和关键词信息的有效性[27,41-43]。长短期记忆(LSTM)模型是一种特定的复发性神经网络(RNN)。LSTM用带有门的内存块替换了一个重复神经网络的隐藏向量。它可以通过训练适当的门控权重来保持长期记忆[44,45]。LSTM还在许多NLP任务上展示了强大的能力,如机器翻译[46],句子表示[47]和关系提取[26]。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于联合学习实体及其关系的混合神经网络。与手工制作的基于特征的方法相比,它可以从给定的句子中学习相关的特征而无需复杂的特征工程工作。当与其他基于神经网络的方法[8]进行比较时,我们的方法考虑了实体标签之间的长距离关系。
3.模型
混合神经网络的框架如图1所示。混合神经网络的第一层是双向LSTM编码层,由命名实体识别(NER)模块和关系分类(RC)模块共享。在编码层之后有两个“通道”,一个链接到NER模块,它是LSTM解码层,另一个链接到CNN层以提取关系。在以下部分中,我们将详细描述这些组件。
- LSTM-ED+CNN
- 优点:
- 联合模型:无错误传递
- 混合神经网络:不用nlp工具(依赖树)
- LSTM-decoder:可以获取标签之间的长关系依赖
- 结构
- 共享编码层:BiLSTM,获取实体的上下文信息
- 实体抽取:LSTM解码器
- decoder:也用Lstm,可以获得标签之间的长关系
- 关系分类:CNN
- 优点:
3.1. Bidirectional LSTM encoding layer
- BiLSTM encoder
- 字嵌入层
- 平行的层
- 前向lstm层 h → \stackrel{\rightarrow}{h} h→
- 考虑前文(1-t)和wt
- 后向lstm层 h ← \stackrel{\leftarrow}{h} h←
- 前向lstm层 h → \stackrel{\rightarrow}{h} h→
- 连接层: h = [ h → ; h ← ] h=[\stackrel{\rightarrow}{h};\stackrel{\leftarrow}{h}] h=[h→;h←]
- LSTM的公式
- i t = δ ( W x i x t + W h i h t − 1 + W c i c t − 1 + b i ) f t = δ ( W x f x t + W h f h t − 1 + W c f c t − 1 + b f ) z t = t a n h ( W x c x t + W h c h t − 1 + b c ) c t = f t c t − 1 + i t z t o t = δ ( W x o x t + W h o h t − 1 + W c o c t + b o ) h t = o t t a n h ( c t ) i_t=\delta(W_{xi}x_t+W_{hi}h_{t-1}+W_{ci}c_{t-1}+b_i)\\ f_t=\delta(W_{xf}x_t+W_{hf}h_{t-1}+W_{cf}c_{t-1}+b_f)\\ z_t=tanh(W_{xc}x_t+W_{hc}h_{t-1}+b_c)\\ c_t=f_tc_{t-1}+i_tz_t\\ o_t=\delta(W_{xo}x_t+W_{ho}h_{t-1}+W_{co}c_t+b_o)\\ h_t=o_ttanh(c_t) it=δ(Wxixt+Whiht−1+Wcict−1+bi)ft=δ(Wxfxt+Whfht−1+Wcfct−1+bf)zt=tanh(Wxcxt+Whcht−1+bc)ct=ftct−1+itztot=δ(Wxoxt+Whoht−1+Wcoct+bo)ht=ottanh(ct)
3.2. Named entity recognition (NER) module:LSTM decoder
- NER:LSTM decoder
- 输入:
- BiLSTM encoder: h t h_t ht
- 先前预测的标签: T t − 1 T_{t-1} Tt−1
- decoder的前隐藏状态: s t − 1 s_{t-1} st−1
- LSTM
- LSTM的公式
- i t = δ ( W x i h t + W h i s t − 1 + W t i T t − 1 + b i ) < − − − 这 个 变 了 f t = δ ( W x f x t + W h f s t − 1 + W c f c t − 1 + b f ) z t = t a n h ( W x c x t + W h c s t − 1 + b c ) c t = f t c t − 1 + i t z t o t = δ ( W x o x t + W h o h t − 1 + W c o c t + b o ) s t = o t t a n h ( c t ) i_t=\delta(W_{xi}h_t+W_{hi}s_{t-1}+W_{ti}T_{t-1}+b_i)<---这个变了\\ f_t=\delta(W_{xf}x_t+W_{hf}s_{t-1}+W_{cf}c_{t-1}+b_f)\\ z_t=tanh(W_{xc}x_t+W_{hc}s_{t-1}+b_c)\\ c_t=f_tc_{t-1}+i_tz_t\\ o_t=\delta(W_{xo}x_t+W_{ho}h_{t-1}+W_{co}c_t+b_o)\\ s_t=o_ttanh(c_t) it=δ(Wxiht+Whist−1+WtiTt−1+bi)<−−−这个变了ft=δ(Wxfxt+Whfst−1+Wcfct−1+bf)zt=tanh(Wxcxt+Whcst−1+bc)ct=ftct−1+itztot=δ(Wxoxt+Whoht−1+Wcoct+bo)st=ottanh(ct)
- 转换 T t = W t s s t + b t s T_t=W_{ts}s_t+b_{ts} Tt=Wtsst+bts
- softmax:
- y t = W y T t + b y y_t=W_yT_t+b_y yt=WyTt+by
- p t i = e x p ( y t i ) Σ j = 1 n t e x p ( y t j ) p_t^i=\frac{exp(y_t^i)}{\Sigma_{j=1}^{nt}exp(y_t^j)} pti=Σj=1ntexp(ytj)exp(yti)
- LSTM的公式
- 因为T类似于tag embedding,而LSTM可以学习长期依赖–>类似于标签交互
- 输入:
3.3. Relation classification (RC) module
- CNN
- 输入:LSTM编码出来的,实体的隐层表示h和实体之间的单词的嵌入表示q
- CNN: R = C N N ( [ h e 1 , w e 1 , w e 1 + 1 . . . w e 2 , h e 2 ] ) R=CNN([h_{e1},w_{e1},w_{e1+1}...w_{e2},h_{e2}]) R=CNN([he1,we1,we1+1...we2,he2])
- s = [ h e 1 , w e 1 , w e 1 + 1 . . . w e 2 , h e 2 ] 卷 积 : z l ( i ) = σ ( W c ( i ) × s l : l + k − 1 + b r ( i ) ) , f i l t e r s 的 尺 寸 ( k , d ) , i − − 第 i 个 f i l t e r s 结 果 : z ( i ) = [ z 1 ( i ) , . . . , z l − k + 1 ( i ) ] m a x − p o o l i n g : z m a x ( i ) = m a x { z ( i ) } = m a x { z 1 ( i ) , . . . , z l − k + 1 ( i ) } s=[h_{e1},w_{e1},w_{e1+1}...w_{e2},h_{e2}]\\ 卷积:z_l^{(i)}=\sigma(W_c^{(i)}\times s_{l:l+k-1}+br^{(i)}),filters的尺寸(k,d),i--第i个filters\\ 结果:z^{(i)}=[z^{(i)}_1,...,z^{(i)}_{l-k+1}]\\ max-pooling:z_{max}^{(i)}=max\{z^{(i)}\}=max\{z^{(i)}_1,...,z^{(i)}_{l-k+1}\} s=[he1,we1,we1+1...we2,he2]卷积:zl(i)=σ(Wc(i)×sl:l+k−1+br(i)),filters的尺寸(k,d),i−−第i个filters结果:z(i)=[z1(i),...,zl−k+1(i)]max−pooling:zmax(i)=max{z(i)}=max{z1(i),...,zl−k+1(i)}–把句子长度所在的维度pool了,获取最显著特征
- 结合多个卷积核(softmax+dropout)
- R s = [ z m a x ( 1 ) , . . . , z m a x ( n r ) ] R_s=[z_{max}^{(1)},...,z_{max}^{(nr)}] Rs=[zmax(1),...,zmax(nr)]
- y r = W R ⋅ ( R s ∘ r ) + b R − − ∘ 是 元 素 级 乘 法 y_r=W_R\cdot (R_s\circ r)+b_R--\circ是元素级乘法 yr=WR⋅(Rs∘r)+bR−−∘是元素级乘法
- p r i = e x p ( y r i ) Σ j = 1 n c e x p ( y r j ) p_r^i=\frac{exp(y_r^i)}{\Sigma_{j=1}^{nc}exp(y_r^j)} pri=Σj=1ncexp(yrj)exp(yri)
- !!: 实体内有多个单词:隐层表示(h)相加以表示实体向量
3.4. Training and implementation
- 目标函数:最大化似然函数
- ner: L n e r = m a x Σ j = 1 ∣ D ∣ Σ t = 1 L j l o g ( p t ( j ) = y t ( j ) ∣ x j , Θ n e r ) L_{ner}=max\Sigma_{j=1}^{|D|}\Sigma_{t=1}^{L_j}log(p_t^{(j)}=y_t^{(j)}|x_j,\Theta_{ner}) Lner=maxΣj=1∣D∣Σt=1Ljlog(pt(j)=yt(j)∣xj,Θner)
- RC: L r c = m a x Σ j = 1 ∣ D ∣ l o g ( p r ( j ) = y r ( j ) ∣ x j , Θ r c ) L_{rc}=max\Sigma_{j=1}^{|D|}log(p_r^{(j)}=y_r^{(j)}|x_j,\Theta_{rc}) Lrc=maxΣj=1∣D∣log(pr(j)=yr(j)∣xj,Θrc)
- 先训练ner,再训练RC
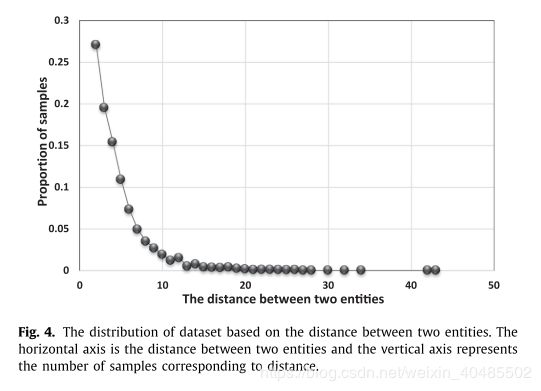
- 如果两个实体的距离> L m a x L_{max} Lmax,则不可能存在关系如图4
- 优化方法:Hinton在[52]中提出的RMSprop
我们首先训练NER模块识别实体并获得实体的编码信息,然后进一步训练RC模块根据编码信息和实体组合对关系进行分类。特别地,我们发现如果两个实体之间存在关系,则两个实体的距离总是小于约20个字,如图4所示。因此,在确定两个实体之间的关系时,我们也充分利用了这个属性,即如果两个实体的距离大于L max,我们认为它们之间不存在关系。基于图4的统计结果,ACE05数据集中的L max约为20。
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental setting
- 数据集
- ACE05
- 考虑关系的方向
- ACE05
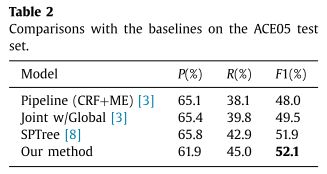
- baseline
- a classical pipeline model [3] :CRF+最大熵模型
- a joint feature-based model called Joint w/Global [3] ,
- 联合w / Global [3]使用单个模型逐步提取实体提及及其关系。他们开发了许多新的有效的全局功能作为软约束,以捕获实体提及和关系之间的相互依赖性。
- an end-to-end NN-based model SPTree [8] .M. Miwa , M. Bansal ,2016
- 通过使用双向顺序和双向树状结构LSTM-RNN来表示单词序列和依存关系树结构。
- 评估
- Precision §, Recall ® and F- Measure (F1)
- 正确:h,r,t均对
- 超参数
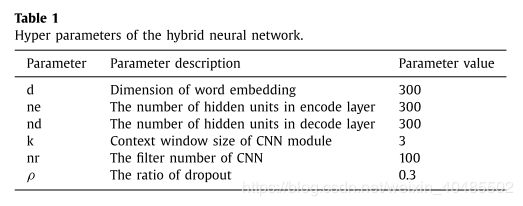
4.2. Results
- 本文模型有效:效果最好
- 神经网络模型和联合模型是可行的
- 联合模型好于pipeline
- 神经网络模型好于基于特征的模型
- 精度差不多,区别集中于recall,本文模型平衡了精度和recall
5. Analysis and discussions
5.1. Analysis of named entity recognition module
NER模块包含双向LSTM编码层和LSTM解码层。我们使用BiLSTM-ED来表示NER模块的结构。为了进一步说明BiLSTM-ED对实体提取任务的有效性,我们将BiLSTM-ED与其不同的变异和其他有效的序列标记模型进行了比较。对比方法是:
- NER:BiLSTM-ED
- 对比
- Forward-LSTM:使用单向LSTM对从w 1到w n的输入语句进行编码,然后还应用LSTM结构对实体标签进行解码。
- Backward-LSTM :具有与Forward-LSTM类似的方式,不同之处在于从w n到w 1的编码顺序。
- BiLSTM-NN:使用双向LSTM编码输入语句,并使用前馈神经网络(NN)体系结构预测实体标签。它忽略了标签之间的关系。
- BiLSTM-NN-2 [8]Miwa:使用双向LSTM编码输入句子,并通过考虑相邻标签信息而不是标签之间的长距离关系使用新颖的前馈神经网络(NN)。
- CRF [53]:是经典且有效的序列标记模型。在本节中,我们使用CRF作为强大的比较方法之一,并且CRF中使用的功能与所使用的[3]相同。
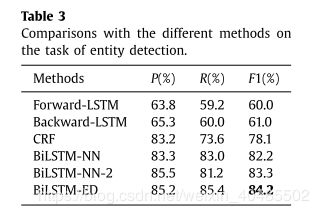
- 结论:
- 考虑其他标签信息好于不考虑
- BiLSTM-NN-2>BiLSTM-NN
- 考虑长距离标签信息比仅考虑相邻标签信息好
- BiLSTM-ED>BiLSTM-NN-2
- 考虑其他标签信息好于不考虑
5.2. Analysis of relation classification module
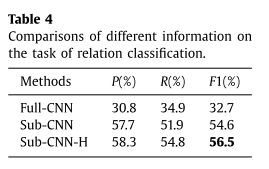
在关系分类模块中,我们使用两种信息:实体之间的子句和从双向LSTM层获得的实体的编码信息。为了说明我们考虑过的这些信息的有效性,
- RC
- 信息有效性:
- 实体间子句
- 实体编码信息(LSTM)
- 信息有效性:
- 实验
- pipeline:我们首先使用NER模块检测句子中的实体,然后使用步骤1的正确实体识别结果来测试RC模块。
- Full-CNN使用整个句子来识别实体的关系。
- sub-CNN仅使用两个实体之间的子句。
- Sub-CNN-H:子句+实体编码信息
- 结果
5.3. The effect of two entities’ distance
从图4中,我们知道当水平轴是两个实体之间的距离时,数据分布显示长尾属性。因此,我们设置阈值L max来过滤数据。如果两个实体的距离大于L max,我们认为这两个实体没有任何关系。为了分析阈值L max的影响,我们使用Sub-CNN来基于不同的L max值来预测实体关系。效果如图5所示.L max越小,过滤的数据越多。因此,如果L max太小,它可能会过滤正确的数据并使F 1结果下降。如果L max太大,则无法过滤噪声数据,这也可能损害最终结果。图5显示当L max在10和25之间时,它可以表现良好。该范围也与图4的统计结果相匹配。
- Lmax用以过滤数据
- 因为长尾性
- 结果与统计相符合
5.4. Error analysis
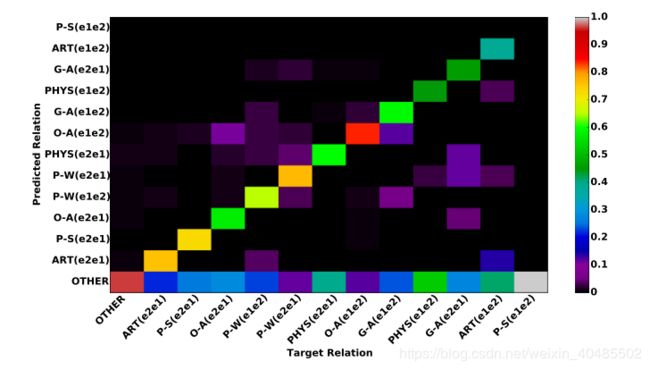
- 对角线:正确结果
- 其他:错误结果
- 结果显示:
- 除了“P-S”.其他表现良好
- 原因:
- 测试集中“P-S”少,因此“P-S”无法反应真实分布.
- “person-social”.多是代词,难以判别
- 原因:
- 大多数被预测为了Other(忽略了某些关系)
- 我们还可以看到预测关系的分布相对分散在“OTHER”的第一行,这意味着大多数特定关系类可以被预测为“OTHER”。
- 也就是说,我们无法识别某些关系,直接导致相对较低的召回率。
- 从“OTHER”的第一列,我们可以看到,如果两个实体之间没有关系,那么模型就可以被有效地区分开来。
- 具有相反方向的相同关系类型易于混淆
- 例如:P-W(e2e1)和P-W(e1e2),ART(e1e1)和ART(e2e1),O-A(e1e1)和O-A(e2e1)。
- 原因是相同的关系类型总是具有类似的描述,即使它们不在同一方向上。
- 除了“P-S”.其他表现良好
6. Conclusion
实体和关系抽取是知识提取中的一个重要问题,在知识库的自动构建中起着至关重要的作用。在本文中,我们提出了一种混合神经网络模型来提取实体及其语义关系,而不需要任何手工制作的特征。当与其他基于神经网络的方法进行比较时,我们的方法考虑了实体标签之间的长距离关系。为了说明我们的方法的有效性,我们在公共数据集ACE05(自动内容提取程序)上进行了实验。公共数据集ACE05的实验结果验证了我们方法的有效性。在未来,我们将探索如何基于神经网络更好地链接这两个模块,以便它可以更好地执行。此外,我们还需要解决忽视某些关系的问题,并试图提升召回价值。
参考文献
[1] D. Nadeau , S. Sekine , A survey of named entity recognition and classification, Lingvisticae Investigationes 30 (1) (2007) 3–26 .
[2] B. Rink , Utd: classifying semantic relations by combining lexical and semantic resources, in: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, 2010, pp. 256–259 .
[3] Q. Li , H. Ji , Incremental joint extraction of entity mentions and relations., in: Proceedings of the 52rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014, pp. 402–412 .
[4] M. Miwa , Y. Sasaki , Modeling joint entity and relation extraction with table representation., in: Proceedings of Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2014, pp. 1858–1869 .
[5] Y.S. Chan , D. Roth , Exploiting syntactico-semantic structures for relation extraction, in: Proceedings of the 49rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2011, pp. 551–560 .
[6] X. Yu , W. Lam , Jointly identifying entities and extracting relations in encyclopedia text via a graphical model approach, in: Proceedings of the 21th COLING International Conference, 2010, pp. 1399–1407 .
[7] L. Li , J. Zhang , L. Jin , R. Guo , D. Huang , A distributed meta-learning system for chinese entity relation extraction, Neurocomputing 149 (2015) 1135–1142 .
[8] M. Miwa , M. Bansal , End-to-end relation extraction using lstms on sequences and tree structures, in: Proceedings of the 54rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016 .
[9] C.N. dos Santos , B. Xiang , B. Zhou , Classifying relations by ranking with convolutional neural networks, in: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, vol. 1, 2015, pp. 626–634 .
[10] Y. Xu , L. Mou , G. Li , Y. Chen , H. Peng , Z. Jin , Classifying relations via long short term memory networks along shortest dependency paths, in: Proceedings of Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2015 .
[11] L. Zou , R. Huang , H. Wang , J.X. Yu , W. He , D. Zhao , Natural language question answering over RDF: a graph data driven approach, in: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data, ACM, 2014, pp. 313–324 .
[12] J. Sang , C. Xu , J. Liu , User-aware image tag refinement via ternary semantic analysis, IEEE Trans. Multimed. 14 (3) (2012) 883–895 .
[13] J. Sang , C. Xu , Right buddy makes the difference: An early exploration of social relation analysis in multimedia applications, in: Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, ACM, 2012, pp. 19–28 .
[14] G. Luo , X. Huang , C.-Y. Lin , Z. Nie , Joint entity recognition and disambiguation, in: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2015, pp. 879–888 .
[m5G; March 8, 2017;1:24 ] 7
[15] J.P. Chiu, E. Nichols, Named entity recognition with bidirectional lstm-cnns, arXiv: 1511.08308 (2015).
[16] Z. Huang, W. Xu, K. Yu, Bidirectional lstm-crf models for sequence tagging, arXiv: 1508.01991 (2015).
[17] G. Lample , M. Ballesteros , S. Subramanian , K. Kawakami , C. Dyer , Neural architectures for named entity recognition, in: Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016 .
[18] K. Xu Y. Feng, S. Huang, D. Zhao, Semantic relation classification via convolutional neural networks with simple negative sampling, arXiv: 1506.07650 (2015).
[19] D. Zeng , K. Liu , G. Zhou , J. Zhao , Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network, in: Proceedings of the 25th COLING International Conference, 2014, pp. 2335–2344 .
[20] A. Passos , V. Kumar , A. McCallum , Lexicon infused phrase embeddings for named entity resolution, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 2014, pp. 78–86 .
[21] R. Collobert , J. Weston , L. Bottou , M. Karlen , K. Kavukcuoglu , P. Kuksa , Natural language processing (almost) from scratch, J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12 (2011) 2493–2537 .
[22] X. Ma, E. Hovy, End-to-end sequence labeling via bi-directional lstm-cnns-crf, arXiv: 1603.01354 (2016).
[23] N. Kambhatla , Combining lexical, syntactic, and semantic features with maximum entropy models for extracting relations, in: Proceedings of the 43th ACL International Conference, 2004, p. 22 .
[24] R. Socher , B. Huval , C.D. Manning , A.Y. Nq , Semantic compositionality through recursive matrix-vector spaces, in: Proceedings of the EMNLP International Conference, 2012, pp. 1201–1211 .
[25] M. Yu , M. Gormleyl , M. Dredze , Factor-based compositional embedding models, in: Proceedings of the NIPS Workshop on Learning Semantics, 2014 .
[26] X. Yan , L. Moul , G. Li , Y. Chen , H. Peng , Z. Jin , Classifying relations via long short term memory networks along shortest dependency paths, in: Proceedings of EMNLP International Conference, 2015 .
[27] C.N. dos Santos , B. Xiangl , B. Zhou , Classifying relations by ranking with convolutional neural networks, in: Proceedings of the 53th ACL International Conference, vol. 1, 2015, pp. 626–634 .
[28] T.-V.T. Nguyen , A. Moschittil , G. Riccardi , Convolution kernels on constituent, dependency and sequential structures for relation extraction, in: Proceedings of the EMNLP International Conference, 2009, pp. 1378–1387 .
[29] P. Qin , W. Xu , J. Guo , An empirical convolutional neural network approach for semantic relation classification, Neurocomputing 190 (2016) 1–9 .
[30] S. Zheng , J. Xu , P. Zhou , H. Bao , Z. Qi , B. Xu , A neural network framework for relation extraction: Learning entity semantic and relation pattern, Knowl. Based Syst. 114 (2016) 12–23 .
[31] D. Zhang D. Wang, Relation classification via recurrent neural network, arXiv: 1508.01006 (2015).
[32] J. Ebrahimi , D. Dou ,Chain based RNN for relation classification, in: Proceedings of the NAACL International Conference, 2015, pp. 1244–1249 .
[33] S. Zhang , D. Zheng , X. Hu , M. Yang , Bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification, in: Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, 2015, pp. 73–78 .
[34] L. Sun , X. Han , A feature-enriched tree kernel for relation extraction, in: Proceedings of the 52th ACL International Conference, 2014, pp. pages 61– 67 .
[35] D. Roth , W.-t. Yih , Global inference for entity and relation identification via a linear programming formulation, in: Introduction to Statistical Relational Learning, 2007, pp. 553–580 .
[36] B. Yang , C. Cardie , Joint inference for fine-grained opinion extraction., in: Proceedings of the 51rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2013, pp. 1640–1649 .
[37] S. Singh , S. Riedel , B. Martin , J. Zheng , A. McCallum ,Joint inference of entities, relations, and coreference, in: Proceedings of the 2013 Workshop on Automated Knowledge Base Construction, ACM, 2013, pp. 1–6 .
[38] Y. LeCun , L. Bottou , Y. Bengio , P. Haffner , Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition, Proc. IEEE 86 (11) (1998) 2278–2324 .
[39] J. Yu, X. Yang, F. Gao, D. Tao, Deep multimodal distance metric learning using click constraints for image ranking, IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2016), doi: 10.1109/ TCYB.2016.2591583 .
[40] J. Yu , B. Zhang , Z. Kuang , D. Lin , J. Fan , Image privacy protection by identifying sensitive objects via deep multi-task learning, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016 .
[41] Y. Kim , Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification, in: Proceedings of the EMNLP International Conference, 2014 .
[42] N. Kalchbrenner , E. Grefenstette , P. Blunsom ,A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences, in: Proceedings of the 52th ACL International Conference, 2014 .
[43] P. Wang , B. Xu , J. Xu , G. Tian , C.-L. Liu , H. Hao , Semantic expansion using word embedding clustering and convolutional neural network for improving short text classification, Neurocomputing 174 (2016) 806–814 .
[44] X. Zhu , P. Sobihani , H. Guo , Long short-term memory over recursive structures, in: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-15), 2015, pp. 1604–1612 .
[45] A. Graves , Supervised Sequence Labelling, Springer, 2012 . [46] M.-T. Luong , I. Sutskever , Q.V. Le , O. Vinyals , W. Zaremba , Addressing the rare word problem in neural machine translation, in: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, 2015, pp. 11–19 .
[47] R. Kiros , Y. Zhu , R.R. Salakhutdinov , R. Zemel , R. Urtasun , A. Torralba , S. Fidler , Skip-thought vectors, in: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, pp. 3276–3284 .
[48] L. Ratinov , D. Roth , Design challenges and misconceptions in named entity recognition, in: Proceedings of the Thirteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Association for Computational Linguistics, 2009, pp. 147–155 .
[49] N. Kalchbrenner , E. Grefenstette , P. Blunsom ,A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences, in: Proceedings of Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2014 .
[50] K. Duan , S.S. Keerthi , W. Chu , S.K. Shevade , A.N. Poo , Multi-category classification by soft-max combination of binary classifiers, in: Multiple Classifier Systems, Springer, 2003, pp. 125–134 .
[51] G.E. Dahl , T.N. Sainath , G.E. Hinton , Improving deep neural networks for LVCSR using rectified linear units and dropout, in: Proceedings of the ICASSP, 2013, pp. 8609–8613 .
[52] T. Tieleman , G. Hinton , Lecture 6.5-rmsprop, COURSERA: Neural networks for machine learning (2012) .
[53] J. Lafferty , A. McCallum , F. Pereira , Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data, in: Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML, vol. 1, 2001, pp. 282–289 .
[54] S.J. Phillips , R.P. Anderson , R.E. Schapire , Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions, Ecol. Modell. 190 (3) (2006) 231–259 .