ArcEngine使用Geoprocessor接口实现工具箱中的方法(以线要素平滑为例)(20190822)
1、前言
接触AE开发也有一段时间了,现在基本的操作也算是熟悉了,既然作为ArcGIS的二次开发,理论上在ArcGIS中能实现的操作用AE都可以实现,尤其是ArcToolbox中的工具,功能非常丰富,在ArcEngine中用Geoprocessor接口调用工具箱即可实现工具箱中的功能,可以说是非常简单,这里以ArcGIS工具箱中“Cartography Tools–>Generalization–>Smooth Line”工具为例来演示Geoprocessor调用工具箱的方法。
2、思路
这里为了举一反三,就不为实现平滑线要素的目的而演示,尽量从寻找接口、确定参数、代码三个方面来说说这类操作的思路
1、确定工具:在ArcGIS中确定了方法之后,在工具右侧的说明下有该工具的帮助按钮,点进去即可看到该工具的详细说明,这里主要看输入参数的说明。

2、确定参数:在帮助说明中可以看到各个参数的数据类型,以及哪些是可选参数,那些是必须参数,实际上,有些参数并非那么严格,基本上在ArcGIS工具中能输入路径的这里就可以直接以路径作为参数,当然,刚开始接触并非一次就可以把参数给弄正确,多试几次就好了。
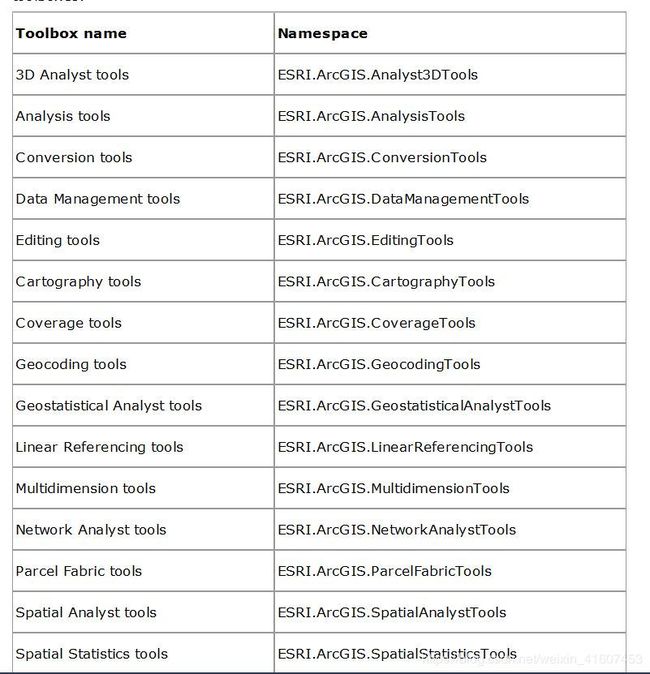
3、确定命名空间:Geoprocessor接口的命名空间是ESRI.ArcGIS.Geoprocessor,这个很好确定,这里最主要是确定工具类的命名空间。实际上,基本上ArcGIS工具箱中每一个工具箱都可以对应一个命名空间,下面的表在ArcEngine的帮助文档中可以找到,打开帮助文档搜索“Geoprocessor managed assembly”就可以查看了;
4、代码实现:上面的三个步骤基本上已经将需求实现了一大部分了,代码都很简单,而且对于每一个工具箱中的工具,可以说都是一个模板直接套进去。首先,实例化Geoprocessor接口,注意这里“P”是小写,如果是大写那就是另外一个接口了,这就是ArcEngine比较坑的地方。接着实例化相应的工具,比如在线要素平滑的需求中就是:
SmoothLine pSmoothLine = new SmoothLine(pContourFeatureClass, outPath, pAlgorithm, Tolerance);
当然,也可以后面再设置参数:
SmoothLine pSmoothLine = new SmoothLine();
pSmoothLine.(参数名)= (参数);
最后,就是执行操作了:
pGeoprocessor.Execute(pSmoothLine, null) as IGeoProcessorResult;
5、提示:有时候我们执行完操作之后报错,但是不知道哪里除了问题,那么如何实现像ArcGIS中的错误日志查看呢?可以参考下面的代码:
try
{
pGeoprocessor.Execute(pSmoothLine, null) as IGeoProcessorResult;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
object sev = null;
MessageBox.Show(pGeoprocessor.GetMessages(ref sev));
}
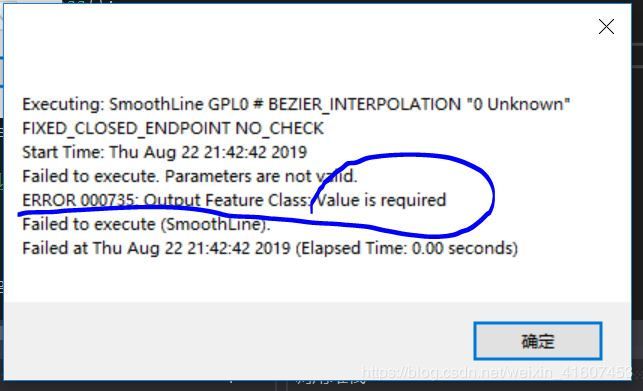
如果哪个参数有什么问题就会弹出类似下图所示的消息,根据他的消息修改输入的参数,调好参数后就可以丢掉try{}catch{}了以提升用户体验。
6、许可问题:工具箱中的工具是需要一定级别的许可的,另外还需要把拓展模块打开,在ArcEngine中这点也是通用的,那么具体怎么操作呢?在licenceControl上有点打开属性设置页,左边的产品列表从上至下权限由小变大,右边是各个产品对应的拓展模块,所以为了省事,直接勾选权限最大的和所有拓展模块。

3、界面设计
知道了需要用到的工具及参数之后界面和代码就很简单了,为了演示这一功能设计了下面的界面:

有一点注意的是我最开始写好代码,license空间和绑定都完成之后,运行程序始终在许可上报错,半天找不到原因,于是我尝试将一个MapControl拖入窗体,就不报错了,为什么,咱不知道,咱也不敢问呀!
4、关键代码
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Carto;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.CartographyTools;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.DataSourcesFile;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Geodatabase;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Geoprocessing;
using ESRI.ArcGIS.Geoprocessor;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace _190820SmoothLine
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
#region 定义变量
IFeatureClass inFeatureClass = null;//待平滑的要素类
string outPath = "";//输出的路径
#endregion
//窗体加载时初始化下拉框
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
comboBox1.SelectedIndex = 0;
comboBox2.SelectedIndex = 0;
}
//选择待平滑的线要素
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string fullPath;
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog.Filter = "shp数据(*.shp)|*.shp";
openFileDialog.Multiselect = false;
if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
fullPath = openFileDialog.FileName;
inFeatureClass = LoadFeaClassFromShp(fullPath);
textBox1.Text = fullPath;
}
}
//选择输出位置
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SaveFileDialog DialogSaveShpPath = new SaveFileDialog();
DialogSaveShpPath.Title = "保存要素类";
DialogSaveShpPath.Filter = "shp文件(*.shp) | *.shp";
DialogSaveShpPath.OverwritePrompt = false;
DialogSaveShpPath.OverwritePrompt = false;
if (DialogSaveShpPath.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
if (File.Exists(DialogSaveShpPath.FileName))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件已存在!");
return;
}
outPath = DialogSaveShpPath.FileName;
textBox2.Text = outPath;
}
}
//根据选择的算法确定输入参数控件的enable属性
private void comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//贝塞尔插值法需要输入容差参数
if (comboBox1.SelectedIndex == 0)
{
textBox3.Enabled = false;
comboBox2.Enabled = false;
}
else
{
textBox3.Enabled = true;
comboBox2.Enabled = true;
}
}
//取消
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
//确定按钮,执行平滑线操作
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//判断文本框下拉框是否为空
if (textBox1.Text.Trim() == "" || textBox2.Text.Trim() == null ||
comboBox1.Text.Trim() == "" || textBox3.Text.Trim() == "" ||
comboBox2.Text.Trim() == "")
{
MessageBox.Show("请输入正确的信息!");
return;
}
//判断输入的容差是否为
if (!Regex.IsMatch(textBox3.Text.Trim(), "^-?\\d+$|^(-?\\d+)(\\.\\d+)?$") && (Convert.ToDouble(textBox3.Text.Trim()) >= 0))
{
MessageBox.Show("容差输入错误");
return;
}
string pAlgorithm = "";
double pTolerence;
try
{
//根据选择的平滑算法来确定参数
switch (comboBox1.Text.Trim())
{
case "贝塞尔插值":
pAlgorithm = "BEZIER_INTERPOLATION";//该方法容差为0
SmoothContour(inFeatureClass, outPath, pAlgorithm, 0);
break;
case "指数核多项式逼近":
pAlgorithm = "PAEK";
pTolerence = Convert.ToDouble(textBox3.Text.Trim());
SmoothContour(inFeatureClass, outPath, pAlgorithm, pTolerence);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
catch (COMException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
return;
}
}
#region 封装方法
///
/// 加载shp的方法
///
/// shp文件的路径
/// 返回shp要素类IFeatureClass
private IFeatureClass LoadFeaClassFromShp(string fullpath)
{
IWorkspaceFactory pWorkspaceFactory = new ShapefileWorkspaceFactory();
IFeatureWorkspace pFeatureWorkspace;
int index = fullpath.LastIndexOf("\\");
string path = fullpath.Substring(0, index);
string name = fullpath.Substring(index + 1);
pFeatureWorkspace = pWorkspaceFactory.OpenFromFile(path, 0) as IFeatureWorkspace;
return pFeatureWorkspace.OpenFeatureClass(name);
}
///
/// 平滑等高线
///
/// 输入的等高线要素类
/// 输出的平滑等高线的位置
/// 平滑算法,贝塞尔算法或指数核多项式逼近法
/// 等高线平滑的容差
/// 返回输出的等高线要素类
private void SmoothContour(IFeatureClass pContourFeatureClass, string outPath, string pAlgorithm, double pTolerance)
{
Geoprocessor pGeoprocessor = new Geoprocessor();
pGeoprocessor.OverwriteOutput = false;
IFeatureLayer pFeatureLayer = new FeatureLayerClass();
pFeatureLayer.FeatureClass = pContourFeatureClass;
SmoothLine pSmoothLine = new SmoothLine(pContourFeatureClass, outPath, pAlgorithm, pTolerance);
IGeoProcessorResult pResult = pGeoprocessor.Execute(pSmoothLine, null) as IGeoProcessorResult;
//在调试的时候,针对工具箱工具用以下代码可以找到参数、环境设置等等问题
//catch (Exception ex)
//{
// object sev = null;
// MessageBox.Show(pGeoprocessor.GetMessages(ref sev));
//}
}
#endregion
}
}
5、代码下载
(1)github: https://github.com/ranhongwu/190820SmoothLine ;
(2)CSDN: https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_41607453/11595290 。