类的继承
- 102.继承
- 103.方法的重写
- 104.object根类
- 105.重写__str__()方法
- 106.多重继承
- 108.super获取父类的定义
- 109.多态
- 110.特殊方法和运算符重载
- 特殊属性
- 对象的浅拷贝和深拷贝
102.继承


class Person:
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name
self.__age = age
def say_age(self):
pass
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,score):
Person.__init__(self,name,age)
self.score = score
print(Student.mro())
s = Student("马宝林",18,80)
s.say_age()
print(s._Person__age)
print(dir(s))
print(s.name)
D:\python\python37\python.exe F:/python/mypro01/mypro07.py
[<class '__main__.Student'>, <class '__main__.Person'>, <class 'object'>]
18
['_Person__age', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'name', 'say_age', 'score']
马宝林
103.方法的重写

class Person:
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name
self.__age = age
def say_age(self):
print('我的年龄是{0}'.format(self.__age))
def say_introduction(self):
print("我的名字是:{}".format(self.name))
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,score):
Person.__init__(self,name,age)
self.score = score
def say_introduction(self):
print("报告老师,我的名字是:{}".format(self.name))
s = Student("马宝林",18,80)
s.say_age()
s.say_introduction()
D:\python\python37\python.exe F:/python/mypro01/mypro08.py
我的年龄是18
报告老师,我的名字是:马宝林
104.object根类

class A:
pass
class B(A):
pass
class C(B):
pass
print(C.mro())
print(C.__mro__)
[<class '__main__.C'>, <class '__main__.B'>, <class '__main__.A'>, <class 'object'>]
(<class '__main__.C'>, <class '__main__.B'>, <class '__main__.A'>, <class 'object'>)
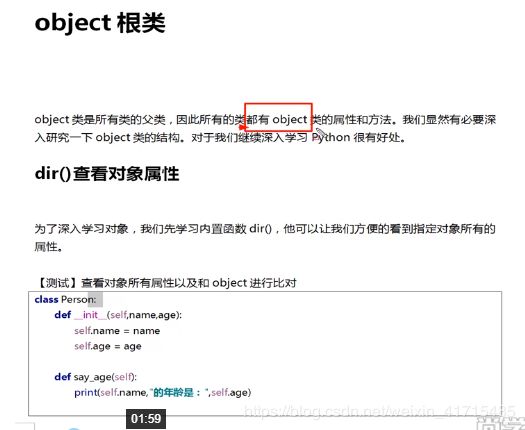
class Person:
def __init__(self,name,age,sex):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.sex = sex
def say_age(self):
print("{0}的年龄为:{1}。".format(self.name,self.age))
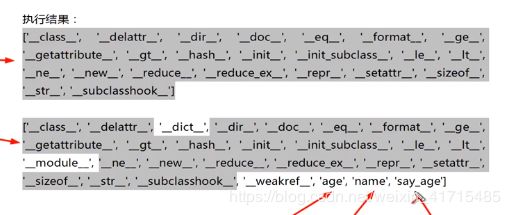
obj = object()
print(dir(obj))
s = Person("马宝林",25,"Man")
print(dir(s))
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__']
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'age', 'name', 'say_age', 'sex']

105.重写__str__()方法

class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def __str__(self):
return "此类的名字是:{}".format(self.name)
p = Person("sxt")
print(p)
106.多重继承

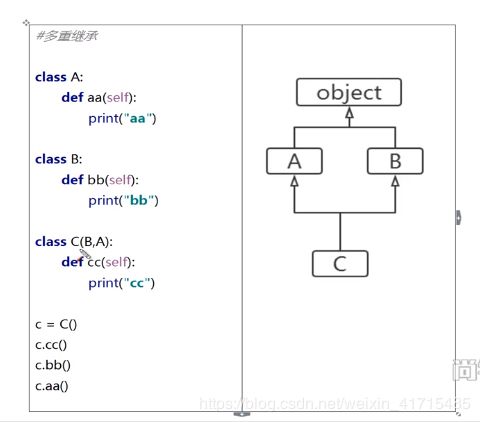
class A:
def aa(self):
print("aa")
class B:
def bb(self):
print("bb")
class C(B,A):
def cc(self):
print("cc")
c = C()
c.cc()
c.bb()
c.aa()
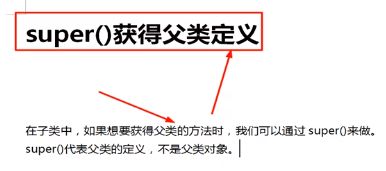
108.super获取父类的定义
class A:
def say(self):
print("A:",self)
class B(A):
def say(self):
super().say()
print("B:",self)
c = B()
c.say()
D:\python\python37\python.exe F:/python/mypro01/mypro11.py
A: <__main__.B object at 0x000001998687D668>
B: <__main__.B object at 0x000001998687D668>
109.多态

class Man:
def eat(self):
print("我饿啦!我要吃饭。")
class Chinese(Man):
def eat(self):
print("中国人用筷子吃饭。")
class English(Man):
def eat(self):
print("英国人用叉子吃饭。")
class Indian(Man):
def eat(self):
print("印度人用右手吃饭。")
def manEat(m):
if isinstance(m,Man):
m.eat()
else:
print("现在不可以吃饭。")
manEat(Chinese())
110.特殊方法和运算符重载
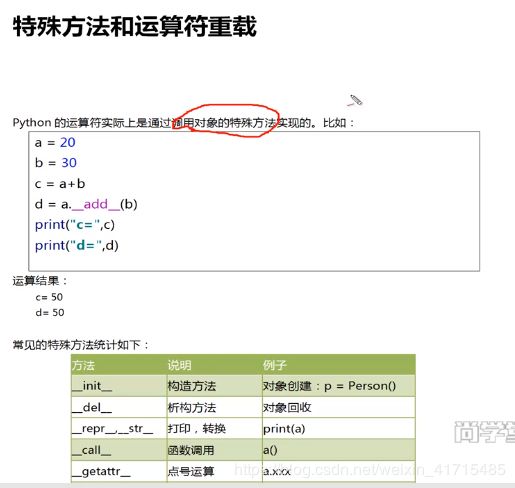
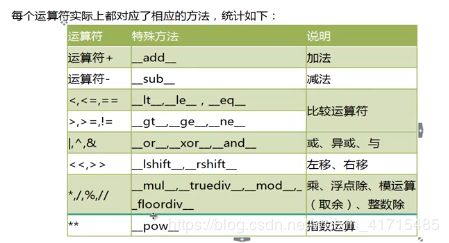
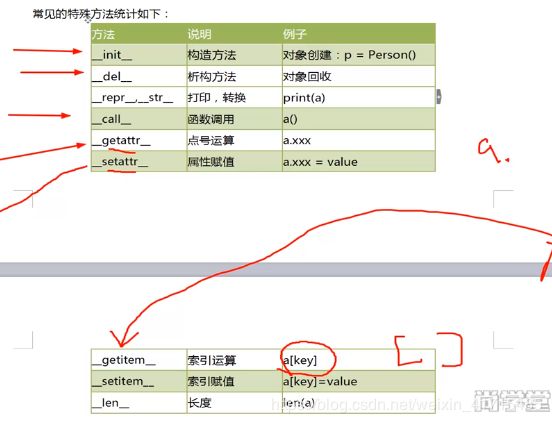
class Person:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def __add__(self,other):
if isinstance(other,Person):
return "{0}--{1}".format(self.name,other.name)
else:
print("不是同一类不可以相加。")
def __mul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other,int):
return self.name*3
p1 = Person("mabaolin")
p2 = Person("maiyulong")
x = p1+p2
print(x)
print(p1*3)
D:\python\python37\python.exe F:/python/mypro01/mypro13.py
mabaolin--maiyulong
mabaolinmabaolinmabaolin
特殊属性
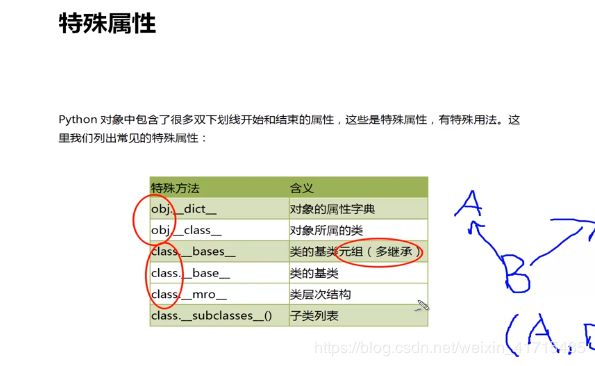
class A:
pass
class B(A):
pass
class C(B):
def __init__(self,nn):
self.nn = nn
pass
c = C(3)
print(dir(c))
print(c.__dict__)
print(c.__class__)
print(C.__bases__)
print(C.__mro__)
print(A.__subclasses__())
['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'nn']
{'nn': 3}
<class '__main__.C'>
(<class '__main__.B'>,)
(<class '__main__.C'>, <class '__main__.B'>, <class '__main__.A'>, <class 'object'>)
[<class '__main__.B'>]
对象的浅拷贝和深拷贝
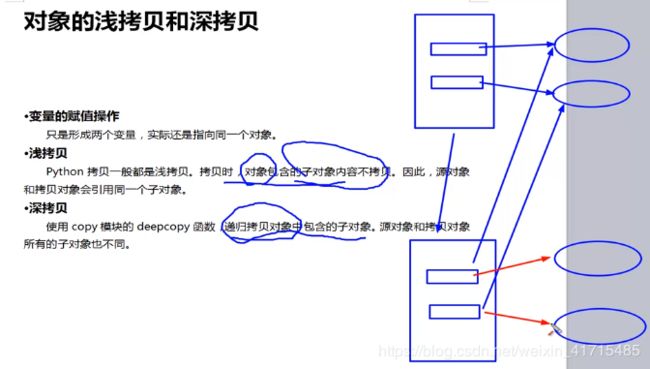
import copy
class MobilPhone:
def __init__(self,cpu,screen):
self.cpu = cpu
self.screen = screen
class CPU:
def calculate(self):
print("数字计算。")
print("cpu对象:",self)
class Screen:
def show(self):
print("显示一幅好看的画。")
print("screen对象:",self)
'''
m1 = MobilPhone()
m2 = m1
print(m1)
print(m2)
'''
c1 = CPU()
s1 = Screen()
m1 = MobilPhone(c1,s1)
m2 = copy.copy(m1)
print("测试浅拷贝")
print(m1,m1.cpu,m1.screen)
print(m2,m2.cpu,m2.screen)
m3 = copy.deepcopy(m1)
print("测试深拷贝")
print(m1,m1.cpu,m1.screen)
print(m3,m3.cpu,m3.screen)
D:\python\python37\python.exe F:/python/mypro01/mypro14.py
测试浅拷贝
<__main__.MobilPhone object at 0x000001E153B3DEF0> <__main__.CPU object at 0x000001E1538560F0> <__main__.Screen object at 0x000001E153B3DE10>
<__main__.MobilPhone object at 0x000001E153B52198> <__main__.CPU object at 0x000001E1538560F0> <__main__.Screen object at 0x000001E153B3DE10>
测试深拷贝
<__main__.MobilPhone object at 0x000001E153B3DEF0> <__main__.CPU object at 0x000001E1538560F0> <__main__.Screen object at 0x000001E153B3DE10>
<__main__.MobilPhone object at 0x000001E153B625F8> <__main__.CPU object at 0x000001E153B625C0> <__main__.Screen object at 0x000001E153B626D8>
















