基于vgg16的迁移学习,训练自己的数据集(含预测结果)
1.vggNet简介
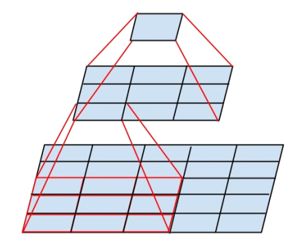
vgg16是2014年由牛津大学提出的一个深度神经网络模型,该模型在2014年的ILSVRC分类比赛中,取得了第二名的成绩,而第一名当属大名鼎鼎的googleNet,vggNet包含5种网络类型,如下图所示:
常见的有vgg16和vgg19。顾名思义vgg16有16层,包含13层卷积池化层和3层全连接层。而vgg19包含16层卷积池化层和3层全连接层。vggNet全部使用1x1,3x3的卷积核,而且vggNet证明了两个3x3的卷积核可以等效为一个5x5的卷积核,下图示
一张5x5的图经两个3x3的卷积核卷积后得到一张1x1的特征图,等效为一个5x5的卷积核。同时在参数量上可以发现,5x5的卷积核的参数量是5x5=25,两个3x3的卷积核是2x3x3=18,参数量是减少了的28%,同时由于与一个5x5的卷积核卷积只需一次非线性激活,而与两个卷积核卷积可以进行两次非线性激活变换,非线性表征加强了,增加了CNN对特征的学习能力。另外1x1卷积核能实现降维,增加非线性。
2.vgg16实现迁移学习
1.数据集准备,我使用8类数据,分别是truck,tiger,flower,kittycat,guitar,houses,plane,person,数据每类训练集500张,验证集300张
2.vgg16预训练权重下载,我把它放在我的百度网盘里了,密码fwi4
3.生成train.txt,val.txt,label.txt
create_labels_files.py
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import os
import os.path
def write_txt(content, filename, mode='w'):
"""保存txt数据
:param content:需要保存的数据,type->list
:param filename:文件名
:param mode:读写模式:'w' or 'a'
:return: void
"""
with open(filename, mode) as f:
for line in content:
str_line = ""
for col, data in enumerate(line):
if not col == len(line) - 1:
# 以空格作为分隔符
str_line = str_line + str(data) + " "
else:
# 每行最后一个数据用换行符“\n”
str_line = str_line + str(data) + "\n"
f.write(str_line)
def get_files_list(dir):
'''
实现遍历dir目录下,所有文件(包含子文件夹的文件)
:param dir:指定文件夹目录
:return:包含所有文件的列表->list
'''
# parent:父目录, filenames:该目录下所有文件夹,filenames:该目录下的文件名
files_list = []
for parent, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(dir):
for filename in filenames:
print("parent is: " + parent)
print("filename is: " + filename)
# print(os.path.join(parent, filename)) # 输出rootdir路径下所有文件(包含子文件)信息
curr_file = parent.split(os.sep)[-1]
if curr_file == 'flower':
labels = 0
elif curr_file == 'guitar':
labels = 1
elif curr_file == 'person':
labels = 2
elif curr_file == 'houses':
labels = 3
elif curr_file == 'plane':
labels = 4
elif curr_file == 'tiger':
labels = 5
elif curr_file == 'kittycat':
labels = 6
elif curr_file == 'truck':
labels = 7
files_list.append([os.path.join(curr_file, filename), labels])
print(files_list)
return files_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_dir = 'dataset/train'
train_txt = 'dataset/train.txt'
train_data = get_files_list(train_dir)
write_txt(train_data, train_txt, mode='w')
val_dir = 'dataset/val'
val_txt = 'dataset/val.txt'
val_data = get_files_list(val_dir)
write_txt(val_data, val_txt, mode='w')
4.制作tf.record文件
create_tf_record.py
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
from PIL import Image
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value]))
# 生成字符串型的属性
def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value]))
# 生成实数型的属性
def float_list_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))
def get_example_nums(tf_records_filenames):
'''
统计tf_records图像的个数(example)个数
:param tf_records_filenames: tf_records文件路径
:return:
'''
nums= 0
for record in tf.python_io.tf_record_iterator(tf_records_filenames):
nums += 1
return nums
def show_image(title,image):
'''
显示图片
:param title: 图像标题
:param image: 图像的数据
:return:
'''
# plt.figure("show_image")
# print(image.dtype)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('on') # 关掉坐标轴为 off
plt.title(title) # 图像题目
plt.show()
def load_labels_file(filename,labels_num=1,shuffle=False):
'''
载图txt文件,文件中每行为一个图片信息,且以空格隔开:图像路径 标签1 标签2,如:test_image/1.jpg 0 2
:param filename:
:param labels_num :labels个数
:param shuffle :是否打乱顺序
:return:images type->list
:return:labels type->list
'''
images=[]
labels=[]
with open(filename) as f:
lines_list=f.readlines()
if shuffle:
random.shuffle(lines_list)
for lines in lines_list:
line=lines.rstrip().split(' ')
label=[]
for i in range(labels_num):
label.append(int(line[i+1]))
images.append(line[0])
labels.append(label)
return images,labels
def read_image(filename, resize_height, resize_width,normalization=False):
'''
读取图片数据,默认返回的是uint8,[0,255]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param normalization:是否归一化到[0.,1.0]
:return: 返回的图片数据
'''
bgr_image = cv2.imread(filename)
if None is bgr_image:
pass
elif len(bgr_image.shape)==2:#若是灰度图则转为三通道
print("Warning:gray image",filename)
bgr_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
print(filename)
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#将BGR转为RGB
# show_image(filename,rgb_image)
# rgb_image=Image.open(filename)
if resize_height>0 and resize_width>0:
rgb_image=cv2.resize(rgb_image,(resize_width,resize_height))
rgb_image=np.asanyarray(rgb_image)
if normalization:
# 不能写成:rgb_image=rgb_image/255
rgb_image=rgb_image/255.0
# show_image("src resize image",image)
return rgb_image
def get_batch_images(images,labels,batch_size,labels_nums,one_hot=False,shuffle=True,num_threads=1):
'''
:param images:图像
:param labels:标签
:param batch_size:
:param labels_nums:标签个数
:param one_hot:是否将labels转为one_hot的形式
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序,一般train时shuffle=True,验证时shuffle=False
:return:返回batch的images和labels
'''
min_after_dequeue = 200
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size # 保证capacity必须大于min_after_dequeue参数值
if shuffle:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue,
num_threads=num_threads)
else:
images_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.batch([images,labels],
batch_size=batch_size,
capacity=capacity,
num_threads=num_threads)
if one_hot:
labels_batch = tf.one_hot(labels_batch, labels_nums, 1, 0)
return images_batch,labels_batch
def read_records(filename,resize_height, resize_width,type=None):
'''
解析record文件:源文件的图像数据是RGB,uint8,[0,255],一般作为训练数据时,需要归一化到[0,1]
:param filename:
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:param type:选择图像数据的返回类型
None:默认将uint8-[0,255]转为float32-[0,255]
normalization:归一化float32-[0,1]
centralization:归一化float32-[0,1],再减均值中心化
:return:
'''
# 创建文件队列,不限读取的数量
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
# create a reader from file queue
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# reader从文件队列中读入一个序列化的样本
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# get feature from serialized example
# 解析符号化的样本
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'height': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'width': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'depth': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
}
)
tf_image = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)#获得图像原始的数据
tf_height = features['height']
tf_width = features['width']
tf_depth = features['depth']
tf_label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
# PS:恢复原始图像数据,reshape的大小必须与保存之前的图像shape一致,否则出错
# tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [-1]) # 转换为行向量
tf_image=tf.reshape(tf_image, [resize_height, resize_width, 3]) # 设置图像的维度
# 恢复数据后,才可以对图像进行resize_images:输入uint->输出float32
# tf_image=tf.image.resize_images(tf_image,[224, 224])
# 存储的图像类型为uint8,tensorflow训练时数据必须是tf.float32
if type is None:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32)
elif type=='normalization':# [1]若需要归一化请使用:
# 仅当输入数据是uint8,才会归一化[0,255]
# tf_image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(tf_image, tf.float32)
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255.0) # 归一化
elif type=='centralization':
# 若需要归一化,且中心化,假设均值为0.5,请使用:
tf_image = tf.cast(tf_image, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5 #中心化
# 这里仅仅返回图像和标签
# return tf_image, tf_height,tf_width,tf_depth,tf_label
return tf_image,tf_label
def create_records(image_dir,file, output_record_dir, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log=5):
'''
实现将图像原始数据,label,长,宽等信息保存为record文件
注意:读取的图像数据默认是uint8,再转为tf的字符串型BytesList保存,解析请需要根据需要转换类型
:param image_dir:原始图像的目录
:param file:输入保存图片信息的txt文件(image_dir+file构成图片的路径)
:param output_record_dir:保存record文件的路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
PS:当resize_height或者resize_width=0是,不执行resize
:param shuffle:是否打乱顺序
:param log:log信息打印间隔
'''
# 加载文件,仅获取一个label
images_list, labels_list=load_labels_file(file,1,shuffle)
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_record_dir)
for i, [image_name, labels] in enumerate(zip(images_list, labels_list)):
image_path=os.path.join(image_dir,images_list[i])
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print('Err:no image',image_path)
continue
image = read_image(image_path, resize_height, resize_width)
image_raw = image.tostring()
if i%log==0 or i==len(images_list)-1:
print('------------processing:%d-th------------' % (i))
print('current image_path=%s' % (image_path),'shape:{}'.format(image.shape),'labels:{}'.format(labels))
# 这里仅保存一个label,多label适当增加"'label': _int64_feature(label)"项
label=labels[0]
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw),
'height': _int64_feature(image.shape[0]),
'width': _int64_feature(image.shape[1]),
'depth': _int64_feature(image.shape[2]),
'label': _int64_feature(label)
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
def disp_records(record_file,resize_height, resize_width,show_nums=4):
'''
解析record文件,并显示show_nums张图片,主要用于验证生成record文件是否成功
:param tfrecord_file: record文件路径
:return:
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image, tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
# 显示前4个图片
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(show_nums):
image,label = sess.run([tf_image,tf_label]) # 在会话中取出image和label
# image = tf_image.eval()
# 直接从record解析的image是一个向量,需要reshape显示
# image = image.reshape([height,width,depth])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(image.shape,image.dtype,label))
# pilimg = Image.fromarray(np.asarray(image_eval_reshape))
# pilimg.show()
show_image("image:%d"%(label),image)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
def batch_test(record_file,resize_height, resize_width):
'''
:param record_file: record文件路径
:param resize_height:
:param resize_width:
:return:
:PS:image_batch, label_batch一般作为网络的输入
'''
# 读取record函数
tf_image,tf_label = read_records(record_file,resize_height,resize_width,type='normalization')
image_batch, label_batch= get_batch_images(tf_image,tf_label,batch_size=4,labels_nums=5,one_hot=False,shuffle=False)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess: # 开始一个会话
sess.run(init)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(4):
# 在会话中取出images和labels
images, labels = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch])
# 这里仅显示每个batch里第一张图片
show_image("image", images[0, :, :, :])
print('shape:{},tpye:{},labels:{}'.format(images.shape,images.dtype,labels))
# 停止所有线程
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 参数设置
resize_height = 224 # 指定存储图片高度
resize_width = 224 # 指定存储图片宽度
shuffle=True
log=5
# 产生train.record文件
image_dir='dataset/train'
train_labels = 'dataset/train.txt' # 图片路径
train_record_output = 'dataset/record/train{}.tfrecords'.format(resize_height)
create_records(image_dir,train_labels, train_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
train_nums=get_example_nums(train_record_output)
print("save train example nums={}".format(train_nums))
# 产生val.record文件
image_dir='dataset/val'
val_labels = 'dataset/val.txt' # 图片路径
val_record_output = 'dataset/record/val{}.tfrecords'.format(resize_height)
create_records(image_dir,val_labels, val_record_output, resize_height, resize_width,shuffle,log)
val_nums=get_example_nums(val_record_output)
print("save val example nums={}".format(val_nums))
# 测试显示函数
# disp_records(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
batch_test(train_record_output,resize_height, resize_width)
5.训练模型
vgg16.py
#vgg16_train_and_val
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pdb
import os
from datetime import datetime
from create_tf_record import *
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
print("Tensorflow version:{}".format(tf.__version__))
labels_nums = 8 # 类别个数
batch_size = 1 #
resize_height = 224 # 指定存储图片高度
resize_width = 224 # 指定存储图片宽度
depths = 3
data_shape = [batch_size, resize_height, resize_width, depths]
# 定义input_images为图片数据
input_images = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, resize_height, resize_width, depths], name='input')
# 定义input_labels为labels数据
# input_labels = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None], name='label')
input_labels = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None, labels_nums], name='label')
# 定义dropout的概率
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='keep_prob')
is_training = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name='is_training')
def net_evaluation(sess,loss,accuracy,val_images_batch,val_labels_batch,val_nums):
val_max_steps = int(val_nums / batch_size)
val_losses = []
val_accs = []
for _ in range(val_max_steps):
val_x, val_y = sess.run([val_images_batch, val_labels_batch])
# print('labels:',val_y)
# val_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: val_x, y: val_y, keep_prob: 1.0})
# val_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x: val_x, y: val_y, keep_prob: 1.0})
val_loss,val_acc = sess.run([loss,accuracy], feed_dict={input_images: val_x, input_labels: val_y, keep_prob:1.0, is_training: False})
val_losses.append(val_loss)
val_accs.append(val_acc)
mean_loss = np.array(val_losses, dtype=np.float32).mean()
mean_acc = np.array(val_accs, dtype=np.float32).mean()
return mean_loss, mean_acc
class Vgg16:
vgg_mean = [103.939, 116.779, 123.68]
def __init__(self, vgg16_npy_path=None,input=None, restore_from=None):
# pre-trained parameters
try:
self.data_dict = np.load(vgg16_npy_path, encoding='latin1').item()
except FileNotFoundError:
print('Please download VGG16 parameters from here https://mega.nz/#!YU1FWJrA!O1ywiCS2IiOlUCtCpI6HTJOMrneN-Qdv3ywQP5poecM\nOr from my Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Spps1Wy0bvrQHH2IMkRfpg')
# self.tfx = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3])
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.tfx = input
self.tfy = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# Convert RGB to BGR
red, green, blue = tf.split(axis=3, num_or_size_splits=3, value=self.tfx * 255.0)
bgr = tf.concat(axis=3, values=[
blue - self.vgg_mean[0],
green - self.vgg_mean[1],
red - self.vgg_mean[2],
])
# pre-trained VGG layers are fixed in fine-tune
conv1_1 = self.conv_layer(bgr, "conv1_1")
conv1_2 = self.conv_layer(conv1_1, "conv1_2")
pool1 = self.max_pool(conv1_2, 'pool1')
conv2_1 = self.conv_layer(pool1, "conv2_1")
conv2_2 = self.conv_layer(conv2_1, "conv2_2")
pool2 = self.max_pool(conv2_2, 'pool2')
conv3_1 = self.conv_layer(pool2, "conv3_1")
conv3_2 = self.conv_layer(conv3_1, "conv3_2")
conv3_3 = self.conv_layer(conv3_2, "conv3_3")
pool3 = self.max_pool(conv3_3, 'pool3')
conv4_1 = self.conv_layer(pool3, "conv4_1")
conv4_2 = self.conv_layer(conv4_1, "conv4_2")
conv4_3 = self.conv_layer(conv4_2, "conv4_3")
pool4 = self.max_pool(conv4_3, 'pool4')
conv5_1 = self.conv_layer(pool4, "conv5_1")
conv5_2 = self.conv_layer(conv5_1, "conv5_2")
conv5_3 = self.conv_layer(conv5_2, "conv5_3")
pool5 = self.max_pool(conv5_3, 'pool5')
# detach original VGG fc layers and
# reconstruct your own fc layers serve for your own purpose
pool5_shape = pool5.get_shape().as_list()
nodes = pool5_shape[1] * pool5_shape[2] * pool5_shape[3]
self.flatten = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, nodes])
self.fc6 = tf.layers.dense(self.flatten, 256, tf.nn.relu, name='fc6')
self.out = tf.layers.dense(self.fc6, labels_nums, name='out')
def max_pool(self, bottom, name):
return tf.nn.max_pool(bottom, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name=name)
def conv_layer(self, bottom, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name): # CNN's filter is constant, NOT Variable that can be trained
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(bottom, self.data_dict[name][0], [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
lout = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, self.data_dict[name][1]))
return lout
def train(self, x, y):
loss, _ = self.sess.run([self.loss, self.train_op], {self.tfx: x, self.tfy: y})
return loss
def save(self, path='./model/'):
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(self.sess, path, write_meta_graph=False)
def train(train_record_file,
train_log_step,
train_param,
val_record_file,
val_log_step,
labels_nums,
data_shape,
snapshot,
snapshot_prefix):
'''
:param train_record_file: 训练的tfrecord文件
:param train_log_step: 显示训练过程log信息间隔
:param train_param: train参数
:param val_record_file: 验证的tfrecord文件
:param val_log_step: 显示验证过程log信息间隔
:param val_param: val参数
:param labels_nums: labels数
:param data_shape: 输入数据shape
:param snapshot: 保存模型间隔
:param snapshot_prefix: 保存模型文件的前缀名
:return:
'''
[base_lr,max_steps]=train_param
[batch_size,resize_height,resize_width,depths]=data_shape
# 获得训练和测试的样本数
train_nums=get_example_nums(train_record_file)
val_nums=get_example_nums(val_record_file)
print('train nums:%d,val nums:%d'%(train_nums,val_nums))
# 从record中读取图片和labels数据
# train数据,训练数据一般要求打乱顺序shuffle=True
train_images, train_labels = read_records(train_record_file, resize_height, resize_width, type='normalization')
train_images_batch, train_labels_batch = get_batch_images(train_images, train_labels,
batch_size=batch_size, labels_nums=labels_nums,
one_hot=True, shuffle=False)
# val数据,验证数据可以不需要打乱数据
val_images, val_labels = read_records(val_record_file, resize_height, resize_width, type='normalization')
val_images_batch, val_labels_batch = get_batch_images(val_images, val_labels,
batch_size=batch_size, labels_nums=labels_nums,
one_hot=True, shuffle=False)
# Define the model:
# with slim.arg_scope(inception_v3.inception_v3_arg_scope()):
# out, end_points = inception_v3.inception_v3(inputs=input_images, num_classes=labels_nums, dropout_keep_prob=keep_prob, is_training=is_training)
vgg = Vgg16(vgg16_npy_path='./vgg16.npy',input=input_images)
out = vgg.out
# Specify the loss function: tf.losses定义的loss函数都会自动添加到loss函数,不需要add_loss()了
tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(onehot_labels=input_labels, logits=out)#添加交叉熵损失loss=1.6
# slim.losses.add_loss(my_loss)
loss = tf.losses.get_total_loss(add_regularization_losses=True)#添加正则化损失loss=2.2
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(out, 1), tf.argmax(input_labels, 1)), tf.float32))
# Specify the optimization scheme:
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=base_lr)
train_op = slim.learning.create_train_op(total_loss=loss,optimizer=optimizer)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
max_acc=0.0
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(max_steps+1):
batch_input_images, batch_input_labels = sess.run([train_images_batch, train_labels_batch])
_, train_loss = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict={input_images:batch_input_images,
input_labels:batch_input_labels,
keep_prob:0.5, is_training:True})
# train测试(这里仅测试训练集的一个batch)
if i%train_log_step == 0:
train_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={input_images:batch_input_images,
input_labels: batch_input_labels,
keep_prob:1.0, is_training: False})
print("%s: Step [%d] train Loss : %f, training accuracy : %g" % (datetime.now(), i, train_loss, train_acc))
# val测试(测试全部val数据)
if i%val_log_step == 0:
mean_loss, mean_acc=net_evaluation(sess, loss, accuracy, val_images_batch, val_labels_batch,val_nums)
print("%s: Step [%d] val Loss : %f, val accuracy : %g" % (datetime.now(), i, mean_loss, mean_acc))
# 模型保存:每迭代snapshot次或者最后一次保存模型
if (i %snapshot == 0 and i >0)or i == max_steps:
print('-----save:{}-{}'.format(snapshot_prefix,i))
saver.save(sess, snapshot_prefix, global_step=i)
# 保存val准确率最高的模型
if mean_acc>max_acc and mean_acc>0.5:
max_acc=mean_acc
path = os.path.dirname(snapshot_prefix)
best_models=os.path.join(path,'best_models_{}_{:.4f}.ckpt'.format(i,max_acc))
print('------save:{}'.format(best_models))
saver.save(sess, best_models)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_record_file='dataset/record/train224.tfrecords'
val_record_file='dataset/record/val224.tfrecords'
train_log_step=100
base_lr = 0.01 # 学习率
max_steps = 200000 # 迭代次数
train_param=[base_lr,max_steps]
val_log_step=200
snapshot=2000#保存文件间隔
snapshot_prefix='./models/model.ckpt'
train(train_record_file=train_record_file,
train_log_step=train_log_step,
train_param=train_param,
val_record_file=val_record_file,
val_log_step=val_log_step,
labels_nums=labels_nums,
data_shape=data_shape,
snapshot=snapshot,
snapshot_prefix=snapshot_prefix)
3结果显示
用实验室服务器训练了20万代,在验证集上的准确率达到了90.75%。以下是预测结果:
test_images\flower1.jpg
test_images\flower1.jpg is: pre labels:[0],name:['flower'] score: [ 1.]
test_images\flower2.jpg
test_images\flower2.jpg is: pre labels:[0],name:['flower'] score: [ 1.]
test_images\kittycat.jpg
test_images\kittycat.jpg is: pre labels:[6],name:['kittycat'] score: [ 0.4819051]
test_images\kittycat2.jpg
test_images\kittycat2.jpg is: pre labels:[6],name:['kittycat'] score: [ 0.4819051]
test_images\lion.jpg
test_images\lion.jpg is: pre labels:[6],name:['kittycat'] score: [ 0.4819051]
test_images\plane.jpg
test_images\plane.jpg is: pre labels:[4],name:['plane'] score: [ 1.]
test_images\plane2.jpg
test_images\plane2.jpg is: pre labels:[1],name:['guitar'] score: [ 1.]
test_images\tiger0.jpg
test_images\tiger0.jpg is: pre labels:[5],name:['tiger'] score: [ 1.]
test_images\tiger1.jpg
test_images\tiger1.jpg is: pre labels:[5],name:['tiger'] score: [ 1.]
还有改进的空间。