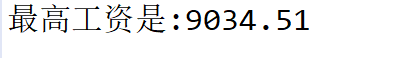Spring框架|JdbcTemplate介绍
文章目录
- JdbcTemplate 概述
- 对JdbcTemplate进行分步演示
- 1:测试数据源
- 2:为IoC容器配置一个JdbcTemplate
- 3:更新,将emp_id=5的记录salary字段改为1300.00
- 4:批量插入
- 5:查询emp_id=5的记录,封装为一个Java对象返回。
- 6:查询salary>4000的记录,封装为List集合返回
- 7:查询最大的salary
- 8:使用具名参数SQL插入一条员工记录,并以Map形式传入参数值。
- 9:使用具名参数SQL插入一条员工记录,并以SqlparamSource传入参数值。
JdbcTemplate 概述
在之前的Javaweb学习中,学习了手动封装JdbcTemplate,其好处是通过(sql语句+参数)模板化了编程。而真正的JdbcTemplate类,是Spring框架为我们写好的。它是 Spring 框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始 Jdbc API 对象的简单封装。除了JdbcTemplate,spring 框架还为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。
- 操作关系型数据的:
JdbcTemplate和HibernateTemplate。 - 操作 nosql 数据库的:RedisTemplate。
- 操作消息队列的:JmsTemplate。
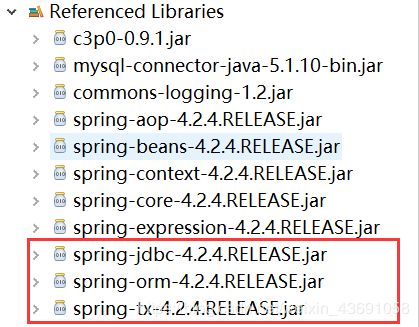
Spring框架的JdbcTemplate在spring-jdbc的jar包中,,除了要导入这个 jar 包
外,还需要导入一个 spring-tx的jar包(它是和事务相关的)。当然连接池的jar包也不能忘记,这里使用的是c3p0。
使用JdbcTemplate一定要导入Spring的数据库模块的三个jar:
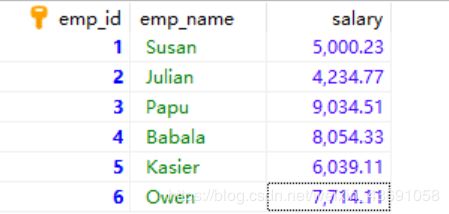
使用JdbcTemplate可以快捷的操作数据库,本文章针对JdbcTemplate进行演示。本文所使用的数据库表为jdbctemplate中的employee,表的内容如下。
对JdbcTemplate进行分步演示
1:测试数据源
数据库配置文件
- jdbctemplate数据库在本地数据库中已经创建。
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=Hudie
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctemplate
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
xml配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dbconfig.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource"
class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}">property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}">property>
bean>
测试获取连接
public class txTest {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
DataSource bean = ioc.getBean(DataSource.class);
Connection connection = bean.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}
}
执行测试,成功获取到连接。![]()
2:为IoC容器配置一个JdbcTemplate
如果通过编码来进行获得一个JdbcTemplate对象,可以使用new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);,不过由于这个对象经常使用,将其放在IoC容器中更合适。
具体配置如下:
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">constructor-arg>
bean>
测试
public class txTest {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate= ioc.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println(jdbcTemplate);
}
}
成功打印出JdbcTemplate对象。
![]()
3:更新,将emp_id=5的记录salary字段改为1300.00
jdbcTemplate.updat():表示更新一条记录。
@Test
public void test3() {
String sql = "update employee set salary = ? where emp_id=?;";
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 1300.00, 5);
System.out.println("更新员工表,影响" + update + "行");
}
4:批量插入
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs):表示批量进行插入,插入一个list集合,返回的是影响的行数。
@Test
public void test4() {
String sql = "insert into employee (emp_name,salary) values(?,?)";
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<Object[]>();
batchArgs.add(new Object[] { "张三", 998.98 });
batchArgs.add(new Object[] { "李四", 998.98 });
batchArgs.add(new Object[] { "王五", 998.98 });
batchArgs.add(new Object[] { "赵六", 998.98 });
// List的长度就是sql语句执行的次数
int[] is = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
for (int i : is) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
int[] is = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);返回的结果是影响的行数。
5:查询emp_id=5的记录,封装为一个Java对象返回。
创建JavaBean
package com.gql.bean;
public class Employee {
private Integer empId;
private String empName;
private Double salary;
//省略setter、getter与toString方法。
}
查询并封装单条记录
@Test
public void test5() {
String sql = "select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,salary from employee where emp_id=?";
// rowMapper:规定每一行记录和JavaBean的属性如何映射
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class), 5);
System.out.println(employee);
}
6:查询salary>4000的记录,封装为List集合返回
@Test
public void test6() {
String sql = "select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,salary from employee where salary>?";
List<Employee> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class), 4000);
for (Employee employee : list) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
7:查询最大的salary
- 使用mysql的max函数可以获得最大的salary,调用queryForObject方法,返回Double类型。
@Test
public void test7() {
String sql = "select max(salary) from employee";
Double object = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Double.class);
System.out.println("最高工资是:" + object);
}
8:使用具名参数SQL插入一条员工记录,并以Map形式传入参数值。
- Spring中使用namedParameterJdbcTemplate来进行含有具名SQL的操作。
将namedParameterJdbcTemplate加到IoC容器中。
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">constructor-arg>
bean>
在测试中以Map形式传入参数值。
public class txTest {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = ioc.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedJdbcTemplate = ioc.getBean(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.class);
@Test
public void test9() {
String sql = "insert into employee (emp_name,salary) values(:empName,:salary)";
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
// 将所有具名参数的值都放在map中
paramMap.put("empName", "小红");
paramMap.put("salary", 12000.00);
int update = namedJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramMap);
System.out.println(update);
}
}
9:使用具名参数SQL插入一条员工记录,并以SqlparamSource传入参数值。
与上一条实验类似,只是选用了不同的参数类型。
@Test
public void test10() {
String sql = "insert into employee (emp_name,salary) values(:empName,:salary)";
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setEmpName("小蓝");
employee.setSalary(9999.00);
int i = namedJdbcTemplate.update(sql, new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee));
System.out.println(i);
}