机器学习之算法-梯度下降画图
梯度下降
import numpy as np
import os
#画图
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#随机种子
np.random.seed(42) #西瓜,绿豆 无所谓多少
#保存图像
PROJECT_ROOT_DIT = "."
MODEL_ID = "linear_models" #线性模型
def save_fig(fig_id,tight_layout = True): #定义一个保存图像的函数 自动填充画布tight_layout
path = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIT,'images',MODEL_ID,fig_id + ".png") #指定保存图像的路劲 手动创建 当前目录下的images文件夹下的model_id文件夹
print("Saving figure",fig_id) #提示函数,正在保存图片
plt.savefig(path,format = 'png',dpi = 300) #保存图片 (需要指定保存路径,保存格式,清晰度)
# "./images/linear_models/xx.png"
#把讨厌的警告信息过滤掉
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(action = 'ignore',message = "^internal gelsd")
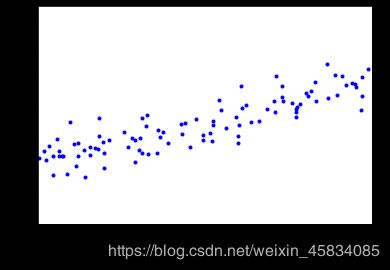
X = 2 * np.random.rand(100,1) #生成训练数据(特征部分)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(100,1)#生成训练数据(标签部分)
plt.plot(X,y,'b.') #画图
plt.xlabel("$x_1$",fontsize = 18)
plt.ylabel("$y$",rotation = 0,fontsize = 18) # rotation 旋转角度
plt.axis([0,2,0,15]) #x 轴的范围是0-2 y轴的范围是0-15
save_fig("generated_data_plot") #调用保存图片函数save_fig
plt.show()
#添加新特征
X_b = np.c_[np.ones((100,1)),X] # 添加一列
X_b
# 创建测试数据
X_new = np.array([[0],[2]])
X_new_b = np.c_[np.ones((2,1)),X_new]
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression #从 sklearn包里导入线性回归模型
lin_reg = LinearRegression() #创建线性回归对象
lin_reg.fit(X,y) #拟合训练数据
lin_reg.intercept_,lin_reg.coef_ #输出截距,斜率
lin_reg.predict(X_new) #对测试集进行预测
批量梯度下降求解线性回归
eta = 0.1 #a法
n_iterations = 1000 #迭代次数固定
m = 100
theta = np.random.randn(2,1)
for iterations in range(n_iterations):
gradients = 1/m * X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-y) #dot 矩阵的乘积 梯度
theta = theta - eta * gradients #更新theta值
theta_path_bgd = []
def plot_gradient_descent(theta,eta,theta_path = None):
m = len(X_b)
plt.plot(X,y,'b.')
n_iterations = 1000
for iterations in range(n_iterations):
if iterations < 10: #画蓝色线
y_predict = X_new_b.dot(theta)
style = "b-"
plt.plot(X_new,y_predict,style)
gradients = 2/m * X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-y) #dot 矩阵的乘积
theta = theta - eta * gradients
if theta_path is not None: #保存更新的theta_path的值
theta_path.append(theta)
plt.xlabel("$x_1$",fontsize = 18)
plt.axis([0,2,0,15]) #x 轴的范围是0-2 y轴的范围是0-15
plt.title(r"$\eta = {}$".format(eta),fontsize = 16) #保存图片
#随机种子
np.random.seed(42)
theta = np.random.randn(2,1) # random initialization
plt.figure(figsize = (10,4))
plt.subplot(131);plot_gradient_descent(theta,eta=0.02)
plt.ylabel("$y$",rotation = 0,fontsize = 18)
plt.subplot(132);plot_gradient_descent(theta,eta=0.1,theta_path=theta_path_bgd) #调用函数
plt.subplot(133);plot_gradient_descent(theta,eta=0.5)
# 第一个代表行数,第二个代表列数,第三个代表索引位置。
# 举个列子:plt.subplot(2, 3, 5) 和 plt.subplot(235) 是一样一样的。需要注意的是所有的数字不能超过10
save_fig("gradient_descent_plot") #调用保存图片函数save_fig
plt.show()
随机梯度下降法
具体过程
theta_path_sgd = []
m = len(X_b)
np.random.seed(42)
n_epochs = 50
theta = np.random.randn(2,1) #随机初始化
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for i in range(m):
if epoch == 0 and i < 20:
y_predict = X_new_b.dot(theta)
style = "p-"
plt.plot(X_new,y_predict,style)
random_index = np.random.randint(m)
xi = X_b[random_index:random_index + 1]
yi = y[random_index:random_index + 1]
gradients = 2 * xi.T.dot(xi.dot(theta)-yi) #dot 矩阵的乘积
eta = 0.1
theta = theta - eta * gradients
theta_path_sgd.append(theta)
plt.plot(X,y,'b.')
plt.xlabel("$x_1$",fontsize = 18)
plt.ylabel("$y$",rotation = 0,fontsize =18)
plt.axis([0,2,0,15]) #x 轴的范围是0-2 y轴的范围是0-15
save_fig("sgd_plot") #调用保存图片函数save_fig
plt.show()
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor
sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(max_iter=50,tol=-np.infty,penalty=None,eta0=0.1,random_state=42) #最大迭代次数 惩罚(结构风险)=None 不考虑l1 l2
sgd_reg.fit(X,y.ravel())
sgd_reg.intercept_,sgd_reg.coef_ #输出截距,斜率
小批量梯度下降Mini-batch gradient descent
theta_path_mgd = []
n_iterations = 50
minibatch_size = 20
np.random.seed(42)
theta = np.random.randn(2,1)
for epoch in range(n_iterations):
shuffled_indices = np.random.permutation(m) #洗牌
X_b_shuffled = X_b[shuffled_indices]
y_shuffled = y[shuffled_indices]
for i in range(0,m,minibatch_size):
xi = X_b_shuffled[i:i+minibatch_size]
yi = y_shuffled[i:i+minibatch_size]
gradients = 2/minibatch_size * xi.T.dot(xi.dot(theta)-yi) #dot 矩阵的乘积
eta = 0.1
theta = theta - eta * gradients
theta_path_mgd.append(theta)
theta
theta_path_bgd = np.array(theta_path_bgd)
theta_path_sgd = np.array(theta_path_sgd)
theta_path_mgd = np.array(theta_path_mgd)
plt.figure(figsize=(7,4))
plt.plot(theta_path_sgd[:,0],theta_path_sgd[:,1],"r-s",linewidth=1,label="Stochastic")
plt.plot(theta_path_mgd[:,0],theta_path_mgd[:,1],"g-+",linewidth=2,label="Mini-batch")
plt.plot(theta_path_bgd[:,0],theta_path_bgd[:,1],"b-o",linewidth=3,label="Batch")
plt.legend(loc="upper left",fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel(r"$\theta_0$",fontsize = 20)
plt.ylabel(r"$\theta_1$",fontsize = 20,rotation = 0)
plt.axis([2.5,4.5,2.3,3.9])
save_fig("gradient_descent_paths_plot")
plt.show()