Elasticsearch 数据建模
数据建模:英文为Data Modeling,为创建数据模型的过程
数据模型(Data Model)
- 对现实世界进行抽象描述的一种工具和方法
- 通过抽象的实体及实体之间联系的形式去描述业务规则,从而实现对现实世界的映射
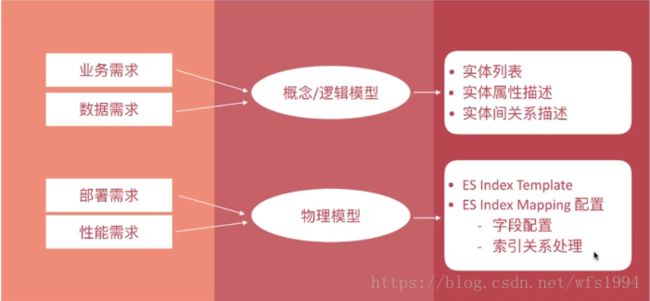
数据建模的过程:
- 概念分析:确定系统的核心需求和范围边界,设计实现和实体间的关系
- 逻辑模型:进一步梳理业务需求,确定每个实体的属性、关系和约束等
- 物理模型:结合具体的数据库产品,在满足业务读写性能等需求的前提下确定最终的定义
ES中的数据建模相关配置
ES是基于Lucene以倒排索引为基础实现的存储体系,不遵循关系型数据库中的范式约定
Mapping字段的相关设置:
| 参数 | 取值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
enbaled |
true|false | 默认为true, false:仅存储,不做搜索或聚合分析(比如cookie|session字段) |
index |
true|false | 控制当前字段是否索引,默认为true,即记录索引,false不记录,即不可搜索 |
index_options |
docs|freqs|positions|offsets | 存储倒排索引的哪些信息,text类型默认配置为positions,其他默认为docs ,记录内容越多,占用空间越大。 |
norms |
true|false | 是否存储归一化相关参数,如果字段仅用于过滤和聚合分析,可关闭 |
doc_values |
true|false | 是否启用doc_values,用于排序和聚合分析 |
field_data |
false|true | 是否为text类型启用fielddata,实现排序和聚合分析 |
store |
false|true | 是否存储该字段值(默认是false) |
coerce |
true|false | 是否开启自动数据类型转换功能,比如字符串转换为数字、浮点转换为整型等(默认是true) |
multifields多字段 |
- | 灵活使用多字段特性来解决多样的业务需求 |
dynamic |
true|false|strict | 控制mapping自动更新 |
date_detection |
true|false | 是否自动识别日期类型 |
Mapping字段属性的设定流程
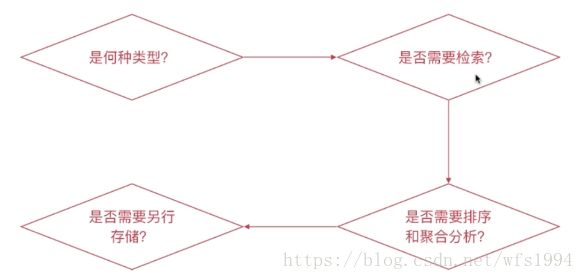
是何种类型?
字符串类型:需要分词设定为text类型,否则设置为keyword类型
枚举类型:基于性能考虑将其设定为keyword类型,即便该数据为整型(如状态码)
数值类型:尽量选择贴近的类型,比如byte即可表示所有数值时,即选用byte,不要用long
其他类型:比如布尔类型、日期、地理位置数据等
是否需要检索?
完全不需要检索、排序、聚合分析的字段:enable设置为false
不需要检索的字段:index设置为false
需要检索的字段,可以通过如下配置设定需要的存储粒度
index_options: 结合需要设定norms: 不需要归一化数据时关闭即可
是否需要排序和聚合分析?
不需要排序或者聚合分析功能:
doc_values设定为falsefielddata设定为false
是否需要专门存储当前字段的数据?
store设定为true,即可存储该字段的原始内容(与_source中的不相关)
一般结合_source的enabled设定为false时使用
ES中的数据建模实例
以博客文章blog_index为例说明创建过程:
| 字段 | 字段名称 | 字段类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 标题 | title | text,子字段keyword |
| 发布日期 | publish_date | date |
| 作者 | author | keyword |
| 摘要 | abstract | text |
| 网络地址 | url | enabled:false(仅存储不做检索分析) |
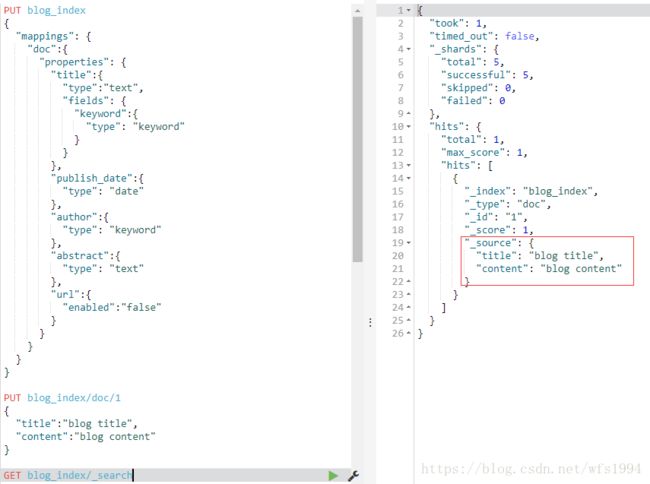
blog_index的mapping设置如下:
PUT blog_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties": {
"title":{
"type":"text",
"fields": {
"keyword":{
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"publish_date":{
"type": "date"
},
"author":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"abstract":{
"type": "text"
},
"url":{
"enabled":"false" #url不需要做搜索,只存储即可
}
}
}
}
}
扩展:在上面的基础上,添加内容content字段,mapping应该如何设计?
| 字段 | 字段名称 | 字段类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 标题 | title | text,子字段keyword |
| 发布日期 | publish_date | date |
| 作者 | author | keyword |
| 摘要 | abstract | text |
| 网络地址 | url | keyword(需要做相应修改) |
| 内容 | content | ??? |
思考:博客的
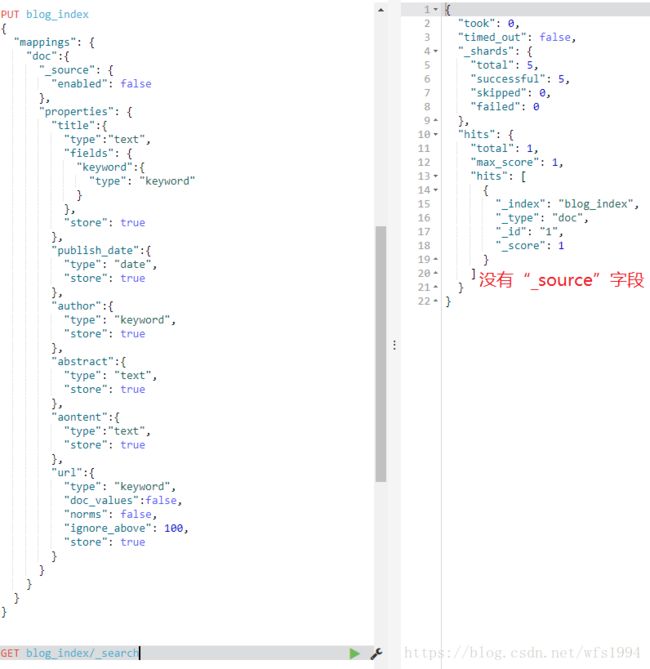
content内容可能会有几百上千字,但是如果博客换成书,content的内容可能会有几十万字,变的非常的大。这样如果content字段依然默认为text类型:在取原始数据时,是通过_source来获取原始内容的,每一次取_source都会把content内容取出来,如果content过大就会导致_source获取过多的内容,降低性能
mapping设置成如下内容:结合_source的enabled设定为false时设置store为true
PUT blog_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"_source": {
"enabled": false
},
"properties": {
"title":{
"type":"text",
"fields": {
"keyword":{
"type": "keyword"
}
},
"store": true
},
"publish_date":{
"type": "date",
"store": true
},
"author":{
"type": "keyword",
"store": true
},
"abstract":{
"type": "text",
"store": true
},
"aontent":{
"type":"text",
"store": true
},
"url":{
"type": "keyword",
"doc_values":false,
"norms": false,
"ignore_above": 100,
"store": true
}
}
}
}
}
查询高亮显示:
GET blog_index/_search
{
"stored_fields": ["title","publish_date","author","abstract","url"], #不获取content字段
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "blog"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {"content": {}}
}
}
Reindex
Reindex指重建所有数据的过程,一般发生在如下情况:
- mapping设置变更,比如字段类型变化,分词字典变更等
- index设置变更,比如分片数更改等
- 迁移数据
ES提供了现成的API用于完成该工作:
_update_by_query在现有索引上重建_reindex在其他索引上重建
官方文档:
Reindex API
Update By Query API
_update_by_query
将twitter的所有文档重建一遍
POST twitter/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed
#conflicts=proceed:如果遇到版本冲突,覆盖并继续执行POST twitter/_update_by_query
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.likes++",
"lang": "painless"
},
"query": {
"term": {
"user": "kimchy"
}
}
}
#script:更新文档的字段值; query:可以更新部分文档
_reindex
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "twitter"
},
"dest": {
"index": "new_twitter"
}
}
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "http://otherhost:9200",
"username": "user",
"password": "pass"
},
"index": "source",
"query": {
"match": {
"test": "data"
}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "dest"
}
}
Task
数据重建的时间受源索引文档规模的影响,当规模越大时,所需的时间越多,此时需要通过设定url参数wait_for_completion为false来异步执行,ES以task来描述此类执行任务
ES提供了Task API来查看任务的执行进度和相关数据
POST blog_index/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed&wait_for_completion=false
{
"task": "q5X8C6RXT1K0d9PrIZOQ7w:3438612"
}
GET _tasks/q5X8C6RXT1K0d9PrIZOQ7w:3438612
其他建议
1.对mapping进行版本管理
包含在代码或者以专门的文件进行管理,添加好注释,并加入git等版本管理仓库中方便回顾
为每个增加一个metadata字段,在其中维护一些文档相关的元数据,方便对数据进行管理
{
"metadata":{
"version":1
},
"username":"alfred",
"job":"engineer"
}
#mapping版本,可以自行制定,比如每次更新mapping设置后,该version加1
2.防止字段过多
字段过多:难于维护,当字段成百上千时,基本很难有人明确知道每个字段的含义;mapping的信息存储在cluster state里面,过多的字段会导致mapping过大,最终导致更新变慢。
通过设置index.mapping.total_fields.limit可以限定索引中最大字段数,默认为1000
可以通过key/value的方式解决字段过多的问题,但并不完美:
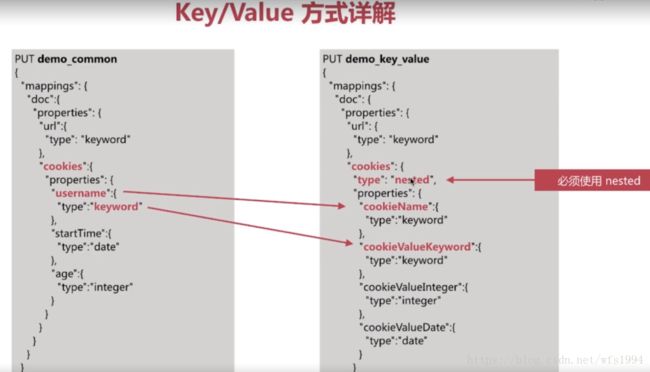
key/value方式缺点:
- query语句复杂度飙升,且有一些可能无法实现,比如聚合分析相关的
- 不利于在kibana中做可视化分析
一般字段过多的原因是由于没有高质量的数据建模导致的,比如dynamic设置为true,考虑拆分多个索引来解决问题。