相关框架
JUnit4、Mockit、PowerMock
相关maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.11version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermockgroupId>
<artifactId>powermock-module-junit4artifactId>
<version>1.6.5version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.powermockgroupId>
<artifactId>powermock-api-mockitoartifactId>
<version>1.6.5version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
代码base
后面的测试代码均是针对下面class的
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public boolean addUser(UserDto userDto) {
int added = userService.addUser(userDto);
if (added <= 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
public boolean delUser(int id) {
try {
userService.delUser(id);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
public void saveUser(UserDto userDto) {
userService.saveUser(userDto);
}
public int countUser() {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int count = 0;
if (ud.getId() > 0) {
count += 1;
}
return count;
}
public boolean modUser(UserDto userDto) {
int moded = userService.modUser(userDto);
return verifyMod(moded);
}
private boolean verifyMod(int moded) {
if (moded <= 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
public interface UserService {
int addUser(UserDto userDto);
int delUser(int id) throws Exception;
int modUser(UserDto userDto);
void saveUser(UserDto userDto);
}
public class UserDto {
private int id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
public class FileHelper {
public static String getName(String name) {
return "A_" + name;
}
}
相关注解:所有测试类均须加上以下注解
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({UserController.class, FileHelper.class})
@PowerMockIgnore("javax.management.*")
其中:
- @RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) :表明用 PowerMockerRunner来运行测试用例,否则无法使用PowerMock
- PrepareForTest({UserController.class}):所有需要测试的类,列在此处,以逗号分隔
- @PowerMockIgnore(“javax.management.*”):为了解决使用powermock后,提示classloader错误
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com.ibm.mq.jms.MQQueueConnectionFactory$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$7cb492ab (initialization failure)
at java.lang.J9VMInternals.initialize(J9VMInternals.java:140)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:60)
……
@Autowired 属性的注入方式
public class UserControllerTest {
@Mock
private UserService userService;
@InjectMocks
private UserController uc = new UserController();
}
几点需要注意一下:
- 上面的方式,将会mock出来一个 user service对象,将将其注入到 UserController 的实例 uc 中去。
- uc后面的那个 new UserController() 也可以不需要的。
mock普通方法
@Test
public void testAddUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.when(userService.addUser(ud)).thenReturn(1);
boolean result = uc.addUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
上面的代码中,有两点需要注意一下:
- userService.addUser() 和 uc.addUser() 所使用的参数值须保持一致,这样才能让powermock在运行的时候进行参数匹配。(本篇最后会讲到,如何进行模糊匹配参数。)
- thenReturn() 返回的值需要与 userService.addUser() 方法声明的返回值的类型保持一致,否则编译将会出错。
- mock语句不能写成下面这样的:
PowerMockito.doReturn(1).when(userService.addUser(ud));
否则将报异常:
org.mockito.exceptions.misusing.UnfinishedStubbingException:
Unfinished stubbing detected here:
……
mock抛异常
@Test
public void testDelUser() throws Exception {
int toDelete = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.delUser(toDelete)).thenThrow(new Exception("mock exception"));
boolean result = uc.delUser(toDelete);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}
有几点需要注意一下:
- 如果 user service 中的 delUser() 方法抛出的是 checked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new Exception()或者其子类
- 如果delUser() 方法抛出的是 unchecked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new RuntimeException()或其子类
mock静态方法
@Test
public void mockFileHelper() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName("lucy")).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
}
有几点需要注意一下:
- 需要在@PrepareForTest注解中加上 FileHelper.class
- 调用 PowerMockito.mockStatic(),参数为 FileHelper.class
mock 返回值为 void 的方法
@Test
public void testSaveUser() throws Exception {
UserDto userDto = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService, "saveUser", userDto);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService).saveUser(userDto);
uc.saveUser(userDto);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
mock私有方法
- 方法一
PS:该方法中,还介绍了 mock私有字段的值 的方法。
@Test
public void testModUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
UserController uc2 = PowerMockito.mock(UserController.class);
Whitebox.setInternalState(uc2, "userService", userService);
PowerMockito.when(uc2.modUser(ud)).thenCallRealMethod();
PowerMockito.when(uc2, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc2.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
需要注意的是:此处的uc2是mock出来的,不是 UserControllerTest 类中的成员变量 uc
@Test
public void testModUser2() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
uc = PowerMockito.spy(uc);
PowerMockito.when(uc, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
使用spy方法可以避免执行被测类中的成员函数,即mock掉不想被执行的私有方法。
测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)
@Test
public void testVerifyMod() throws Exception {
Method method = PowerMockito.method(UserController.class, "verifyMod", int.class);
boolean result = (boolean) method.invoke(uc, 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
@Test
public void testVerifyMod2() throws Exception {
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(uc, "verifyMod", 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
mock新建对象
@Test
public void testCountUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
ud.setId(1);
PowerMockito.whenNew(UserDto.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(ud);
int count = uc.countUser();
Assert.assertEquals(count, 1);
}
mock返回值为 void 的 static 方法 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(xxxUtil.class, "xxxStaticMethod", 1,"mysql");
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(xxxUtil.class);
xxxUtil.xxxStaticMethod(1, 2);
mock 同一方法,返回不同的值 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = connection.getMetaData();
ResultSet schemaSet = dbMetaData.getSchemas();
while (schemaSet.next()) {
schemaList.add(schemaSet.getString("TABLE_SCHEM"));
}
上面这个代码,我们是想让schemaSet返回true,好让测试代码能进入while循环。但是我们又不能让它一直返回 true,否则,while将陷入死循环。针对这种需求,应该怎么来处理呢?请看:
Connection connection = PowerMockito.mock(Connection.class);
DatabaseMetaData databaseMetaData = PowerMockito.mock(DatabaseMetaData.class);
ResultSet resultSet = PowerMockito.mock(ResultSet.class);
PowerMockito.when(connection.getMetaData()).thenReturn(databaseMetaData);
PowerMockito.when(databaseMetaData.getSchemas()).thenReturn(resultSet);
PowerMockito.when(resultSet.next()).thenReturn(true, false);
PowerMockito.when(resultSet.getString("TABLE_SCHEM")).thenReturn("mock schema");
上面的关键步骤中,thenReturn()方法返回了两个值,一个是true,一个是false。它的意思是,当next()第一次被调用时,将会返回 true,第二次及第二次以后的调用将会返回false。这就满足了我们的需求啦。
mock 泛型 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
List nodes = new ArrayList<>();
nodeService.getAllChildren(nodeId, nodes);
上面的代码,我们在进行Test时,一般都会把nodeService中的getAllChildren()方法给mock掉,但是这样会导致nodes这个List的内容一直为空(因为它的的返回值为void)。为了满足在getAllChildren()被mock掉的情况下,nodes的内容又不能为空这一需求,我们可以将 ArrayList 的 构造函数给mock掉。但是,ArrayList是一个泛型类,那么在mock它的构造函数时,要如何指定泛型的类型呢?
- 方法一
在构造ArrayList时,不指定泛型类型。
PS:此种方法中,nodes变量的类型必须是 ArrayList,不能是 List。
ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList() {{
Node n = new Node();
n.setId(1);
this.add(n);
}};
PowerMockito.whenNew(ArrayList.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(nodes);
- 方法二
通过使用PowerMock的 Answer 机制。
final List nodes = new ArrayList() {{
Node n = new Node();
n.setId(1);
this.add(n);
}};
PowerMockito.whenNew(ArrayList.class).withNoArguments().thenAnswer(new Answer>() {
@Override
public List answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable {
return nodes;
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
mock可变参数
public List getFlowByPrjId(int prjId, Integer ...status) {
}
像上面这种方法,它有一个被称为varargs的参数,像这种参数应该如何来模拟呢?
其实很简单,因为varargs参数实际上是被当成数组来处理的,所以,我们只需要像下面这样来处理即可:
when(xxxClass.getFlowByPrjId(Matchers.anyInt(), (Integer[])Matchers.anyVararg())).thenReturn(nodeList);
mock final方法
final 与普通方法一样mock,但是需要将其所在class添加到@PrepareForTest注解中,即
@PrepareForTest({XXXClassWithFinalMethod.class})
XXXClassWithFinalMethod obj = mock(XXXClassWithFinalMethod.class);
when(obj.xxxFinalMethod()).thenReturn(xxxxxxx);
不然,会报类似下面的异常,让人很迷惑(因为我们明显就是在 mock 出来的对象上调用的方法):
when() requires an argument which has to be 'a method call on a mock'
mock 私有内部静态类对象
public class ClassA {
private static class InnerClassA {
private InnerClassA(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
对于上面这个类,如果我们想去测试InnerClassA类的run方法,该怎么做呢?
首先,因为InnerClassA是一个private的内部类,所以我们是无法像下面这样来mock它的(编译就会报错,这个内部类是不可见的):
ClassA.InnerClassA aaa = mock(ClassA.InnerClassA.class);
这种情况下,能想到的办法就是通过反射获取到InnerClassA的构造函数,然后生成一个对象。
那么如何来做呢?Whitebox可以帮你实现这一点:
Class clazz = Whitebox.getInnerClassType(ClassA.class, "InnerClassA");
Constructor constructor = Whitebox.getConstructor(clazz, String.class);
Object object = constructor.newInstance("mock name");
Whitebox.invokeMethod(object, "run");
mock super关键字
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
对于上面这个类的init方法,我们在测试时,一个难点就是,如何把父类中的init给mock掉。因为它不像我们其他情况下的方法调用,所以不好通过when().xxx()这种方式来mock。这种情况下,就轮到suppress方法出面了,下面直接给出mock方式:
@Test
public void testInit() throws Exception {
DispatcherServlet ds = spy(new DispatcherServlet());
suppress(method(GenericServlet.class, "init", ServletConfig.class));
ds.init(mock(ServletConfig.class))
}
这里为什么是GenericServlet.class而不是HttpServlet.class,因为init(ServletConfig config)这个方法是定义在GenericServlet中而非HttpServlet中。
spy 使用的注意点
public void getAllChildren(int parentNodeId, List allChildren) {
List children = getChildren(parentNodeId);
allChildren.addAll(children);
}
public List getChildren(int nodeId) {
List children = nodeMapper.getChildren(nodeId);
return children;
}
我本意是要测试getAllChildren()这个方法,在这个方法中,它调用了getChildren()方法,自然而然地,我准备将getChildren() mock掉,所以我写了下面的mock语句:
private XXXService ns = new XXXService();
ns = spy(ns);
when(ns.getChildren(Matchers.anyInt())).thenReturn(nodes);
List result = new ArrayList<>();
ns.getAllChildren(1, result);
assertEquals(result.size(), 2);
本以为这样写,测试肯定可以通过的。
但是事实总是残酷的,运行之后,一直报错,说result.size()的值是0不是2。
这我就很纳闷了啊,明明返回的是长度为2的list啊,为什么却一直是0呢?
就是这么一个不起眼的问题,花了我5个小时来检查。
最终在网上一个贴子的点醒下,发现了问题所在。
问题出就出在下面这句看似理所当然的mock语句上:
when(ns.getChildren(Matchers.anyInt())).thenReturn(nodes);
它的目的是当ns的getChildren()被调用且参数是任意int类型的值时,都返回nodes这个list。但是这样写的话,它相当于只是mock了当参数为0的场合下才返回nodes这个list。具体原因如下(摘自org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito.doReturn()方法的javadoc)
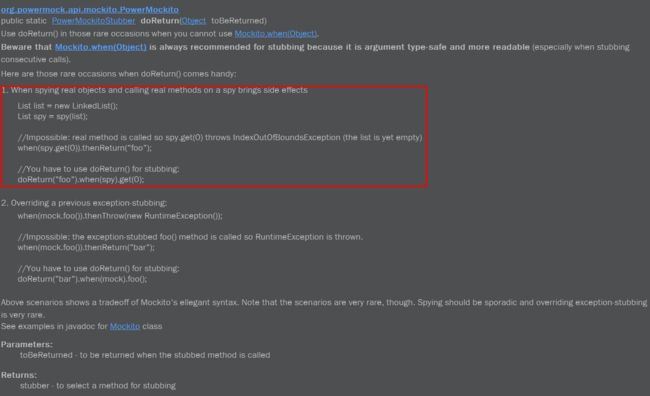
从这里的说明,我们知道我们的问题是什么了,上面的那种mock写法,其实就是相当于:
when(ns.getChildren(0)).thenReturn(nodes);
因为Matchers.anyInt()的返回值就是0.
所以,只有当参数值为0的时候,它才会返回nodes这个list。
然后,根据Javadoc,我们只需要按照如下来修改一下mock语句即可:
doReturn(nodes).when(ns).getChildren(Matchers.anyInt());
参数的模糊匹配
上面的测试用例中,在mock一个方法时,这个方法的参数都是事先准备好的。那么,有没有什么方式,使用在mock方法时,可以无视方法所需要的参数值呢?答案肯定有的,它就是org.mockito.Matchers。在这个类中,提供了很多 any*的方法,如:
- anyObject()
- anyString
- anyList()
- ……
我们可以使用这些方法去避免构建那些难以模拟的输入参数,如:
@Test
public void mockFileHelper2() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName(Matchers.anyString())).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("hanmeimei"), "lily");
}
Matchers的方便之处,各位可以自己尝试,包你用得爽~
不过,有一点需要注意一下:如果对某一个参数使用了Matcher,那么,这个方法的所有其他参数也必须使用Matcher,否则将会报错。
Power Mock 实现原理(转)
- 当某个测试方法被注解@PrepareForTest标注以后,在运行测试用例时,会创建一个新的org.powermock.core.classloader.MockClassLoader实例,然后加载该测试用例使用到的类(系统类除外)。
- PowerMock会根据你的mock要求,去修改写在注解@PrepareForTest里的class文件(当前测试类会自动加入注解中),以满足特殊的mock需求。例如:去除final方法的final标识,在静态方法的最前面加入自己的虚拟实现等。
- 如果需要mock的是系统类的final方法和静态方法,PowerMock不会直接修改系统类的class文件,而是修改调用系统类的class文件,以满足mock需求。
参考文档:
- 官方文档:https://github.com/jayway/powermock
- WhiteBox 介绍:https://github.com/jayway/powermock/wiki/BypassEncapsulation
- 官方spring sample: https://github.com/jayway/powermock/tree/master/examples/spring-mockito
- 关于 @Autowired 的注入问题:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/36799240/mock-final-class-and-inject-it-to-autowired-data-member-and-overcome-postconstru
- http://agiledon.github.io/blog/2013/11/21/play-trick-with-powermock/
- http://blog.csdn.net/jackiehff/article/details/14000779
- http://www.cnblogs.com/jiyuqi/p/3564621.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/dfqin/article/details/6604610
- http://blog.csdn.net/booboo2006/article/details/7495863
最后附上测试类完整代码
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Matchers;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PowerMockIgnore;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
import org.powermock.reflect.Whitebox;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({UserController.class, FileHelper.class})
@PowerMockIgnore("javax.management.*")
public class UserControllerTest {
@Mock
private UserService userService;
@InjectMocks
private UserController uc;
/**
* mock普通方法
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testAddUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.when(userService.addUser(ud)).thenReturn(1);
boolean result = uc.addUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock抛异常
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDelUser() throws Exception {
int toDelete = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.delUser(toDelete)).thenThrow(new Exception("mock exception"));
boolean result = uc.delUser(toDelete);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}
/**
* mock静态方法
*/
@Test
public void mockFileHelper() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName("lucy")).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
}
/**
* mock 返回值为 void 的方法
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() throws Exception {
UserDto userDto = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService, "saveUser", userDto);
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService).saveUser(userDto);
uc.saveUser(userDto);
}
/**
* mock私有方法
* 方法一
* PS:该方法中,还介绍了 mock私有字段的值 的方法。
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testModUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
UserController uc2 = PowerMockito.mock(UserController.class);
Whitebox.setInternalState(uc2, "userService", userService);
PowerMockito.when(uc2.modUser(ud)).thenCallRealMethod();
PowerMockito.when(uc2, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc2.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock私有方法
* 方法二
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testModUser2() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
uc = PowerMockito.spy(uc);
PowerMockito.when(uc, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* 测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)
* 方法一
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testVerifyMod() throws Exception {
Method method = PowerMockito.method(UserController.class, "verifyMod", int.class);
boolean result = (boolean) method.invoke(uc, 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* 测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)
* 方法二
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testVerifyMod2() throws Exception {
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(uc, "verifyMod", 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock新建对象
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testCountUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
ud.setId(1);
PowerMockito.whenNew(UserDto.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(ud);
int count = uc.countUser();
Assert.assertEquals(count, 1);
}
/**
* 参数的模糊匹配
*/
@Test
public void mockFileHelper2() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName(Matchers.anyString())).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("hanmeimei"), "lily");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
