万能的Attention及其代码实现
最近看到以前的代码,想到了attention,趁着代码还在就来整理一下。
文章目录
- [Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507)
- [Concurrent Spatial and Channel ‘Squeeze &Excitation’ in Fully Convolutional Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02579)
- [CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.06521)
Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
这是最有名的SEnet(也就是channel attention), 感兴趣的可以看论文
看图:


这里用到的操作:全局平均池化(将W X H X C的特征 变成1 X 1 X C ),全连接FC(两层,用两个FC层比用一个FC层的好处:具有更多非线性,可以更好拟合通道间复杂的相关性;极大的减少了参数量和计算量。缺点:不能保持spatial information),最后进行点乘,这个attention在很多网络结构都有了,例如Resnet
代码实现如下(python,超清晰明了简洁):
from torch import nn
import torch
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size() # b为batch
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
#return x * y.expand_as(x)
return torch.mul(x,y)
Concurrent Spatial and Channel ‘Squeeze &Excitation’ in Fully Convolutional Networks
这是scSEnet,也就是把spatia和channel两种attention合并,下面把我ppt内容贴上来,感兴趣的可以仔细看论文
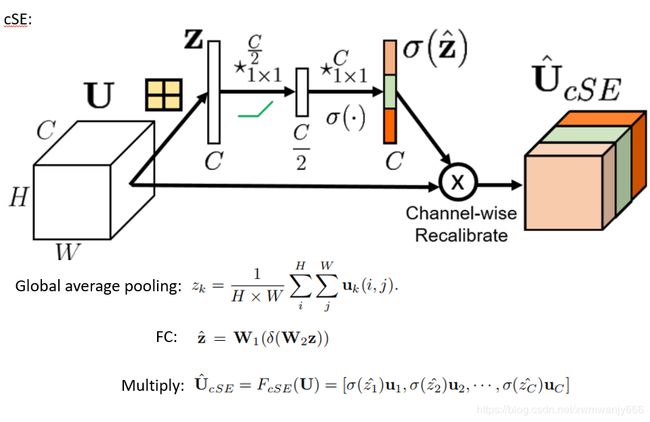
上面这张图就是channel attention ,和上一篇一样

这张图加了一个spatial attention, 至于操作呢,很简单粗暴,用1*1卷积直接把channel变为1,(也就是降维,将W X H X C的特征 变成 W X H X 1 ),最后也是点乘
最最后把两个attention 对应相加
代码实现如下(python,超清晰明了简洁):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SCSEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SCSEBlock, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.channel_excitation = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(channel, int(channel//reduction)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(int(channel//reduction), channel),
nn.Sigmoid())
self.spatial_se = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(channel, 1, kernel_size=1,
stride=1, padding=0),
nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, x):
bahs, chs, _, _ = x.size()
# Returns a new tensor with the same data as the self tensor but of a different size.
chn_se = self.avg_pool(x).view(bahs, chs)
chn_se = self.channel_excitation(chn_se).view(bahs, chs, 1, 1)
chn_se = torch.mul(x, chn_se)
spa_se = self.spatial_se(x)
spa_se = torch.mul(x, spa_se)
return torch.add(chn_se, 1, spa_se)
CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module
这个题目已经告诉你了,它叫CBAM,直接上图吧,感兴趣的可以仔细看论文
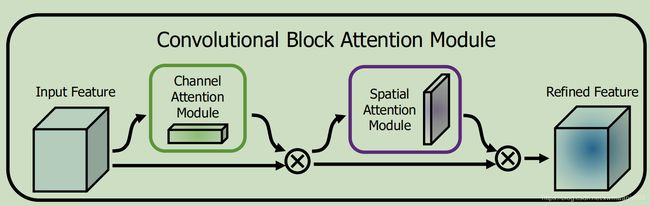
看到这个图,是不是觉得就是SCSE 呢,怎么还可以发论文呢,人家有其他创新啦

对的就是你看到的,它在channel attention,spatial attention上分别动了手脚,用了两种不同的pooling,感兴趣的可以仔细看论文。
代码实现如下(python,超清晰明了简洁):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class CBAMBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(CBAMBlock, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.channel_excitation = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(channel,int(channel//reduction),bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(int(channel//reduction),channel,bias=False),
)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.spatial_excitation = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size=7,
stride=1, padding=3, bias=False),
)
def forward(self, x):
bahs, chs, _, _ = x.size()
# Returns a new tensor with the same data as the self tensor but of a different size.
chn_avg = self.avg_pool(x).view(bahs, chs)
chn_avg = self.channel_excitation(chn_avg).view(bahs, chs, 1, 1)
chn_max = self.max_pool(x).view(bahs, chs)
chn_max = self.channel_excitation(chn_max).view(bahs, chs, 1, 1)
chn_add=chn_avg+chn_max
chn_add=self.sigmoid(chn_add)
chn_cbam = torch.mul(x, chn_add)
avg_out = torch.mean(chn_cbam, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(chn_cbam, dim=1, keepdim=True)
cat = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
spa_add = self.spatial_excitation(cat)
spa_add=self.sigmoid(spa_add)
spa_cbam = torch.mul(chn_cbam, spa_add)
return spa_cbam
以上三种attention都可以无缝隙的用在任何网络中,且不会改变W H C, 很方便,另外我们会发现,经过attention之后都会使用nn.sigmoid层,使得得到的结果变为(0-1)之间。至于效果嘛,看具体任务,详细内容可参考:attention