Android 蓝牙开发,蓝牙连打印机。
目录
效果:
开发环境
涉及知识点
集成配置
蓝牙连接
蓝牙打印
GitHub
效果:
特别声明:较之前的版本有很大的调整,之前的版本是未适配8.0的,现在是适配了的,接入方式也不一样,包括代码逻辑都有调整,不过梳理清楚流程之后也就不难了,非常简单。(更新时间:2020-03-27)
开发环境
- Gprinter佳博打印机,型号GP-2120TU
- Android Studio 3.6.1,gradle 3.5.3
本文可能内容比较长,但是难度不大。文末附github地址。
涉及知识点
- 蓝牙相关
- 多线程开发
- 线程池
- 构建者模式
- 单例模式
- 运行时权限
- BroadcastReceiver
- startActivityForResult
- 等等
集成配置
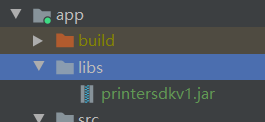
1.添加jar包,在app目录下新建libs文件夹,拷入jar文件并Add As Library
2.在main目录下新建jniLibs目录,并拷入so文件
3.配置我们的manifest文件,添加必要的权限
ok,基本的配置完成,开始进入正题。
基本大的流程分为两部分,一是蓝牙连接,二是打印,下面开始一一介绍。
蓝牙连接
分为几个小步骤
1.因为蓝牙涉及到隐私权限,所以先检查、请求权限
private void checkPermission() {
for (String permission : permissions) {
if (PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED != ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission)) {
per.add(permission);
}
}
}
private void requestPermission() {
if (per.size() > 0) {
String[] p = new String[per.size()];
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, per.toArray(p), REQUEST_CODE);
}
}2.点击连接按钮,通过startActivityForResult启动一个蓝牙列表页面,实际上显示为一个dialog
public void btnConnect(View view) {
startActivityForResult(new Intent(MainActivity.this, BluetoothListActivity.class), BLUETOOTH_REQUEST_CODE);
}3.这个页面的作用就是判断蓝牙是否可用、是否开启,显示已配对和未配对的蓝牙设备列表
/**
* 初始化蓝牙
*/
private void initBluetooth() {
// 获取蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
// 检查蓝牙是否可用
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null) {
Toast.makeText(this, "当前设备不支持蓝牙", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
// 检查蓝牙是否打开
if (!mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
Intent enableIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);
} else {
getDeviceList();
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode == REQUEST_ENABLE_BT) {
if (resultCode == Activity.RESULT_OK) {
// bluetooth is opened
getDeviceList();
} else {
// bluetooth is not open
Toast.makeText(this, "蓝牙没有开启", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
/**
* 蓝牙设备列表
*/
protected void getDeviceList() {
// 初始化一个数组适配器,用来显示已匹对和未匹对的设备
mDevicesArrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, R.layout.bluetooth_device_name_item);
lvPairedDevice.setAdapter(mDevicesArrayAdapter);
lvPairedDevice.setOnItemClickListener(mDeviceClickListener);
// 已匹对数据
Set pairedDevices = mBluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
// 添加一个item显示信息
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add("已配对:");
if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) {
//遍历填充数据
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add(device.getName() + "\n" + device.getAddress());
}
} else {
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add("没有已配对设备");
}
}
/**
* 接收扫描设备的广播
* changes the title when discovery is finished
*/
private final BroadcastReceiver mFindBlueToothReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
// 每当发现一个蓝牙设备时
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
// Get the BluetoothDevice object from the Intent
//获取设备
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
// If it's already paired, skip it, because it's been listed
// 未匹对的情况下添加显示
if (device.getBondState() != BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED) {
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add(device.getName() + "\n" + device.getAddress());
}
// 扫描结束
} else if (BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)) {
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(false);
setTitle("选择蓝牙设备");
//此处-2是减去我们手动添加的两个区分显示的item
Log.i("tag", "finish discovery" + (mDevicesArrayAdapter.getCount() - 2));
if (mDevicesArrayAdapter.getCount() == 0) {
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add("没有找到蓝牙设备");
}
}
}
};
/**
* 扫描设备
*/
private void discoveryDevice() {
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
setTitle("扫描中");
// 添加一个item区分显示信息
mDevicesArrayAdapter.add("未配对:");
// If we're already discovering, stop it
if (mBluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
}
// 开始扫描,每扫描到一个设备,都会发送一个广播
mBluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
}
4.点击一个列表item的时候 即表示连接此设备,通过setResult返回该item对应的设备mac地址
private OnItemClickListener mDeviceClickListener = new OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView av, View v, int arg2, long arg3) {
// Cancel discovery because it's costly and we're about to connect
// Get the device MAC address, which is the last 17 chars in the View
String info = ((TextView) v).getText().toString();
String noDevices = "没有已配对设备";
String noNewDevice = "没有找到蓝牙设备";
Log.i("TAG", info);
// info 不是我们手动添加的信息 即表示为真实蓝牙设备信息
if (!info.equals(noDevices) && !info.equals(noNewDevice) && !info.equals("未配对") && !info.equals("已配对")) {
mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
//mac 地址
String address = info.substring(info.length() - 17);
// 设置信息并返回
// Set result and finish this Activity
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICE_ADDRESS, address);
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, intent);
finish();
}
}
};5.在MainActivity的onActivityResult中获取mac地址,并通过设备连接管理类DeviceConnFactoryManager进行连接
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
//蓝牙连接
if (requestCode == BLUETOOTH_REQUEST_CODE) {
closePort();
//获取蓝牙mac地址
String macAddress = data.getStringExtra(BluetoothListActivity.EXTRA_DEVICE_ADDRESS);
//初始化DeviceConnFactoryManager 并设置信息
new DeviceConnFactoryManager.Build()
//设置标识符
.setId(id)
//设置连接方式
.setConnMethod(DeviceConnFactoryManager.CONN_METHOD.BLUETOOTH)
//设置连接的蓝牙mac地址
.setMacAddress(macAddress)
.build();
//配置完信息,就可以打开端口连接了
Log.i("TAG", "onActivityResult: 连接蓝牙" + id);
threadPool = ThreadPool.getInstantiation();
threadPool.addTask(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].openPort();
}
});
}
}
}这里可以看到,我们是先拿到了mac地址,然后通过管理类的构建者模式进行设置参数,最后再通过管理类调用openPort方法去连接的。
6.在连接管理类中通过jar包封装的方法进行连接,并通过广播Broadcast把连接状态发送出去
public void openPort() {
deviceConnFactoryManagers[id].isOpenPort = false;
sendStateBroadcast(CONN_STATE_CONNECTING);
switch (deviceConnFactoryManagers[id].connMethod) {
case BLUETOOTH:
System.out.println("id -> " + id);
mPort = new BluetoothPort(macAddress);
isOpenPort = deviceConnFactoryManagers[id].mPort.openPort();
break;
default:
break;
}
//端口打开成功后,检查连接打印机所使用的打印机指令ESC、TSC
if (isOpenPort) {
queryCommand();
} else {
if (this.mPort != null) {
this.mPort = null;
}
sendStateBroadcast(CONN_STATE_FAILED);
}
}
这里通过实例化BluetoothPort把mac地址传入,然后调用了PortManager的openPort方法返回了一个状态。
往下看,这个switch代码块之后就是对这个状态的判断,当状态为已连接的时候调用了queryCommand方法,这个方法里面有一些操作,其中一个就是通过广播把已连接的状态发出去。
7.在MainActivity中接收广播,并根据状态对界面进行显示处理
private BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.ACTION_CONN_STATE.equals(action)) {
int state = intent.getIntExtra(DeviceConnFactoryManager.STATE, -1);
int deviceId = intent.getIntExtra(DeviceConnFactoryManager.DEVICE_ID, -1);
switch (state) {
case DeviceConnFactoryManager.CONN_STATE_DISCONNECT:
if (id == deviceId) mTvState.setText("未连接");
break;
case DeviceConnFactoryManager.CONN_STATE_CONNECTING:
mTvState.setText("连接中");
break;
case DeviceConnFactoryManager.CONN_STATE_CONNECTED:
mTvState.setText("已连接");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "已连接", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case CONN_STATE_FAILED:
mTvState.setText("未连接");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "连接失败!重试或重启打印机试试", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
/* Usb连接断开、蓝牙连接断开广播 */
} else if (ACTION_USB_DEVICE_DETACHED.equals(action)) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(CONN_STATE_DISCONN).sendToTarget();
}
}
};既然知道状态了就可以根据自己的需求去处理,这里只是简单的提示。
ok,到这连接的部分就介绍完毕了,下面开始介绍打印的部分。
蓝牙打印
打印其实是软件与硬件之间的交互,而这部分恰恰是sdk的职责所在,所以留给我们的任务已经不多了,也就相对简单很多。
1.通过线程池添加打印任务
public void printLabel() {
Log.i("TAG", "准备打印");
threadPool = ThreadPool.getInstantiation();
threadPool.addTask(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
}
});
}因为打印是耗时任务,所以不管是为了避免卡顿还是ANR,我们应该用线程池进行优化,为了方便再用单例封装起来。
2.打印之前也要先做蓝牙状态的判断,只有做到足够的严谨,才能看起来万无一失。。
public void printLabel() {
Log.i("TAG", "准备打印");
threadPool = ThreadPool.getInstantiation();
threadPool.addTask(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//先判断打印机是否连接
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id] == null ||
!DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].getConnState()) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(CONN_PRINTER).sendToTarget();
return;
}
...
}
});
}这里呢,因为是在子线程,所以通过handler在主线程更新ui或者给个提示
@SuppressLint("HandlerLeak")
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case CONN_STATE_DISCONN:
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id] != null || !DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].getConnState()) {
DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].closePort(id);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "成功断开连接", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case PRINTER_COMMAND_ERROR:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "请选择正确的打印机指令", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case CONN_PRINTER:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "请先连接打印机", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}; public void printLabel() {
Log.i("TAG", "准备打印");
threadPool = ThreadPool.getInstantiation();
threadPool.addTask(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//先判断打印机是否连接
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id] == null ||
!DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].getConnState()) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(CONN_PRINTER).sendToTarget();
return;
}
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].getCurrentPrinterCommand() == PrinterCommand.TSC) {
Log.i("TAG", "开始打印");
sendLabel();
} else {
mHandler.obtainMessage(PRINTER_COMMAND_ERROR).sendToTarget();
}
}
});
}4.设置打印数据,发送打印数据
private void sendLabel() {
LabelCommand tsc = new LabelCommand();
tsc.addSize(40, 30); // 设置标签尺寸,按照实际尺寸设置
tsc.addGap(1); // 设置标签间隙,按照实际尺寸设置,如果为无间隙纸则设置为0
tsc.addDirection(LabelCommand.DIRECTION.FORWARD, LabelCommand.MIRROR.NORMAL);// 设置打印方向
tsc.addQueryPrinterStatus(LabelCommand.RESPONSE_MODE.ON);//开启带Response的打印,用于连续打印
tsc.addReference(0, 0);// 设置原点坐标
tsc.addTear(EscCommand.ENABLE.ON); // 撕纸模式开启
tsc.addCls();// 清除打印缓冲区
// 绘制简体中文
tsc.addText(30, 30, LabelCommand.FONTTYPE.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1,
"这是标题");
tsc.addText(200, 30, LabelCommand.FONTTYPE.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1,
"序号:" + "1");
tsc.addText(30, 90, LabelCommand.FONTTYPE.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1,
"价格:" + "99.00");
tsc.addText(30, 140, LabelCommand.FONTTYPE.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1,
"数量:" + "99");
tsc.addText(30, 190, LabelCommand.FONTTYPE.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1, LabelCommand.FONTMUL.MUL_1,
"日期:" + "2020-02-02");
// 绘制图片
// Bitmap b = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
// tsc.addBitmap(20, 50, LabelCommand.BITMAP_MODE.OVERWRITE, b.getWidth(), b);
//二维码
tsc.addQRCode(200, 90, LabelCommand.EEC.LEVEL_L, 4, LabelCommand.ROTATION.ROTATION_0, "www.baidu.com");
tsc.addPrint(1, 1); // 打印标签
tsc.addSound(2, 100); // 打印标签后 蜂鸣器响
/* 发送数据 */
Vector data = tsc.getCommand();
if (DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id] == null) {
Log.i("TAG", "sendLabel: 打印机为空");
return;
}
DeviceConnFactoryManager.getDeviceConnFactoryManagers()[id].sendDataImmediately(data);
} 数据及显示的位置,根据自己的需求做调整。
ok,以上基本是核心代码了,注释都有,按照上面这个顺序来走的话思路还是很清晰的
GitHub