SpringBoot集成Spring Security(6)——登录管理
文章目录
- 一、自定义认证成功、失败处理
- 1.1 CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler
- 1.2 CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler
- 1.3 修改 WebSecurityConfig
- 1.4 运行程序
- 二、Session 超时
- 三、限制最大登录数
- 四、踢出用户
- 五、退出登录
- 六、Session 共享
- 6.1 配置 Redis
- 6.2 配置 Session 共享
- 6.3 运行程序
在本篇中,主要关注登录的管理,因此代码使用最原始版本的即可,即《SpringBoot集成Spring Security(1)——入门程序》源码即可。
源码地址:https://github.com/jitwxs/blog_sample
一、自定义认证成功、失败处理
有些时候我们想要在认证成功后做一些业务处理,例如添加积分;有些时候我们想要在认证失败后也做一些业务处理,例如记录日志。
在之前的文章中,关于认证成功、失败后的处理都是如下配置的:
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
// .antMatchers().permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.failureUrl("/login/error")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/")
.permitAll()
...;
即 failureUrl() 指定认证失败后Url,defaultSuccessUrl() 指定认证成功后Url。我们可以通过设置 successHandler() 和 failureHandler() 来实现自定义认证成功、失败处理。
PS:当我们设置了这两个后,需要去除
failureUrl()和defaultSuccessUrl()的设置,否则无法生效。这两套配置同时只能存在一套。
1.1 CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler
自定义 CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler 类来实现 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口,用来处理认证成功后逻辑:
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
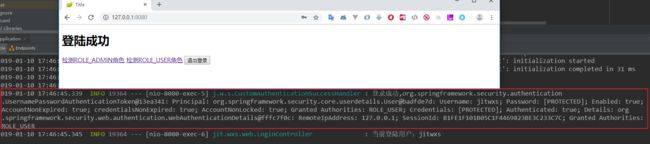
logger.info("登录成功,{}", authentication);
response.sendRedirect("/");
}
}
onAuthenticationSuccess() 方法的第三个参数 Authentication 为认证后该用户的认证信息,这里打印日志后,重定向到了首页。
1.2 CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler
自定义 CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler 类来实现 AuthenticationFailureHandler 接口,用来处理认证失败后逻辑:
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
logger.info("登陆失败");
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(exception.getMessage()));
}
}
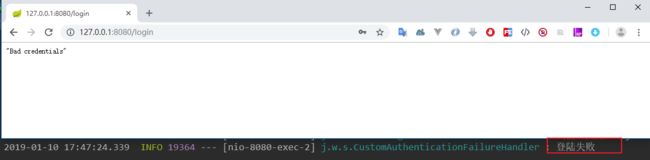
onAuthenticationFailure()方法的第三个参数 exception 为认证失败所产生的异常,这里也是简单的返回到前台。
1.3 修改 WebSecurityConfig
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler customAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler customAuthenticationFailureHandler;
...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
// .antMatchers().permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.successHandler(customAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(customAuthenticationFailureHandler)
// .failureUrl("/login/error")
// .defaultSuccessUrl("/")
.permitAll()
...;
// 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
...
}
- 首先将
customAuthenticationSuccessHandler和customAuthenticationFailureHandler注入进来 - 配置
successHandler()和failureHandler() - 注释
failureUrl()和defaultSuccessUrl()
1.4 运行程序
运行程序,当我们成功登陆后,发现日志信息被打印出来,页面被重定向到了首页:
当我们认证失败后,发现日志中“登陆失败”被打印出来,页面展示了认证失败的异常消息:
二、Session 超时
当用户登录后,我们可以设置 session 的超时时间,当达到超时时间后,自动将用户退出登录。
Session 超时的配置是 SpringBoot 原生支持的,我们只需要在 application.properties 配置文件中配置:
# session 过期时间,单位:秒
server.servlet.session.timeout=60
Tip:
从用户最后一次操作开始计算过期时间。
过期时间最小值为 60 秒,如果你设置的值小于 60 秒,也会被更改为 60 秒。
我们可以在 Spring Security 中配置处理逻辑,在 session 过期退出时调用。修改 WebSecurityConfig 的 configure() 方法,添加:
.sessionManagement()
// 以下二选一
//.invalidSessionStrategy()
//.invalidSessionUrl();
Spring Security 提供了两种处理配置,一个是 invalidSessionStrategy(),另外一个是 invalidSessionUrl()。
这两个的区别就是一个是前者是在一个类中进行处理,后者是直接跳转到一个 Url。简单起见,我就直接用 invalidSessionUrl()了,跳转到 /login/invalid,我们需要把该 Url 设置为免授权访问, 配置如下:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
.antMatchers("/login/invalid").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
...
.sessionManagement()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/invalid");
// 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
在 controller 中写一个接口进行处理:
@RequestMapping("/login/invalid")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)
@ResponseBody
public String invalid() {
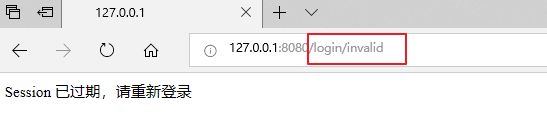
return "Session 已过期,请重新登录";
}
运行程序,登陆成功后等待一分钟(或者重启服务器),刷新页面:
三、限制最大登录数
接下来实现限制最大登陆数,原理就是限制单个用户能够存在的最大 session 数。
在上一节的基础上,修改 configure() 为:
.sessionManagement()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/invalid")
.maximumSessions(1)
// 当达到最大值时,是否保留已经登录的用户
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
// 当达到最大值时,旧用户被踢出后的操作
.expiredSessionStrategy(new CustomExpiredSessionStrategy())
增加了下面三行代码,其中:
maximumSessions(int):指定最大登录数maxSessionsPreventsLogin(boolean):是否保留已经登录的用户;为true,新用户无法登录;为 false,旧用户被踢出expiredSessionStrategy(SessionInformationExpiredStrategy):旧用户被踢出后处理方法
maxSessionsPreventsLogin()可能不太好理解,这里我们先设为 false,效果和 QQ 登录是一样的,登陆后之前登录的账户被踢出。
编写 CustomExpiredSessionStrategy 类,来处理旧用户登陆失败的逻辑:
public class CustomExpiredSessionStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
// private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onExpiredSessionDetected(SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException, ServletException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("code", 0);
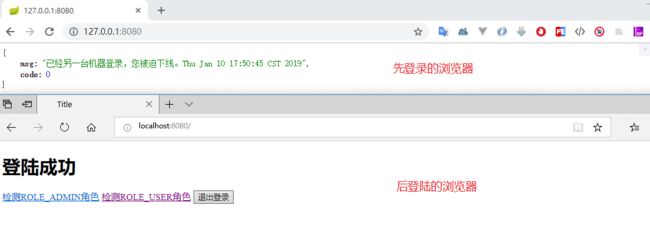
map.put("msg", "已经另一台机器登录,您被迫下线。" + event.getSessionInformation().getLastRequest());
// Map -> Json
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map);
event.getResponse().setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
event.getResponse().getWriter().write(json);
// 如果是跳转html页面,url代表跳转的地址
// redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(event.getRequest(), event.getResponse(), "url");
}
}
在 onExpiredSessionDetected() 方法中,处理相关逻辑,我这里只是简单的返回一句话。
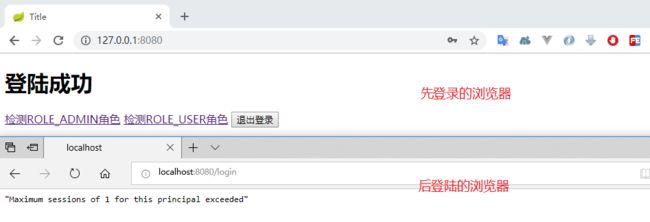
执行程序,打开两个浏览器,登录同一个账户。因为我设置了 maximumSessions(1),也就是单个用户只能存在一个 session,因此当你刷新先登录的那个浏览器时,被提示踢出了。
下面我们来测试下 maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true) 时的情况,我们发现第一个浏览器登录后,第二个浏览器无法登录:
四、踢出用户
下面来看下如何主动踢出一个用户。
首先需要在容器中注入名为 SessionRegistry 的 Bean,这里我就简单的写在 WebSecurityConfig 中:
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
修改 WebSecurityConfig 的 configure() 方法,在最后添加一行 .sessionRegistry():
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Bean
public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry() {
return new SessionRegistryImpl();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
.antMatchers("/login/invalid").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.successHandler(customAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(customAuthenticationFailureHandler)
.permitAll().and()
.logout().and()
.sessionManagement()
.invalidSessionUrl("/login/invalid")
.maximumSessions(1)
// 当达到最大值时,是否保留已经登录的用户
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)
// 当达到最大值时,旧用户被踢出后的操作
.expiredSessionStrategy(new CustomExpiredSessionStrategy())
.sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry());
// 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
}
编写一个接口用于测试踢出用户:
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry;
...
@GetMapping("/kick")
@ResponseBody
public String removeUserSessionByUsername(@RequestParam String username) {
int count = 0;
// 获取session中所有的用户信息
List<Object> users = sessionRegistry.getAllPrincipals();
for (Object principal : users) {
if (principal instanceof User) {
String principalName = ((User)principal).getUsername();
if (principalName.equals(username)) {
// 参数二:是否包含过期的Session
List<SessionInformation> sessionsInfo = sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(principal, false);
if (null != sessionsInfo && sessionsInfo.size() > 0) {
for (SessionInformation sessionInformation : sessionsInfo) {
sessionInformation.expireNow();
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
return "操作成功,清理session共" + count + "个";
}
}
sessionRegistry.getAllPrincipals();获取所有 principal 信息- 通过 principal.getUsername 是否等于输入值,获取到指定用户的 principal
sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(principal, false)获取该 principal 上的所有 session- 通过
sessionInformation.expireNow()使得 session 过期
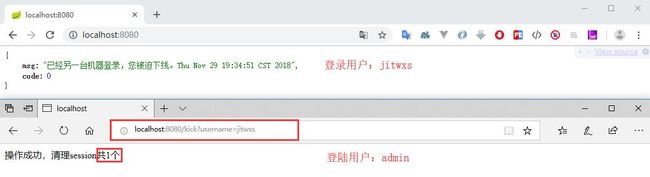
运行程序,分别使用 admin 和 jitwxs 账户登录,admin 访问 /kick?username=jitwxs 来踢出用户 jitwxs,jitwxs 刷新页面,发现被踢出。
五、退出登录
补充一下退出登录的内容,在之前,我们直接在 WebSecurityConfig 的 configure() 方法中,配置了:
http.logout();
这就是 Spring Security 的默认退出配置,Spring Security 在退出时候做了这样几件事:
- 使当前的 session 失效
- 清除与当前用户有关的 remember-me 记录
- 清空当前的 SecurityContext
- 重定向到登录页
Spring Security 默认的退出 Url 是 /logout,我们可以修改默认的退出 Url,例如修改为 /signout:
http.logout()
.logoutUrl("/signout");
我们也可以配置当退出时清除浏览器的 Cookie,例如清除 名为 JSESSIONID 的 cookie:
http.logout()
.logoutUrl("/signout")
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID");
我们也可以配置退出后处理的逻辑,方便做一些别的操作:
http.logout()
.logoutUrl("/signout")
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID")
.logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler);
创建类 DefaultLogoutSuccessHandler:
@Component
public class CustomLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
String username = ((User) authentication.getPrincipal()).getUsername();
log.info("退出成功,用户名:{}", username);
// 重定向到登录页
response.sendRedirect("/login");
}
}
最后把它注入到 WebSecurityConfig 即可:
@Autowired
private CustomLogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler;
退出登录的比较简单,我就直接贴代码,不截图了。
六、Session 共享
在最后补充下关于 Session 共享的知识点,一般情况下,一个程序为了保证稳定至少要部署两个,构成集群。那么就牵扯到了 Session 共享的问题,不然用户在 8080 登录成功后,后续访问了 8060 服务器,结果又提示没有登录。
这里就简单实现下 Session 共享,采用 Redis 来存储。
6.1 配置 Redis
为了方便起见,我直接使用 Docker 快速部署,如果你需要传统方式安装,可以参考文章《Redis初探(1)——Redis的安装》。
docker pull redis
docker run --name myredis -p 6379:6379 -d redis
docker exec -it myredis redis-cli
这样就启动了 redis,并且进入到 redis 命令行中。
6.2 配置 Session 共享
首先需要导入依赖,因为我们采用 Redis 方式实现,因此导入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.sessiongroupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
在 application.xml 中新增配置指定 redis 地址以及 session 的存储方式:
spring.redis.host=192.168.139.129
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.session.store-type=redis
然后为主类添加 @EnableRedisHttpSession 注解。
@EnableRedisHttpSession
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
6.3 运行程序
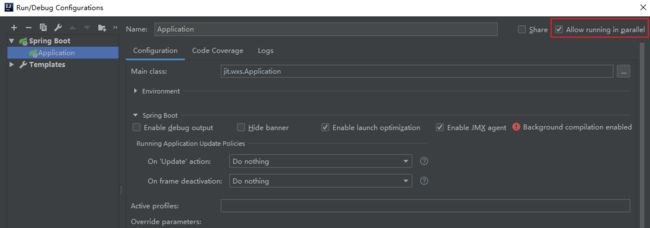
这样就完成了基于 Redis 的 Session 共享,下面来测试下。首先修改 IDEA 配置来允许项目在多端口运行,勾选 Allow running in parallel:
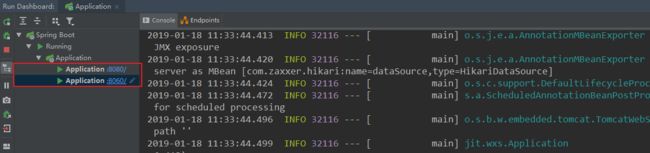
运行程序,然后修改配置文件,将 server.port 更改为 8060,再次运行。这样项目就会分别在默认的 8080 端口和 8060 端口运行。
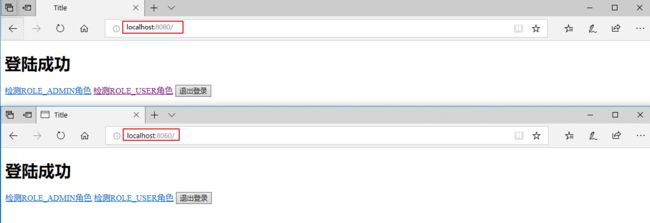
先访问 localhost:8080,登录成功后,再访问 localhost:8060,发现无需登录。
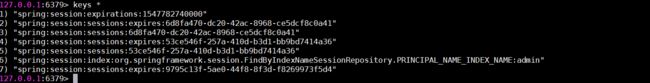
然后我们进入 Redis 查看下 key:
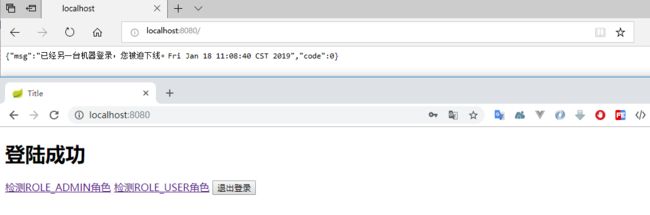
最后再测试下之前配置的 session 设置是否还有效,使用其他浏览器登陆,登陆成功后发现原浏览器用户的确被踢出。