在ubuntu16.04下安装clion
安装CLion
1、从CLion官网下载最新版CLion安装包,其Linux版是.tar.gz的压缩包。
方法一:去官网直接下载 https://www.jetbrains.com/clion/
https://www.jetbrains.com/clion/download/#section=linux
方法二:使用 wget命令, wget https://download.jetbrains.8686c.com/cpp/CLion-2016.2.2.tar.gz
2、下载完成后,解压压缩包。
|
1
|
netcon@conwlt:~$
tar
-zxvf CLion-2016.2.2.
tar
.gz
|
3、进入到安装目录下的bin目录下,运行clion.sh即可。
|
1
2
|
netcon@conwlt:~$
cd
clion-2016.2.2
/bin/
netcon@conwlt:~
/clion-2016
.2.2
/bin
$ .
/clion
.sh
后,解压压缩包
|
运行 ./clion.sh 时如果出现 图形界面 不能显示的错误,就 运行
第一次打开点击ok
![]()
然后同意就行
![]()
CLion是收费的,可以选择试用30天,搭建了一个破解的服务器,地址是:http://idea.lanyus.com/
![]()
5.
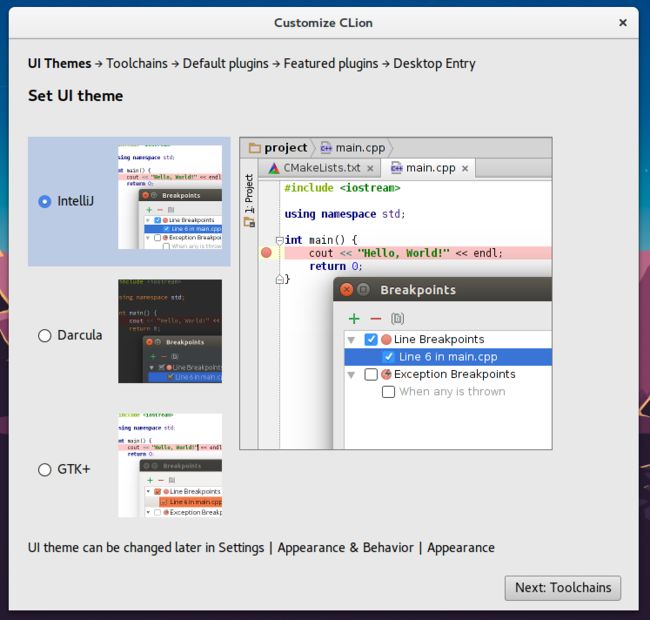
选择自己喜欢的主题。
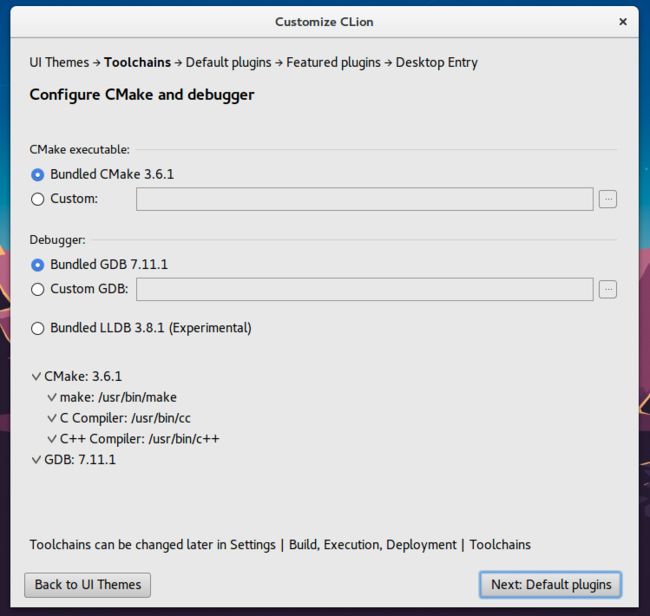
6、配置CMake及debugger,默认即可。
7、默认插件,无须改变,继续即可。
8、特色插件,按需安装,这里只是演示我没有安装,也可以以后安装。
9、最后一步,创建桌面菜单图标。
至此,CLion已经被我们成功安装!
二、创建工程及编写代码
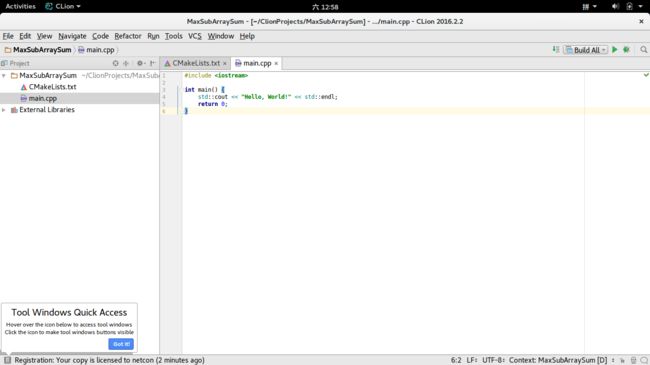
1、安装成功后我们可以在应用程序列表中找到CLion,打开后进入创建工程页面。
2、创建完成后就可以看到CLion的主界面了,左侧是工程目录,MaxSubArraySum就是我们刚刚创建的工程,展开它并打开main.cpp,我们的代码讲在这里编写(如果觉得字体不合适请自行百度如何修改,这里不再介绍)。
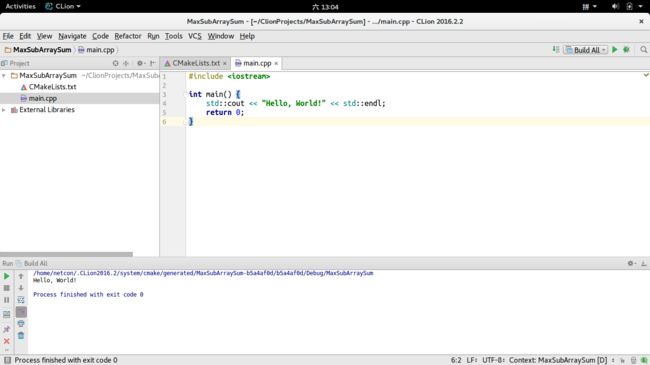
3、点击Run -> Run 'Build All',即可运行程序。(首次运行可能要求编辑配置文件,只需要将Target设置为MaxSubArraySum即可)。
运行成功!在下方的控制台可以看到结果!
三、使用Coding.net存放代码
我们已经完成了编写代码的任务,接下来把代码push到远程git仓库吧!
CLion当然支持版本控制工具,建立好Git仓库后,右键项目名称,依次选择Git -> Repositories -> push即可。
我们可以在CLion中方便的使用Git的各种功能而不用输入Git命令,但是个人还是喜欢Shell操作。
项目地址:https://coding.net/u/netcon/p/MaxSubArraySum/git
关于最大连续子数列和问题的解法可以参考这篇文章:
经典算法问题 - 最大连续子数列和
关于Coding.net和Git的使用可以参考这两篇文章:
1、Coding.net简单使用指南
2、Git简易使用指南
四、测试代码
1、单元测试
由于代码使用C++语言编写, CLion没有官方的CUnit单元测试插件(貌似这方面就VS做得好,可惜不能跨平台),如果使用的话可以把测试框架的源码拷贝到工程中,与其多此一举,不如直接在Shell中测试,我这里采用了Google的GTest测试框架,并进行了简单配置,以下时配置后的GTest目录结构:
netcon@conwlt:~/gtest$ tree -L 2
.
├── codes
│ ├── main.cpp
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── test.cpp
├── include
│ └── gtest
└── src
├── gtest-all.cc
├── gtest.cc
├── gtest-death-test.cc ├── gtest-filepath.cc ├── gtest-internal-inl.h ├── gtest_main.cc ├── gtest-port.cc ├── gtest-printers.cc ├── gtest-test-part.cc └── gtest-typed-test.cc 4 directories, 13 files netcon@conwlt:~/gtest$
下面是其Makefile。
GTEST_DIR = .. USER_DIR = . CPPFLAGS += -isystem $(GTEST_DIR)/include CXXFLAGS += -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread TESTS = run_test GTEST_HEADERS = $(GTEST_DIR)/include/gtest/*.h \ $(GTEST_DIR)/include/gtest/internal/*.h FILES = $(foreach d, $(USER_DIR), $(wildcard $(d)/*.cpp)) OBJS = $(patsubst %.cpp, %.o, $(FILES)) all : $(TESTS) clean : rm -f $(TESTS) gtest_main.a *.o GTEST_SRCS_ = $(GTEST_DIR)/src/*.cc $(GTEST_DIR)/src/*.h $(GTEST_HEADERS) gtest-all.o : $(GTEST_SRCS_) $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) -I$(GTEST_DIR) $(CXXFLAGS) -c \ $(GTEST_DIR)/src/gtest-all.cc gtest_main.o : $(GTEST_SRCS_) $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) -I$(GTEST_DIR) $(CXXFLAGS) -c \ $(GTEST_DIR)/src/gtest_main.cc gtest_main.a : gtest-all.o gtest_main.o $(AR) $(ARFLAGS) $@ $^ %.o : %.cpp $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -c $< -o $@ $(TESTS) : $(OBJS) gtest_main.a $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) -lpthread $^ -o $@
我们用其测试以下MaxSubArraySum项目中nlogn分支下的代码,这份代码是采用分治法解决这个问题的,源码及测试代码如下:
/** * File name: main.cpp * * 最大连续子数列问题的O(NlogN)解法,分治法 * * Author: netcon * Email: [email protected] * Blog: http://conw.net * */ //N是数组长度,num是待计算的数组 int solve(int N, int *num, int left, int right) { //数列长度为1时 if(left == right) return num[left]; //划分为两个规模更小的问题 int mid = (left + right) >> 1; int lans = solve(N, num, left, mid); int rans = solve(N, num, mid + 1, right); //横跨分割点的情况 int sum = 0, lmax = num[mid], rmax = num[mid + 1]; for(int i = mid; i >= left; i--) { sum += num[i]; if(sum > lmax) lmax = sum; } sum = 0; for(int i = mid + 1; i <= right; i++) { sum += num[i]; if(sum > rmax) rmax = sum; } //答案是三种情况的最大值 int ans = lmax + rmax; if(lans > ans) ans = lans; if(rans > ans) ans = rans; return ans; }
/** * File name: test.cpp */ #include "gtest/gtest.h" int solve(int, int *, int, int); int N[3] = {5, 5, 8}; int num[3][8] = { {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, {-1, -2, -3, -4, -5}, {} }; int ans[3] = {15, -1, 14}; TEST(MaxSubArraySum, Positive) { EXPECT_EQ(ans[0], solve(N[0], num[0], 0, N[0] - 1)); } TEST(MaxSubArraySum, Negative) { EXPECT_EQ(ans[1], solve(N[1], num[1], 0, N[1] - 1)); } TEST(MaxSubArraySum, Random) { EXPECT_EQ(ans[2], solve(N[2], num[2], 0, N[2] - 1)); }
测试结果:
netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ ls main.cpp Makefile test.cpp netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ make g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c main.cpp -o main.o g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c test.cpp -o test.o g++ -isystem ../include -I.. -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c \ ../src/gtest-all.cc g++ -isystem ../include -I.. -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c \ ../src/gtest_main.cc ar rv gtest_main.a gtest-all.o gtest_main.o ar: creating gtest_main.a a - gtest-all.o a - gtest_main.o g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -lpthread main.o test.o gtest_main.a -o run_test netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ ./run_test Running main() from gtest_main.cc [==========] Running 3 tests from 1 test case. [----------] Global test environment set-up. [----------] 3 tests from MaxSubArraySum [ RUN ] MaxSubArraySum.Positive [ OK ] MaxSubArraySum.Positive (0 ms) [ RUN ] MaxSubArraySum.Negative [ OK ] MaxSubArraySum.Negative (0 ms) [ RUN ] MaxSubArraySum.Random [ OK ] MaxSubArraySum.Random (0 ms) [----------] 3 tests from MaxSubArraySum (0 ms total) [----------] Global test environment tear-down [==========] 3 tests from 1 test case ran. (0 ms total) [ PASSED ] 3 tests. netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ make clean rm -f run_test gtest_main.a *.o netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$
2、大规模数据测试
大量的数据测试是最能体现代码正确性的,这里我写了一个生成数据的脚本自动生成数据。
# generate the test data import random # N is the length of the sequence N = 10000000 # MAX_ABS is the max absolute value of the numbers in the sequence MAX_ABS = 1024 def rand(n): return int((random.random() - 0.5) * 2 * n) out = str(rand(MAX_ABS)) for i in range(1, N): out += ' ' + str(rand(MAX_ABS)) print(N) print(out)
上述Python脚本会生成一千万规模的数据!那么如何测试呢,我们使用一个O(N)的算法与一个O(NlogN)的程序比较结果是否相同。
先看一下各文件的内容:
/** * File name: nlogn.cpp * * 最大连续子数列问题的O(NlogN)解法,分治法 * * Author: netcon * Email: [email protected] * Blog: http://conw.net * */ #include//N是数组长度,num是待计算的数组,放在全局区是因为可以开很大的数组 int N, num[16777216]; int solve(int left, int right) { //数列长度为1时 if(left == right) return num[left]; //划分为两个规模更小的问题 int mid = (left + right) >> 1; int lans = solve(left, mid); int rans = solve(mid + 1, right); //横跨分割点的情况 int sum = 0, lmax = num[mid], rmax = num[mid + 1]; for(int i = mid; i >= left; i--) { sum += num[i]; if(sum > lmax) lmax = sum; } sum = 0; for(int i = mid + 1; i <= right; i++) { sum += num[i]; if(sum > rmax) rmax = sum; } //答案是三种情况的最大值 int ans = lmax + rmax; if(lans > ans) ans = lans; if(rans > ans) ans = rans; return ans; } int nlogn() { freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); //输入数据 scanf("%d", &N); for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) scanf("%d", &num[i]); int ans = solve(1, N); return ans; }
/** * File name: on.cpp * * 最大连续子数列问题的O(N)解法,空间复杂度O(1) * * Author: netcon * Email: [email protected] * Blog: http://conw.net * */ #includeint on() { int N, n, s, ans, m = 0; freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); scanf("%d%d", &N, &n); //读取数组长度和数列中的第一个数 ans = s = n; //把ans初始化为数列中的的第一个数 for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) { if(s < m) m = s; scanf("%d", &n); s += n; if(s - m > ans) ans = s - m; } return ans; }
测试文件很简单:
/** * File name: test.cpp */ #include "gtest/gtest.h" int on(); int nlogn(); TEST(MaxSubArraySum, Positive) { EXPECT_EQ(on(), nlogn()); }
测试结果:
netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ ls in.txt Makefile nlogn.cpp on.cpp test.cpp test.py netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ python test.py > in.txt netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ make g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c on.cpp -o on.o g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c test.cpp -o test.o g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c nlogn.cpp -o nlogn.o g++ -isystem ../include -I.. -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c \ ../src/gtest-all.cc g++ -isystem ../include -I.. -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -c \ ../src/gtest_main.cc ar rv gtest_main.a gtest-all.o gtest_main.o ar: creating gtest_main.a a - gtest-all.o a - gtest_main.o g++ -isystem ../include -g -Wall -Wextra -pthread -lpthread on.o test.o nlogn.o gtest_main.a -o run_test netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ ./run_test Running main() from gtest_main.cc [==========] Running 1 test from 1 test case. [----------] Global test environment set-up. [----------] 1 test from MaxSubArraySum [ RUN ] MaxSubArraySum.Positive [ OK ] MaxSubArraySum.Positive (2790 ms) [----------] 1 test from MaxSubArraySum (2790 ms total) [----------] Global test environment tear-down [==========] 1 test from 1 test case ran. (2790 ms total) [ PASSED ] 1 test. netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$ make clean rm -f run_test gtest_main.a *.o netcon@conwlt:~/gtest/codes$
测试通过!而且速度很快!一千万的数据不到三秒的时间两个程序都跑完了,我觉得,这还是IO占了很大一部分时间,而且O(NlogN)也确实会比O(N)慢很多。
| 用例编号 | 用例描述 | 输入数据 | 预期输出数据 | 实际输出数据 | 通过/不通过 | 评价 |
| 0 | 全是正数的测试样例 | 1 2 3 4 5 | 15 | 15 | 通过 | 输入数据全是正数, 结果必然时数列的和 |
| 1 | 全是负数的测试样例 | -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 | -1 | -1 | 通过 | 输入数据全是负数,结 果必然时数列中最小值 |
| 2 | 正数负数混合的随机数列 | -2 6 -1 5 4 -7 2 3 | 14 | 14 | 通过 | 输入数据正负数混合,则 需要考虑多种情况。 |
| 3 | 一千万规模的数据 | 不能展示 | 不同版本程序输出相同 | 不同版本程序输出相同 | 通过 | 用很大规模的数据测试 程序,可以覆盖程序尽可 能多的情况,并且考察程 序的执行效率。虽无法知道 数据的正确结果,但多个版 本的算法都得到相同答案, 可基本证明程序没问题。 |