一文搞定Spring MVC (世上最全知识点一网打尽)
Spring MVC
Spring MVC 是目前主流的实现 MVC 设计模式的企业级开发框架,Spring 框架的一个子模块,无需整合,开发起来更加便捷。
什么是 MVC 设计模式?
将应用程序分为 Controller、Model、View 三层,Controller 接收客户端请求,调用 Model 生成业务数据,传递给 View。
Spring MVC 就是对这套流程的封装,屏蔽了很多底层代码,开放出接口,让开发者可以更加轻松、便捷地完成基于 MVC 模式的 Web 开发。
Spring MVC 的核心组件
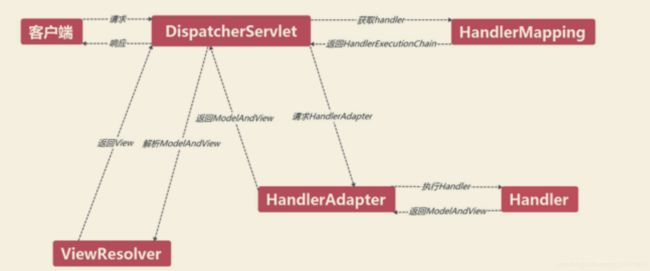
- DispatcherServlet:前置控制器,是整个流程控制的核心,控制其他组件的执行,进行统一调度,降低组件之间的耦合性,相当于总指挥。
- Handler:处理器,完成具体的业务逻辑,相当于 Servlet 或 Action。
- HandlerMapping:DispatcherServlet 接收到请求之后,通过 HandlerMapping 将不同的请求映射到不同的 Handler。
- HandlerInterceptor:处理器拦截器,是一个接口,如果需要完成一些拦截处理,可以实现该接口。
- HandlerExecutionChain:处理器执行链,包括两部分内容:Handler 和 HandlerInterceptor(系统会有一个默认的 HandlerInterceptor,如果需要额外设置拦截,可以添加拦截器)。
- HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,Handler 执行业务方法之前,需要进行一系列的操作,包括表单数据的验证、数据类型的转换、将表单数据封装到 JavaBean 等,这些操作都是由 HandlerApater 来完成,开发者只需将注意力集中业务逻辑的处理上,DispatcherServlet 通过 HandlerAdapter 执行不同的 Handler。
- ModelAndView:装载了模型数据和视图信息,作为 Handler 的处理结果,返回给 DispatcherServlet。
- ViewResolver:视图解析器,DispatcheServlet 通过它将逻辑视图解析为物理视图,最终将渲染结果响应给客户端。
Spring MVC 的工作流程
- 客户端请求被 DispatcherServlet 接收。
- 根据 HandlerMapping 映射到 Handler。
- 生成 Handler 和 HandlerInterceptor。
- Handler 和 HandlerInterceptor 以 HandlerExecutionChain 的形式一并返回给 DisptacherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 通过 HandlerAdapter 调用 Handler 的方法完成业务逻辑处理。
- Handler 返回一个 ModelAndView 给 DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 将获取的 ModelAndView 对象传给 ViewResolver 视图解析器,将逻辑视图解析为物理视图 View。
- ViewResovler 返回一个 View 给 DispatcherServlet。
- DispatcherServlet 根据 View 进行视图渲染(将模型数据 Model 填充到视图 View 中)。
- DispatcherServlet 将渲染后的结果响应给客户端。
Spring MVC 流程非常复杂,实际开发中很简单,因为大部分的组件不需要开发者创建、管理,只需要通过配置文件的方式完成配置即可,真正需要开发者进行处理的只有 Handler 、View 、Modle。
Spring MVC 特点
- 清晰的角色划分
- 灵活的配置功能
- 提供了大量控制器接口跟实现类
- 分离View层的实现
- 国际化支持
- 面向接口coding
如何使用?
- 创建 Maven 工程,pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.0.11.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 在 web.xml 中配置 DispatcherServlet。
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Applicationdisplay-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServletservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServletservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
- springmvc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.southwind">context:component-scan>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/">property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp">property>
bean>
beans>
- 创建 Handler
package com.southwind.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloHandler {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
}
Spring MVC 注解
-
注意一点,大部分情况下框架越复杂,自己要写的代码就越简单。反而框架越简单自己要写的代码越复杂。
-
@RequestMapping
Spring MVC 通过 @RequestMapping 注解将 URL 请求与业务方法进行映射,在 Handler 的类定义处以及方法定义处都可以添加 @RequestMapping ,在类定义处添加,相当于客户端多了一层访问路径。
- @Controller
@Controller 在类定义处添加,将该类交给IoC 容器来管理(结合 springmvc.xml 的自动扫描配置使用),同时使其成为一个控制器,可以接收客户端请求。
package com.southwind.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloHandler {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
}
- @RequestMapping 相关参数
1、value:指定 URL 请求的实际地址,是 @RequestMapping 的默认值。
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
等于
@RequestMapping(value="/index")
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
2、method:指定请求的 method 类型,GET、POST、PUT、DELET。
@RequestMapping(value = "/index",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
上述代码表示 index 方法只能接收 GET 请求。如果method= 缺失了,则get,post 方法都OK。
3、params:指定请求中必须包含某些参数,否则无法调用该方法。
@RequestMapping(value = "/index",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = {"name","id=10"})
public String index(){
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
上述代码表示请求中必须包含 name 和 id 两个参数,同时 id 的值必须是 10。
关于参数绑定,在形参列表中通过添加 @RequestParam 注解完成 HTTP 请求参数与业务方法形参的映射。
@RequestMapping(value = "/index",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = {"name","id=10"})
public String index(@RequestParam("name") String str,@RequestParam("id") int age){
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("执行了index...");
return "index";
}
上述代码表示将请求的参数 name 和 id 分别赋给了形参 str 和 age ,同时自动完成了数据类型转换,将 “10” 转为了 int 类型的 10,再赋给 age,这些工作都是由 HandlerAdapter 来完成的。
Spring MVC 也支持 RESTful 风格的 URL。
传统类型:http://localhost:8080/hello/index?name=zhangsan&id=10
REST:http://localhost:8080/hello/index/zhangsan/10
@RequestMapping("/rest/{name}/{id}") // REST风格写法
public String rest(@PathVariable("name") String name,@PathVariable("id") int id){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(id);
return "index";
}
通过 @PathVariable 注解完成请求参数与形参的映射。
- 映射 Cookie
Spring MVC 通过映射可以直接在业务方法中获取 Cookie 的值。
@RequestMapping("/cookie")
public String cookie(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID") String sessionId){
System.out.println(sessionId);
return "index";
}
- 使用 JavaBean 绑定参数
Spring MVC 会根据请求参数名和 JavaBean 属性名进行自动匹配,自动为对象填充属性值,同时支持及联属性。
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Address {
private String value;
}
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private Address address;
}
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/24
Time: 13:47
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>registertitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/hello/save" method="post">
用户ID :<input type="text" name="id">br>
姓名:<input type="text" name="name">br>
地址信息: <input type="text" name="address.value">br>
<input type="submit" value="注册"/>
form>
body>
html>
@RequestMapping(value = "/save",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "index";
}
如果出现中文乱码问题,只需在 web.xml 添加 Spring MVC 自带的过滤器即可。
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encodingparam-name>
<param-value>UTF-8param-value>
init-param>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
- JSP 页面的转发和重定向:
Spring MVC 默认是以转发的形式响应 JSP。比如这个登陆页面点击后 地址栏是以前的URL,但是网页显示信息是index.jsp的
@RequestMapping("/forward")
public String forward(){// 关键字
return "forward:/index.jsp"; //跟下面一样功能
// return "index";
}
2、重定向 页面跳转 地址栏会改变
@RequestMapping("/redirect")
public String redirect(){ //关键字
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
Spring MVC 数据绑定
数据绑定:在后端的业务方法中直接获取客户端 HTTP 请求中的参数,将请求参数映射到业务方法的形参中,Spring MVC 中数据绑定的工作是由 HandlerAdapter 来完成的。
![]()
- 基本数据类型
package com.southwind.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@RequestMapping("/data")
@Controller
public class DataBindHandler {
@RequestMapping("/baseType")
@ResponseBody
public String baseType(int id){
return 1+""; // 会自动调用系统的逻辑视图解析器
}
}
@ResponseBody 表示 Spring MVC 会直接将业务方法的返回值响应给客户端,如果不加 @ResponseBody 注解,Spring MVC 会将业务方法的放回值传递给 DispatcherServlet,再由 DisptacherServlet 调用 ViewResolver 对返回值进行解析,映射到一个 JSP 资源。
- 包装类
@RequestMapping("/packageType")
@ResponseBody
public String packageType(@RequestParam(value = "num",required = false,defaultValue = "0") Integer id){
return id+"";
}
包装类可以接收 null,当 HTTP 请求没有参数时,使用包装类定义形参的数据类型,程序不会抛出异常。
@RequestParam
value = “num”:将 HTTP 请求中名为 num 的参数赋给形参 id。
requried:设置 num 是否为必填项,true 表示必填,false 表示非必填,默认值true。
defaultValue = “0”:如果 HTTP 请求中没有 num 参数,默认值为0.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/data")
public class DataBindHandler {
@RequestMapping("/array")
public String array(String[] name){
String str = Arrays.toString(name);
return str;
}
}
@RestController 表示该控制器会直接将业务方法的返回值响应给客户端,不进行视图解析。
@Controller 表示该控制器的每一个业务方法的返回值都会交给视图解析器进行解析,如果只需要将数据响应给客户端,而不需要进行视图解析,则需要在对应的业务方法定义处添加 @ResponseBody。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/data")
public class DataBindHandler {
@RequestMapping("/array")
public String array(String[] name){
String str = Arrays.toString(name);
return str;
}
}
等同于
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/data")
public class DataBindHandler {
@RequestMapping("/array")
@ResponseBody //重复书写
public String array(String[] name){
String str = Arrays.toString(name);
return str;
}
}
- List
Spring MVC 不支持 List 类型的直接转换,需要对 List 集合进行包装。
集合封装类
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class UserList {
private List<User> users;
}
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/24
Time: 15:51
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/data/list" method="post">
用户1编号:<input type="text" name="users[0].id"/>
用户1姓名:<input type="text" name="users[0].name"/>
用户2编号:<input type="text" name="users[1].id"/>
用户2姓名:<input type="text" namea="users[1].name"/>
用户3编号:<input type="text" name="users[2].id"/>
用户3姓名:<input type="text" name="users[2].name"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>
业务方法
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String list(UserList userList){
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
for(User user:userList.getUsers()){
str.append(user);
}
return str.toString();
}
处理 @ResponseBody 中文乱码,在 springmvc.xml 中配置消息转换器。
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8">property>
bean>
mvc:message-converters>
mvc:annotation-driven>
- Map
自定义封装类
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
public class UserMap {
private Map<String,User> users;
}
业务方法
@RequestMapping("/map")
public String map(UserMap userMap){
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
for(String key:userMap.getUsers().keySet()){
User user = userMap.getUsers().get(key);
str.append(user);
}
return str.toString();
}
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/24
Time: 15:51
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/data/map" method="post">
用户1编号:<input type="text" name="users['a'].id"/>
用户1姓名:<input type="text" name="users['a'].name"/>
用户2编号:<input type="text" name="users['b'].id"/>
用户2姓名:<input type="text" namea="users['b'].name"/>
用户3编号:<input type="text" name="users['c'].id"/>
用户3姓名:<input type="text" name="users['c'].name"/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>
- JSON
客户端发送JSON 格式的数据,直接通过 Spring MVC 绑定到业务方法的形参中。
处理 Spring MVC 无法加载静态资源,在 web.xml 中添加配置即可。
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>defaultservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/24
Time: 17:15
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
var user = {
"id":1,
"name":"张三"
};
$.ajax({
url:"/data/json",
data:JSON.stringify(user),
type:"POST",
contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8",
dataType:"JSON",
success:function(data){
alter(data.id+"---"+data.name);
}
})
});
script>
head>
<body>
body>
html>
业务方法
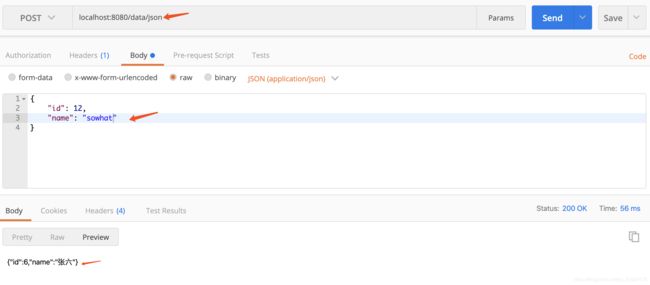
@RequestMapping("/json")
public User json(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println(user);
user.setId(6);
user.setName("张六");
return user;
}
Spring MVC 中的 JSON 和 JavaBean 的转换需要借助于 fastjson,fastjson,pom.xml 引入相关依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.32version>
dependency>
springmvc.xml 添加 fastjson 配置。
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8">property>
bean>
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter4">bean>
mvc:message-converters>
mvc:annotation-driven>
如果不太了解js代码的话 直接通过postman来测试
Spring MVC 模型数据解析
对于MVC框架来说,模型数据是最重要的,因为控制是为了产生模型数据,而试图是为了渲染模型数据。
我们都知道SpringMVC通过@RequestMapping将请求引导到处理方法上,使用合适的方法签名将请求消息绑定到入参中。方法入参绑定请求消息只是处理方法的第一步,还有更重要的任务等待完成,即:根据入参执行的相关逻辑,产生模型数据,导向到特定视图中。将模型数据暴露给视图是SpringMVC的一项重要工作。
模型数据的绑定是由 ViewResolver 来完成的,实际开发中,我们需要先添加模型数据,再交给 ViewResolver 来绑定。Spring MVC 提供了以下几种方式添加模型数据:
- Map
- Model
- ModelAndView
- @SessionAttribute
- @ModelAttribute
JSP 四大作用域对应的内置对象:pageContext、request、session、application。
将模式数据绑定到 request 对象。
1、Map
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/view")
public class ViewHandler {
@RequestMapping("/map") // 此时自动关将数据组装到模型 然后引入到视图中
public String map(Map<String, User> map) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
map.put("user", user);
return "view";
// 巧重点: map 是模型数据 view 就是视图, 模型数据会自动通过 ViewResolver 传送到 视图 view.jsp (这个视图中存在一个kv 数据跟map一样)
}
}
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/26
Time: 23:31
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
${requestScope.user}
body>
html>
@RequestMapping("/model")
public String model(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowat");
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "view";
}
3、ModelAndView
// 相当于讲上面到model 跟view 整合到一起了
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView")
public ModelAndView modelAndView(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("user",user);
modelAndView.setViewName("view");
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView2")
public ModelAndView modelAndView2(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("user",user);
View view = new InternalResourceView("/view.jsp");
modelAndView.setView(view);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView3")
public ModelAndView modelAndView3(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setName("sowhat");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("view");
modelAndView.addObject("user",user);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView4")
public ModelAndView modelAndView4(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
View view = new InternalResourceView("/view.jsp");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(view);
modelAndView.addObject("user",user);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView5")
public ModelAndView modelAndView5(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
Map<String,User> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("view",map);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView6")
public ModelAndView modelAndView6(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
Map<String,User> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("user",user);
View view = new InternalResourceView("/view.jsp");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(view,map);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView7")
public ModelAndView modelAndView7(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("view","user",user);
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView8")
public ModelAndView modelAndView8(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
View view = new InternalResourceView("/view.jsp");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(view,"user",user);
return modelAndView;
}
上面到都是间接添加的返回数据,先讲数据添加到模型,然后模型传送到view中。
4、直接讲数据添加到 HttpServletRequest
@RequestMapping("/request")
public String request(HttpServletRequest request){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
request.setAttribute("user",user); // 直接讲数据添加到requset
return "view";
}
5、@ModelAttribute
- 第一步 定义一个方法,该方法专门用来返回要填充到模型数据中的对象 该方法会在 任何请求方法之前执行 讲数据添加到模型中,切记。
@ModelAttribute // 这个优先于业务方法执行会,
public User getUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
return user; // 必须要返回的 !!!
}
@ModelAttribute
public void getUser(Map<String,User> map){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
map.put("user",user);
}
@ModelAttribute
public void getUser(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setName("张三");
model.addAttribute("user",user);
}
- 第二步 业务方法中无需再处理模型数据,只需返回视图即可。
@RequestMapping("/modelAttribute")
public String modelAttribute(){
return "view";
}
将模型数据绑定到 session 对象
因为session本来就是从request中拿出来的。
1、直接使用原生的 Servlet API。
@RequestMapping("/session") // 这里相当于 让handler 给我们创建一个request 然后再回去session
public String session(HttpServletRequest request){
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
session.setAttribute("user",user);
return "view";
}
@RequestMapping("/session2") // 直接帮我们创建好session
public String session2(HttpSession session){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("sowhat");
session.setAttribute("user",user);
return "view";
}
2、@SessionAttribute
这个一般不推荐使用,在类上定义影响到所以数据。
@SessionAttributes(value = {"user","address"}) // 相当于讲request 中所以数据 同步到了session中 “user” 名字要一样
public class ViewHandler {
}
对于 ViewHandler 中的所有业务方法,只要向 request 中添加了 key = “user”、key = “address” 的对象时,Spring MVC 会自动将该数据添加到 session 中,保存 key 不变。
@SessionAttributes(types = {User.class,Address.class})
public class ViewHandler { // 也可以通过类型添加
}
对于 ViewHandler 中的所有业务方法,只要向 request 中添加了数据类型是 User 、Address 的对象时,Spring MVC 会自动将该数据添加到 session 中,保存 key 不变。
将模型数据绑定到 application 对象
@RequestMapping("/application")
public String application(HttpServletRequest request){
ServletContext application = request.getServletContext();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setName("张三");
application.setAttribute("user",user);
return "view";
}
Spring MVC 自定义数据转换器
数据转换器是指将客户端 HTTP 请求中的参数转换为业务方法中定义的形参,自定义表示开发者可以自主设计转换的方式,HandlerApdter 已经提供了通用的转换,String 转 int,String 转 double,表单数据的封装等,但是在特殊的业务场景下,HandlerAdapter 无法进行转换,就需要开发者自定义转换器。
客户端输入 String 类型的数据 “2019-03-03”,自定义转换器将该数据转为 Date 类型的对象。
- 创建 DateConverter 转换器,实现 Conveter 接口。
package com.southwind.converter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
private String pattern;
public DateConverter(String pattern){
this.pattern = pattern;
}
@Override
public Date convert(String s) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(this.pattern);
Date date = null;
try {
date = simpleDateFormat.parse(s);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
}
- springmvc.xml 配置转换器。
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="com.southwind.converter.DateConverter">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="yyyy-MM-dd">constructor-arg>
bean>
list>
property>
bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService">
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8">property>
bean>
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter4">bean>
mvc:message-converters>
mvc:annotation-driven>
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: sowhat
Date: 2020-02-27
Time: 14:47
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/converter/date" method="post">
请输入日期:<input type="text" name="date"/>(yyyy-MM-dd)<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>
- Handler
package com.southwind.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/converter")
public class ConverterHandler {
@RequestMapping("/date")
public String date(Date date){
return date.toString();
}
}
String 转 Student
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
StudentConverter
package com.southwind.converter;
import com.southwind.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
public class StudentConverter implements Converter<String, Student> {
@Override
public Student convert(String s) {
String[] args = s.split("-");
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(Long.parseLong(args[0]));
student.setName(args[1]);
student.setAge(Integer.parseInt(args[2]));
return student;
}
}
springmvc.xml
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="com.southwind.converter.DateConverter">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="yyyy-MM-dd">constructor-arg>
bean>
<bean class="com.southwind.converter.StudentConverter">bean>
list>
property>
bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService">
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8">property>
bean>
<bean class="com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter4">bean>
mvc:message-converters>
mvc:annotation-driven>
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/27
Time: 00:40
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/converter/student" method="post">
请输入学生信息:<input type="text" name="student"/>(id-name-age)<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form>
body>
html>``
Handler
```java
@RequestMapping("/student")
public String student(Student student){
return student.toString();
}
Spring MVC REST
REST:Representational State Transfer,资源表现层状态转换,是目前比较主流的一种互联网软件架构,它结构清晰、标准规范、易于理解、便于扩展。
- 资源(Resource)
网络上的一个实体,或者说网络中存在的一个具体信息,一段文本、一张图片、一首歌曲、一段视频等等,总之就是一个具体的存在。可以用一个 URI(统一资源定位符)指向它,每个资源都有对应的一个特定的 URI,要获取该资源时,只需要访问对应的 URI 即可。
- 表现层(Representation)
资源具体呈现出来的形式,比如文本可以用 txt 格式表示,也可以用 HTML、XML、JSON等格式来表示。
- 状态转换(State Transfer)
客户端如果希望操作服务器中的某个资源,就需要通过某种方式让服务端发生状态转换,而这种转换是建立在表现层之上的,所有叫做"表现层状态转换"。
特点
- URL 更加简洁。
- 有利于不同系统之间的资源共享,只需要遵守一定的规范,不需要进行其他配置即可实现资源共享。
如何使用
REST 具体操作就是 HTTP 协议中四个表示操作方式的动词分别对应 CRUD 基本操作。
GET 用来表示获取资源。
POST 用来表示新建资源。
PUT 用来表示修改资源。
DELETE 用来表示删除资源。
Handler
package com.southwind.controller;
import com.southwind.entity.Student;
import com.southwind.entity.User;
import com.southwind.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Collection;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class RESTHandeler {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public Collection<Student> findAll(HttpServletResponse response){
response.setContentType("text/json;charset=UTF-8");
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/findById/{id}")
public Student findById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
return studentRepository.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public void save(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public void update(@RequestBody Student student){
studentRepository.saveOrUpdate(student);
}
@DeleteMapping("/deleteById/{id}")
public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") long id){
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
StudentRepository
package com.southwind.repository;
import com.southwind.entity.Student;
import java.util.Collection;
public interface StudentRepository {
public Collection<Student> findAll();
public Student findById(long id);
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student);
public void deleteById(long id);
}
StudentRepositoryImpl
package com.southwind.repository.impl;
import com.southwind.entity.Student;
import com.southwind.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Repository
public class StudentRepositoryImpl implements StudentRepository {
private static Map<Long,Student> studentMap;
static{
studentMap = new HashMap<>();
studentMap.put(1L,new Student(1L,"张三",22));
studentMap.put(2L,new Student(2L,"李四",23));
studentMap.put(3L,new Student(3L,"王五",24));
}
@Override
public Collection<Student> findAll() {
return studentMap.values();
}
@Override
public Student findById(long id) {
return studentMap.get(id);
}
@Override
public void saveOrUpdate(Student student) {
studentMap.put(student.getId(),student);
}
@Override
public void deleteById(long id) {
studentMap.remove(id);
}
}
Spring MVC 文件上传下载
单文件上传
底层是使用 Apache ==fileupload ==组件完成上传,Spring MVC 对这种方式进行了封装。
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-iogroupId>
<artifactId>commons-ioartifactId>
<version>2.5version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId>
<version>1.3.3version>
dependency>
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020/2/27
Time: 11:10
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: sowhat
Date: 2020-02-27
Time: 09:09
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/file/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="img"/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
form>
<img src="${path}">
body>
html>
1、input 的 type 设置为 file。
2、form 的 method 设置为 post(get 请求只能将文件名传给服务器)
3、from 的 enctype 设置为 multipart-form-data(如果不设置只能将文件名传给服务器)
- Handler
package com.southwind.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/file")
public class FileHandler {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(MultipartFile img, HttpServletRequest request){
if(img.getSize()>0){
//获取保存上传文件的file路径
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
//获取上传的文件名
String name = img.getOriginalFilename();
File file = new File(path,name);
try {
img.transferTo(file);
//保存上传之后的文件路径
request.setAttribute("path","/file/"+name);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return "upload";
}
}
- springmvc.xml
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">bean>
- web.xml 添加如下配置,否则客户端无法访问 png
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>defaultservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.pngurl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
多文件上传
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>jstlgroupId>
<artifactId>jstlartifactId>
<version>1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibsgroupId>
<artifactId>standardartifactId>
<version>1.1.2version>
dependency>
JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: sowhat
Date: 2020-02-27
Time: 09:09
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form action="/file/uploads" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
file1:<input type="file" name="imgs"/><br/>
file2:<input type="file" name="imgs"/><br/>
file3:<input type="file" name="imgs"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
form>
<c:forEach items="${files}" var="file" >
<img src="${file}" width="300px">
c:forEach>
body>
html>
Handler
@PostMapping("/uploads")
public String uploads(MultipartFile[] imgs,HttpServletRequest request){
List<String> files = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile img:imgs){
if(img.getSize()>0){
//获取保存上传文件的file路径
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
//获取上传的文件名
String name = img.getOriginalFilename();
File file = new File(path,name);
try {
img.transferTo(file);
//保存上传之后的文件路径
files.add("/file/"+name);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
request.setAttribute("files",files);
return "uploads";
}
下载
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020-02-27
Time::36
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<a href="/file/download/1">1.pnga>
<a href="/file/download/2">2.pnga>
<a href="/file/download/3">3.pnga>
body>
html>
- Handler
@GetMapping("/download/{name}")
public void download(@PathVariable("name") String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
if(name != null){
name += ".png";
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("file");
File file = new File(path,name);
OutputStream outputStream = null;
if(file.exists()){
response.setContentType("application/forc-download");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+name);
try {
outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file));
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(outputStream != null){
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
Spring MVC 表单标签库
- Handler
@GetMapping("/get")
public ModelAndView get(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("tag");
Student student = new Student(1L,"张三",22);
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
return modelAndView;
}
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020-02-27
Time: 16:53
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>学生信息h1>
<form:form modelAttribute="student">
学生ID:<form:input path="id"/><br/>
学生姓名:<form:input path="name"/><br/>
学生年龄:<form:input path="age"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
form:form>
body>
html>
1、JSP 页面导入 Spring MVC 表单标签库,与导入 JSTL 标签库的语法非常相似,前缀 prefix 可以自定义,通常定义为 from。
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
2、将 form 表单与模型数据进行绑定,通过 modelAttribute 属性完成绑定,将 modelAttribute 的值设置为模型数据对应的 key 值。
Handeler:modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
JSP:<form:form modelAttribute="student">
3、form 表单完成绑定之后,将模型数据的值取出绑定到不同的标签中,通过设置标签的 path 属性完成,将 path 属性的值设置为模型数据对应的属性名即可。
学生ID:
学生姓名:
学生年龄:
常用的表单标签
- form
渲染的是 HTML 中的,通过 modelAttribute 属性绑定具体的模型数据。
- input
渲染的是 HTML 中的 ,form 标签绑定的是模型数据,input 标签绑定的是模型数据中的属性值,通过 path 属性可以与模型数据中的属性名对应,并且支持及联操作。
- password
渲染的是 HTML 中的 ,通过 path 属性与模型数据的属性值进行绑定,password 标签的值不会在页面显示。
- checkbox
student.setFlag(false);
checkbox:
渲染的是 HTML 中的 ,通过 path 与模型数据的属性值进行绑定,可以绑定 boolean、数组和集合。
如果绑定 boolean 值,若该变量的值为 true,则表示该复选框选中,否则表示不选中。
如果绑定数组或者集合,数组/集合中的元素等于 checkbox 的 value 值,则选中。
student.setHobby(Arrays.asList("读书","看电影","玩游戏"));
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
爱好:<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="摄影">form:checkbox>摄影<br/>
<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="读书">form:checkbox>读书<br/>
<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="听音乐">form:checkbox>听音乐<br/>
<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="看电影">form:checkbox>看电影<br/>
<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="旅游">form:checkbox>旅游<br/>
<form:checkbox path="hobby" value="玩游戏">form:checkbox>玩游戏<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
- checkboxes
渲染的是 HTML 中的一组 ,是对
student.setHobby(Arrays.asList("摄影","读书","听音乐","看电影","旅游","玩游戏"));
student.setSelectHobby(Arrays.asList("摄影","读书","听音乐"));
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
爱好:<form:checkboxes path="selectHobby" items="${student.hobby}"/><br/>
需要注意的是 path 可以直接绑定模型数据的属性值,items 则需要通过 EL 表达式的形式从域对象中获取数据,不能直接写属性名。
- radiobutton
<from:radiobutton path="radioId" value="0"/>
渲染的是 HTML 中的一个 ,绑定的数据与标签的 value 值相等则为选中,否则不选中。
student.setRadioId(1);
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
radiobutton:<form:radiobutton path="radioId" value="1"/>radiobutton<br/>
- radiobuttons
<form:radiobuttons itmes="${student.grade}" path="selectGrade"/>
渲染的是 HTML 中的一组 ,这里需要结合 items 和 path 两个属性来使用,items 绑定被遍历的集合或数组,path 绑定被选中的值,items 为全部的可选类型,path 为默认选中的选项,用法与
Map<Integer,String> gradeMap = new HashMap<>();
gradeMap.put(1,"一年级");
gradeMap.put(2,"二年级");
gradeMap.put(3,"三年级");
gradeMap.put(4,"四年级");
gradeMap.put(5,"五年级");
gradeMap.put(6,"六年级");
student.setGradeMap(gradeMap);
student.setSelectGrade(3);
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
学生年级:<form:radiobuttons items="${student.gradeMap}" path="selectGrade"/><br/>
- select
<form:select items="${student.citys}" path="selectCity"/>
渲染的是 HTML 中的一个 标签( 下拉框形式),需要结合 items 和 path 两个属性来使用,items 绑定被遍历的集合或数组,path 绑定被选中的值,用法与
Map<Integer,String> cityMap = new HashMap<>();
cityMap.put(1,"北京");
cityMap.put(2,"上海");
cityMap.put(3,"广州");
cityMap.put(4,"深圳");
student.setCityMap(cityMap);
student.setSelectCity(3);
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
所在城市:<form:select items="${student.cityMap}" path="selectCity">form:select><br/>
- options
form:select 结合 form:options 的使用,from:select 只定义 path 属性,在 form:select 标签内部添加一个子标签 form:options ,设置 items 属性,获取被遍历的集合,跟前面的select 类似功能。
所在城市:<form:select path="selectCity">
<form:options items="${student.cityMap}">form:options>
form:select><br/>
- option
form:select结合form:option的使用,from:select定义 path 属性,给每一个form:option设置 value 值,path 的值与哪个 value 值相等,该项默认选中。
所在城市:<form:select path="selectCity">
<form:option value="1">杭州form:option>
<form:option value="2">成都form:option>
<form:option value="3">西安form:option>
form:select><br/>
- textarea
渲染的是 HTML 中的一个,path 绑定模型数据的属性值,作为文本输入域的默认值。
student.setIntroduce("你好,我是...");
modelAndView.addObject("student",student);
信息:<form:textarea path="introduce"/><br/>
- errors
处理错误信息,一般用在数据校验,该标签需要结合 Spring MVC 的验证器结合起来使用。
Spring MVC 数据校验
Spring MVC 提供了两种数据校验的方式:1、基于 Validator 接口。2、使用 Annotation JSR - 303 标准进行校验。
基于 Validator 接口的方式需要自定义 Validator 验证器,每一条数据的验证规则需要开发者手动完成,使用 Annotation JSR - 303 标准则不需要自定义验证器,通过注解的方式可以直接在实体类中添加每个属性的验证规则,这种方式更加方便,实际开发中推荐使用。
基于 Validator 接口
- 实体类 Account
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Account {
private String name;
private String password;
}
- 自定义验证器 AccountValidator,实现 Validator 接口。
package com.southwind.validator;
import com.southwind.entity.Account;
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
public class AccountValidator implements Validator {
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return Account.class.equals(aClass);
}
@Override
public void validate(Object o, Errors errors) {
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors,"name",null,"姓名不能为空");
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors,"password",null,"密码不能为空");
}
}
- 控制器
package com.southwind.controller;
import com.southwind.entity.Account;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/validator")
public class ValidatorHandler {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(Model model){
model.addAttribute("account",new Account());
return "login";
}
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(@Validated Account account, BindingResult bindingResult){
if(bindingResult.hasErrors()){
return "login";
}
return "index";
}
}
- springmvc.xml 配置验证器。
<bean id="accountValidator" class="com.southwind.validator.AccountValidator">bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="accountValidator">mvc:annotation-driven>
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: liujinjie
Date: 2020-02-27
Time: 17:31
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="from" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<form:form modelAttribute="account" action="/validator/login" method="post">
姓名:<form:input path="name"/><from:errors path="name">from:errors><br/>
密码:<form:input path="password"/><from:errors path="password">from:errors><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
form:form>
body>
html>
Annotation JSR - 303 标准
使用 Annotation JSR - 303 标准进行验证,需要导入支持这种标准的依赖 jar 文件,这里我们使用 Hibernate Validator。
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernategroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validatorartifactId>
<version>5.3.6.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validationgroupId>
<artifactId>validation-apiartifactId>
<version>2.0.1.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.logginggroupId>
<artifactId>jboss-loggingartifactId>
<version>3.3.2.Finalversion>
dependency>
- 通过注解的方式直接在实体类中添加相关的验证规则。
package com.southwind.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
@Data
public class Person {
@NotEmpty(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@Size(min = 6,max = 12,message = "密码6-12位")
private String password;
@Email(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z0-9_.-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9-]+(\\\\.[a-zA-Z0-9-]+)*\\\\.[a-zA-Z0-9]{2,6}$",message = "请输入正确的邮箱格式")
private String email;
@Pattern(regexp = "^((13[0-9])|(14[5|7])|(15([0-3]|[5-9]))|(18[0,5-9]))\\\\\\\\d{8}$",message = "请输入正确的电话")
private String phone;
}
- ValidatorHandler
@GetMapping("/register")
public String register(Model model){
model.addAttribute("person",new Person());
return "register";
}
@PostMapping("/register")
public String register(@Valid Person person, BindingResult bindingResult){
if(bindingResult.hasErrors()){
return "register";
}
return "index";
}
- springmvc.xml
<mvc:annotation-driven />
- JSP
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: southwind
Date: 2019-03-18
Time: 11:29
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
Title
用户名:
密码:
邮箱:
电话:
校验规则详解:
@Null 被注解的元素必须为null
@NotNull 被注解的元素不能为null
@Min(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@Max(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于于等于指定的最大值
@Email 被注解的元素必须是电子邮箱地址
@Pattern 被注解的元素必须符合对应的正则表达式
@Length 被注解的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
@NotEmpty 被注解的字符串的值必须非空
Null 和 Empty 是不同的结果,String str = null,str 是 null,String str = “”,str 不是 null,其值为空。
参考
B站楠哥笔记