Spring框架、依赖注入、控制反转详解及代码说明
Spring框架是一个轻量级框架,被称为javaEE的春天,是当前的主流框架。也是非侵入性的。
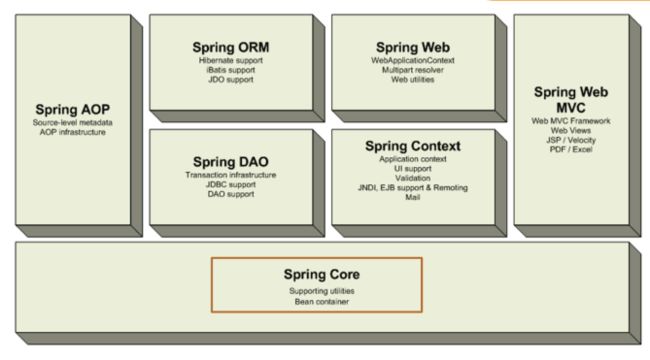
1、Spring Core
Core封装包是框架的最基础部分,提供IOC和依赖注入特性。这里的基础概念是BeanFactory,它提供对Factory模式的经典实现来消除对程序性单例模式的需要,并真正地允许你从程序逻辑中分离出依赖关系和配置。
2.Spring Context
构建于Core封装包基础上的 Context封装包,提供了一种框架式的对象访问方法,有些象JNDI注册器。Context封装包的特性得自于Beans封装包,并添加了对国际化(I18N)的支持(例如资源绑定),事件传播,资源装载的方式和Context的透明创建,比如说通过Servlet容器。
3、Spring DAO
DAO (Data Access Object)提供了JDBC的抽象层,它可消除冗长的JDBC编码和解析数据库厂商特有的错误代码。 并且,JDBC封装包还提供了一种比编程性更好的声明性事务管理方法,不仅仅是实现了特定接口,而且对所有的POJOs(plain old Java objects)都适用。
4、Spring ORM
ORM 封装包提供了常用的“对象/关系”映射APIs的集成层。 其中包括JPA、JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis 。利用ORM封装包,可以混合使用所有Spring提供的特性进行“对象/关系”映射,如前边提到的简单声明性事务管理。
5、Spring AOP
Spring的 AOP 封装包提供了符合AOP Alliance规范的面向方面的编程实现,让你可以定义,例如方法拦截器(method-interceptors)和切点(pointcuts),从逻辑上讲,从而减弱代码的功能耦合,清晰的被分离开。而且,利用source-level的元数据功能,还可以将各种行为信息合并到你的代码中。
6、Spring Web
Spring中的 Web 包提供了基础的针对Web开发的集成特性,例如多方文件上传,利用Servlet listeners进行IOC容器初始化和针对Web的ApplicationContext。当与WebWork或Struts一起使用Spring时,这个包使Spring可与其他框架结合。
7、Spring Web MVC
Spring中的MVC封装包提供了Web应用的Model-View-Controller(MVC)实现。Spring的MVC框架并不是仅仅提供一种传统的实现,它提供了一种清晰的分离模型,在领域模型代码和Web Form之间。并且,还可以借助Spring框架的其他特性。
依赖注入:
下面主要结合代码来了解什么是控制反转和依赖注入:
在Spring IOC容器读取Bean,在配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化。只有在容器实例化后,才可以从IOC容器里获取Bean实例并使用。
Spring提供了两种类型的IOC容器实现:
BeanFactory:IOC容器的底层基本实现
ApplicationContext:提供了更多的高级特性,是BeanFactory的子接口。
首先创建一个bean:
package com.jredu.spring1;
public class Hello {
private String name1;
private String laugen1;
private String name2;
private String laugen2;
public String getName1() {
return name1;
}
public void setName1(String name1) {
this.name1 = name1;
}
public String getLaugen1() {
return laugen1;
}
public void setLaugen1(String laugen1) {
this.laugen1 = laugen1;
}
public String getName2() {
return name2;
}
public void setName2(String name2) {
this.name2 = name2;
}
public String getLaugen2() {
return laugen2;
}
public void setLaugen2(String laugen2) {
this.laugen2 = laugen2;
}
public void showInfo1(){
System.out.println(name1+"说:“"+laugen1+"”");
}
public void showInfo2(){
System.out.println(name2+"说:“"+laugen2+"”");
}
}
id:Bean的名称在IOC容器中必须是唯一的,若id没有指定,Spring自动将类名作为Bean的名字。
在一个测试类中进行测试:
package com.jredu.spring1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Hello hello=(Hello)app.getBean("laugen");
hello.showInfo1();
hello.showInfo2();
}
}

从IOC容器中获取Bean,调用ApplicatonCntext的getBean方法。
XML配置Bean——依赖注入方式
Spring支持3中依赖注入的方式:属性注入、构造器注入、工厂方式注入(很少使用,不推荐)
属性注入:即通过setter方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象使用
属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式。
上述applicationContext.xml配置文件里就是应用的属性注入。
构造注入:通过构造方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了Bean实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入在
代码示例:
package com.jredu.spring1;
public class HelloSpring2 {
private String name;
private int age;
//构造注入
public HelloSpring2(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public HelloSpring2() {
super();
};
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println(name+":"+age);
}
}
在applicationContext.xml中配置:
按索引匹配入参:
在测试类中运行代码:
package com.jredu.spring1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloSpring2 hello=(HelloSpring2) app.getBean("hello2");
hello.showInfo();
}
}构造注入还有一种方式是:按类型匹配入参:
实体类:
package com.jredu.spring1;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 地区
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Areas {
private List list;
private Map map;
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
}
北京
上海
杭州
济南
烟台
package com.jredu.spring1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Areas area = (Areas) app.getBean("area");
System.out.println(area.getList());
System.out.println(area.getMap());
}
}

P命名空间:
为了简化XML文件的配置,越来越多的XML文件采用属性而非子元素配置信息。Spring从2.5版本开始引入一个新的p命名空间,可以通过
package com.jredu.spring1;
/**
* 采用属性注入的方式
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Address {
private double latitude;//纬度
private double longitude;//经度
private String name;//名称
public double getLatitude() {
return latitude;
}
public void setLatitude(double latitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
}
public double getLongitude() {
return longitude;
}
public void setLongitude(double longitude) {
this.longitude = longitude;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.jredu.spring1;
public class Person {
private String name;//姓名
private String sex;//性别
private Address address;//地区
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
package com.jredu.spring1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person p2= (Person) app.getBean("p2");
System.out.println(p2.getAddress().getName());
}
}
非