墨客科普 | MOAC BlockChain SafeMath库
在编写智能合约的时候需要注意的一个主要的安全特性:防止溢出和下溢。为了防止这些情况,OpenZeppelin建立了一个叫做SafeMath的库(library),默认情况下可以防止这些问题。
什么是溢出(overflow)
假设我们有一个uint8, 只能存储8 bit数据。这意味着我们能存储的最大数字就是二进制11111111(或者说十进制的2^8-1 =255).
来看看下面的代码。最后 number 将会是什么值?
在这个例子中,我们导致了溢出---虽然我们加了1,但是number出乎意料地等于0了。
下溢(underflow)也类似,如果你从一个等于0的uint8减去1, 它将变成255 (因为uint是无符号的,其不能等于负数)。
分析 SafeMath源码
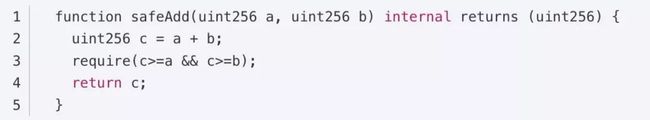
1.加法,仅限内部调用,返回 uint256
require(c>=a && c>=b); //验证结果: 两个正数相加,和一定大于每个加数
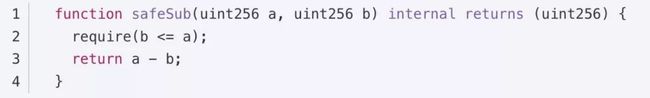
2.减法,仅限内部调用,返回 uint256
require(b <= a) 因为返回值需要是 正数,所以此处判断 b必须小于等于a
3.乘法,仅限内部调用,返回 uint256
uint256 c = a * b; 容易溢出,比如 a=2,b=2^255 乘积 2^256 刚好溢出。结果取后面的256位(全为0),导致 c=0。
所以使用 (a == 0 || c / a == b),验证结果的一致性。
4.除法,仅限内部调用,返回 uint256
require(b > 0), 确保被除数不能为0
require(a == b * c + a % b);防止溢出,验证结果的一致性
总结:
不要直接使用简单的 "+-*/" ,尽量使用 library SafeMath 中的函数,避免整数溢出的隐患。
附:完整源码
pragma solidity ^0.4.24;
library SafeMath {
/**
* @dev Returns the addition of two unsigned integers, reverting on
* overflow.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `+` operator.
*
* Requirements:
* - Addition cannot overflow.
*/
function safeAdd(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
uint256 c = a + b;
require(c >= a, "SafeMath: addition overflow");
return c;
}
/**
* @dev Returns the subtraction of two unsigned integers, reverting on
* overflow (when the result is negative).
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `-` operator.
*
* Requirements:
* - Subtraction cannot overflow.
*/
function safeSub(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
return safeSub(a, b, "SafeMath: subtraction overflow");
}
/**
* @dev Returns the subtraction of two unsigned integers, reverting with custom message on
* overflow (when the result is negative).
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `-` operator.
*
* Requirements:
* - Subtraction cannot overflow.
*
* NOTE: This is a feature of the next version of OpenZeppelin Contracts.
* @dev Get it via `npm install @openzeppelin/contracts@next`.
*/
function safeSub(uint256 a, uint256 b, string memory errorMessage) internal pure returns (uint256) {
require(b <= a, errorMessage);
uint256 c = a - b;
return c;
}
/**
* @dev Returns the multiplication of two unsigned integers, reverting on
* overflow.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `*` operator.
*
* Requirements:
* - Multiplication cannot overflow.
*/
function safeMul(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
// Gas optimization: this is cheaper than requiring 'a' not being zero, but the
// benefit is lost if 'b' is also tested.
if (a == 0) {
return 0;
}
uint256 c = a * b;
require(c / a == b, "SafeMath: multiplication overflow");
return c;
}
/**
* @dev Returns the integer division of two unsigned integers. Reverts on
* division by zero. The result is rounded towards zero.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `/` operator. Note: this function uses a
* `revert` opcode (which leaves remaining gas untouched) while Solidity
* uses an invalid opcode to revert (consuming all remaining gas).
*
* Requirements:
* - The divisor cannot be zero.
*/
function safeDiv(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
return safeDiv(a, b, "SafeMath: division by zero");
}
/**
* @dev Returns the integer division of two unsigned integers. Reverts with custom message on
* division by zero. The result is rounded towards zero.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `/` operator. Note: this function uses a
* `revert` opcode (which leaves remaining gas untouched) while Solidity
* uses an invalid opcode to revert (consuming all remaining gas).
*
* Requirements:
* - The divisor cannot be zero.
* NOTE: This is a feature of the next version of OpenZeppelin Contracts.
* @dev Get it via `npm install @openzeppelin/contracts@next`.
*/
function safeDiv(uint256 a, uint256 b, string memory errorMessage) internal pure returns (uint256) {
// Solidity only automatically asserts when dividing by 0
require(b > 0, errorMessage);
uint256 c = a / b;
return c;
}
/**
* @dev Returns the remainder of dividing two unsigned integers. (unsigned integer modulo),
* Reverts when dividing by zero.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `%` operator. This function uses a `revert`
* opcode (which leaves remaining gas untouched) while Solidity uses an
* invalid opcode to revert (consuming all remaining gas).
*
* Requirements:
* - The divisor cannot be zero.
*/
function safeMod(uint256 a, uint256 b) internal pure returns (uint256) {
return safeMod(a, b, "SafeMath: modulo by zero");
}
/**
* @dev Returns the remainder of dividing two unsigned integers. (unsigned integer modulo),
* Reverts with custom message when dividing by zero.
*
* Counterpart to Solidity's `%` operator. This function uses a `revert`
* opcode (which leaves remaining gas untouched) while Solidity uses an
* invalid opcode to revert (consuming all remaining gas).
*
* Requirements:
* - The divisor cannot be zero.
*
* NOTE: This is a feature of the next version of OpenZeppelin Contracts.
* @dev Get it via `npm install @openzeppelin/contracts@next`.
*/
function safeMod(uint256 a, uint256 b, string memory errorMessage) internal pure returns (uint256) {
require(b != 0, errorMessage);
return a % b;
}
}