Android蓝牙ble源码解析
低功耗蓝牙拥有低功耗、短距离无线传输的特性。由于这个特点,低功耗蓝牙有很多的应用场景,常见的有运动手环、运动手表、轮胎压力监测系统(Tire Pressure Monitoring System,TPMS),以及各种我们能想到的短距离的人与设备交互的场景。如果哪天有个产品经理推出一款这种场景下的革命性的产品出来,拥有低功耗蓝牙开发经验的程序员就能更早踏足这个领域。本文是对android系统的蓝牙ble相关的api的源码的解析。
入口 BluetoothManager
BluetoothManager是Android蓝牙开发的入口。它用于获取 BluetoothAdapter 的高级管理类,BluetoothAdapter进行蓝牙的主要操作(扫描、开启关闭蓝牙等),它还进行所有的蓝牙管理,查看蓝牙设备的连接情况。
可以通过 android.content.Context#getSystemService(String),参数为 Context#BLUETOOTH_SERVICE,来创建一个 BluetoothManager 对象,然后调用 #getAdapter 方法来获取到一个 BluetoothAdapter对象。
你还可以只是调用BluetoothAdapter的静态方法 BluetoothAdapter#getDefaultAdapter来获取到BluetoothAdapter对象。
BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManager) context.getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
或者是
BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
BluetoothManager拥有的成员变量是 BluetoothAdapter mAdapter。
来看一下BluetoothManager的构造方法:
/**
* @hide
*/
public BluetoothManager(Context context) {
context = context.getApplicationContext();
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"context not associated with any application (using a mock context?)");
}
// Legacy api - getDefaultAdapter does not take in the context
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
}
由这个@hide标签,我们可以知道这个构造方法是不对外公开的,但可以通过反射来使用这种构造方法。
下面是常用的获取到BluetoothAdapter的方法。
/**
* Get the default BLUETOOTH Adapter for this device.
*
* @return the default BLUETOOTH Adapter
*/
public BluetoothAdapter getAdapter() {
return mAdapter;
}
判断蓝牙链接情况的方法:
/**
* Get the current connection state of the profile to the remote device.
*
* This is not specific to any application configuration but represents
* the connection state of the local Bluetooth adapter for certain profile.
* This can be used by applications like status bar which would just like
* to know the state of Bluetooth.
*
* @param device Remote bluetooth device.
* @param profile GATT or GATT_SERVER
* @return State of the profile connection. One of
* {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_CONNECTED}, {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_CONNECTING},
* {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_DISCONNECTED},
* {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_DISCONNECTING}
*/
@RequiresPermission(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH)
public int getConnectionState(BluetoothDevice device, int profile) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG,"getConnectionState()");
List connectedDevices = getConnectedDevices(profile);
for(BluetoothDevice connectedDevice : connectedDevices) {
if (device.equals(connectedDevice)) {
return BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED;
}
}
return BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED;
}
获取配置文件到远程设备的当前连接状态。
开始操作蓝牙 BluetoothAdapter
表示本地设备蓝牙适配器。
BluetoothAdapter让你执行基本的蓝牙任务,如:
- 启动设备发现扫描
- 查询绑定(配对)设备的列表
- 用已知的MAC地址来初始化BluetoothDevice对象。
- 创建一个BluetoothServerSocket对象去监听其他设备的连接请求。(经典蓝牙相关)
- 开启扫描Bluetooth LE 设备。
获取一个代表本地蓝牙适配器的BluetoothAdapter,当运行在 JELLY_BEAN_MR1和以下版本时,调用静态方法 getDefaultAdapter方法;当运行在JELLY_BEAN_MR2 或更高时,调用上一节所讲的 BluetoothManager#getAdapter方法。
从根本上来说,这是进行所有蓝牙操作的起始点。一旦你拥有本地适配器,你可以通过getBondedDevices()方法来获取一系列的BluetoothDevices的对象,这些对象代表了所有配对过的设备。
调用startDiscovery()来开始扫描经典蓝牙。或者创建一个BluetoothServerSocket来监听即将到来的连接请求,通过listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(String,UUID)方法;或者开始一个低功耗设备的扫描,startLeScan(LeScanCallback callback)。
需要的权限:android.Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH,android.Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH_ADMIN。
- 扫描蓝牙startLeScan与停止扫描stopLeScan
关于蓝牙ble设备的搜索,首先要了解 LeScanCallback 接口。
/**
* 用于返回蓝牙ble设备扫描结果的回调接口
* Callback interface used to deliver LE scan results.
*
* @see #startLeScan(LeScanCallback)
* @see #startLeScan(UUID[], LeScanCallback)
*/
public interface LeScanCallback {
/**
* Callback reporting an LE device found during a device scan initiated
* by the {@link BluetoothAdapter#startLeScan} function.
*
* @param device Identifies the remote device 代表远程设备的设备对象
* @param rssi The RSSI value for the remote device as reported by the
* Bluetooth hardware. 0 if no RSSI value is available. 信号强度
* @param scanRecord The content of the advertisement record offered by
* the remote device. 远程设备的广播内容
*/
public void onLeScan(BluetoothDevice device, int rssi, byte[] scanRecord);
}
startLeScan方法:
/**
开启一个蓝牙ble设备的扫描,寻找广播给予服务的设备
* Starts a scan for Bluetooth LE devices, looking for devices that
* advertise given services.
*
* Devices which advertise all specified services are reported using the
* {@link LeScanCallback#onLeScan} callback.
*
* @param serviceUuids Array of services to look for 寻找指定UUID服务的设备
* @param callback the callback LE scan results are delivered LE设备搜索结果的回调
* @return true, if the scan was started successfully 如果返回true,则表示开启搜索成功
* @deprecated use {@link BluetoothLeScanner#startScan(List, ScanSettings, ScanCallback)}
* instead.
*/
@Deprecated
@RequiresPermission(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN)
public boolean startLeScan(final UUID[] serviceUuids, final LeScanCallback callback) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "startLeScan(): " + Arrays.toString(serviceUuids));
// 如果callback为空,就会返回false,即开启搜索失败
if (callback == null) {
if (DBG) Log.e(TAG, "startLeScan: null callback");
return false;
}
// BluetoothLeScanner是实际搜索蓝牙的对象,sBluetoothLeScanner是BLuetoothAdapter类的成员变量
BluetoothLeScanner scanner = getBluetoothLeScanner();
if (scanner == null) {
if (DBG) Log.e(TAG, "startLeScan: cannot get BluetoothLeScanner");
return false;
}
synchronized(mLeScanClients) {
if (mLeScanClients.containsKey(callback)) {
if (DBG) Log.e(TAG, "LE Scan has already started");
return false;
}
try {
IBluetoothGatt iGatt = mManagerService.getBluetoothGatt();
if (iGatt == null) {
// BLE is not supported
return false;
}
ScanCallback scanCallback = new ScanCallback() {
@Override
public void onScanResult(int callbackType, ScanResult result) {
if (callbackType != ScanSettings.CALLBACK_TYPE_ALL_MATCHES) {
// Should not happen.
Log.e(TAG, "LE Scan has already started");
return;
}
ScanRecord scanRecord = result.getScanRecord();
if (scanRecord == null) {
return;
}
if (serviceUuids != null) {
List uuids = new ArrayList();
for (UUID uuid : serviceUuids) {
uuids.add(new ParcelUuid(uuid));
}
List scanServiceUuids = scanRecord.getServiceUuids();
if (scanServiceUuids == null || !scanServiceUuids.containsAll(uuids)) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "uuids does not match");
return;
}
}
callback.onLeScan(result.getDevice(), result.getRssi(),
scanRecord.getBytes());
}
};
ScanSettings settings = new ScanSettings.Builder()
.setCallbackType(ScanSettings.CALLBACK_TYPE_ALL_MATCHES)
.setScanMode(ScanSettings.SCAN_MODE_LOW_LATENCY).build();
List filters = new ArrayList();
if (serviceUuids != null && serviceUuids.length > 0) {
// Note scan filter does not support matching an UUID array so we put one
// UUID to hardware and match the whole array in callback.
ScanFilter filter = new ScanFilter.Builder().setServiceUuid(
new ParcelUuid(serviceUuids[0])).build();
filters.add(filter);
}
scanner.startScan(filters, settings, scanCallback);
mLeScanClients.put(callback, scanCallback);
return true;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
return false;
}
代码有点复杂,就不深究太多了,只需知道在LeScanCallback的回调方法里面就能获取到搜索到的设备和广播数据就行了。
- 获取BluetoothDevice对象getRemoteDevice(String address)
/**
用一个地址字符串来获取BluetoothDevice对象
* Get a {@link BluetoothDevice} object for the given Bluetooth hardware
* address.
有效的蓝牙地址必须是大写字母,比如这个格式"00:11:22:33:AA:BB".有一个帮助类可以检验给定的一个地址字符串是否是有效的
* Valid Bluetooth hardware addresses must be upper case, in a format
* such as "00:11:22:33:AA:BB". The helper {@link #checkBluetoothAddress} is
* available to validate a Bluetooth address.
*
A {@link BluetoothDevice} will always be returned for a valid
* hardware address, even if this adapter has never seen that device.
*
* @param address valid Bluetooth MAC address
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if address is invalid
*/
public BluetoothDevice getRemoteDevice(String address) {
return new BluetoothDevice(address);
}
- 判断蓝牙状态isEnabled,蓝牙开启或关闭的状态getState,在进行了一些条件的判断后,最终通过mService调用相关方法来获取到状态。mService是通过AIDL来实现跨进程通信,来获取到系统底层的蓝牙服务的。
getState方法,获取当前蓝牙状态:
/**
* Get the current state of the local Bluetooth adapter.
* Possible return values are
* {@link #STATE_OFF},
* {@link #STATE_TURNING_ON},
* {@link #STATE_ON},
* {@link #STATE_TURNING_OFF}.
*
* @return current state of Bluetooth adapter
*/
@RequiresPermission(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH)
@AdapterState
public int getState() {
int state = BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF;
try {
mServiceLock.readLock().lock();
if (mService != null) {
// 通过 mService获取蓝牙的状态,mService是Binder对象,跨进程来获取蓝牙服务的状态
state = mService.getState();
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "", e);
} finally {
mServiceLock.readLock().unlock();
}
// Consider all internal states as OFF 视所有中间状态为OFF状态
if (state == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_BLE_ON
|| state == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_BLE_TURNING_ON
|| state == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_BLE_TURNING_OFF) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "Consider " + BluetoothAdapter.nameForState(state) + " state as OFF");
state = BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF;
}
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "" + hashCode() + ": getState(). Returning " + BluetoothAdapter.nameForState(state));
return state;
}
蓝牙是否开启:
/**
如果蓝牙当前可用并且准备使用,则返回true
* Return true if Bluetooth is currently enabled and ready for use.
等同于 上文提及的 getBluetoothState() == STATE_ON 状态
* Equivalent to:
* getBluetoothState() == STATE_ON
*
* @return true if the local adapter is turned on
*/
@RequiresPermission(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH)
public boolean isEnabled() {
try {
mServiceLock.readLock().lock();
// 通过 mService来获取蓝牙是否为开启
if (mService != null)
return mService.isEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "", e);
} finally {
mServiceLock.readLock().unlock();
}
return false;
}
蓝牙设备类 BluetoothDevice
表示远程蓝牙设备。BluetoothDevice类让您创建与相应设备的连接或查询它的信息,例如名称、地址、类和绑定状态。
这个类是一个对蓝牙设备地址的薄封装。这个类的对象是不可变的。这个类的操作在远程蓝牙硬件地址上执行,使用BluetoothAdapter类可以创建一个BluetoothDevice对象。
获取一个BluetoothDevice对象,可以使用BluetoothAdapter#getRemoteDevice(String)来创建一个知道MAC地址的设备的对象(你可以BluetoothAdapter来搜索扫描设备来发现)或者从已绑定过的设备中获取一个,通过BluetoothAdapter#getBondedDevices()来获取到已绑定过的设备。你可以使用createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(UUID)来打开一个BluetoothSocket去与远程设备进行通信。
成员变量表示连接状态
private static final int CONNECTION_STATE_DISCONNECTED = 0;//断开状态
private static final int CONNECTION_STATE_CONNECTED = 1;//连接状态
这两个常量和蓝牙设备的连接状态有密切联系:
/**
该设备是否有一个开放的连接
* Returns whether there is an open connection to this device.
* Requires {@link android.Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH}.
*
如果这个设备至少有一个连接,就返回true
* @return True if there is at least one open connection to this device.
* @hide
*/
@SystemApi
public boolean isConnected() {
if (sService == null) {
// BT is not enabled, we cannot be connected.
return false;
}
try {
// 如果sService.getConnectionsState(this)返回的状态不为 CONNECTION_STATE_DISCONNECTED 就是连接状态了
return sService.getConnectionState(this) != CONNECTION_STATE_DISCONNECTED;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "", e);
return false;
}
}
蓝牙的广播接收者相关的成员变量,不过这是经典蓝牙扫描相关的。还记得BLE是怎么扫描的吗?是用BluetoothAdapter#startLeScan(),这部分就当作是扩展了解的吧,只做BLE的话不需要去记。
public static final String ACTION_FOUND =
"android.bluetooth.device.action.FOUND";//发现设备
public static final String ACTION_DISAPPEARED =
"android.bluetooth.device.action.DISAPPEARED";//设备远离
public static final String ACTION_ACL_CONNECTED =
"android.bluetooth.device.action.ACL_CONNECTED";
public static final String ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED =
"android.bluetooth.device.action.BOND_STATE_CHANGED";//绑定状态改变
/**
* Used as a Parcelable {@link BluetoothDevice} extra field in every intent
* broadcast by this class. It contains the {@link BluetoothDevice} that
* the intent applies to.
*/
public static final String EXTRA_DEVICE = "android.bluetooth.device.extra.DEVICE";//设备的数据,附带一个BluetooothDevice对象
/**
* Used as an optional short extra field in {@link #ACTION_FOUND} intents.
* Contains the RSSI value of the remote device as reported by the
* Bluetooth hardware.
*/
public static final String EXTRA_RSSI = "android.bluetooth.device.extra.RSSI";
获取蓝牙的名字:
/**
获取一个友好的蓝牙设备的名字(像下面那个蓝牙MAC地址对用户是极其不友好的)
* Get the friendly Bluetooth name of the remote device.
*
* The local adapter will automatically retrieve remote names when
* performing a device scan, and will cache them. This method just returns
* the name for this device from the cache.
*
* @return the Bluetooth name, or null if there was a problem.
*/
@RequiresPermission(Manifest.permission.BLUETOOTH)
public String getName() {
if (sService == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "BT not enabled. Cannot get Remote Device name");
return null;
}
try {
return sService.getRemoteName(this);
} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.e(TAG, "", e);}
return null;
}
获取蓝牙的地址(MAC):
/**
* Returns the hardware address of this BluetoothDevice.
* For example, "00:11:22:AA:BB:CC".
* @return Bluetooth hardware address as string
*/
public String getAddress() {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "mAddress: " + mAddress);
return mAddress;
}
蓝牙设备的操作 — 连接:
/**
连接到GATT的服务端,调用者像是一个GATT客户端,回调方法用于传送结果给调用者,比如连接的状态和GATT客户端的一些操作(比如读写操作等)。
* Connect to GATT Server hosted by this device. Caller acts as GATT client.
* The callback is used to deliver results to Caller, such as connection status as well
* as any further GATT client operations.
这个方法返回一个BluetoothGatt的对象实例。之后就可以使用这个BluetoothGatt对象去控制GATT客户端的操作了。
* The method returns a BluetoothGatt instance. You can use BluetoothGatt to conduct
* GATT client operations.
* @param callback GATT callback handler that will receive asynchronous callbacks.
* @param autoConnect Whether to directly connect to the remote device (false)
* or to automatically connect as soon as the remote
* device becomes available (true).是否直接连接到远程设备(false),或者等到远程设备变得可用时就自动连接。
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if callback is null
*/
public BluetoothGatt connectGatt(Context context, boolean autoConnect,
BluetoothGattCallback callback)
先来看看BluetoothGattCallback类:
/**
* This abstract class is used to implement {@link BluetoothGatt} callbacks.
*/
public abstract class BluetoothGattCallback{
/**
当调用了BluetoothGatt#setPreferredPhy方法时会触发这个回调方法,或者远程设备的PHY值改变了也会触发
* Callback triggered as result of {@link BluetoothGatt#setPreferredPhy}, or as a result of
* remote device changing the PHY.
public void onPhyUpdate(BluetoothGatt gatt, int txPhy, int rxPhy, int status) {
}
/**
当调用了BluetoothGatt#readPhy方法时回调这个方法
* Callback triggered as result of {@link BluetoothGatt#readPhy}
*
* @param gatt GATT client
发射的
* @param txPhy the transmitter PHY in use. One of {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_1M},
* {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_2M}, and {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_CODED}.
接收的
* @param rxPhy the receiver PHY in use. One of {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_1M},
* {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_2M}, and {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_CODED}.
* @param status Status of the PHY read operation.
* {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the operation succeeds.
*/
public void onPhyRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, int txPhy, int rxPhy, int status) {
}
/**
当GATT客户端与GATT服务端的连接状态发生改变时会回调这个方法
* Callback indicating when GATT client has connected/disconnected to/from a remote
* GATT server.
*
* @param gatt GATT client
* @param status Status of the connect or disconnect operation.
* {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the operation succeeds.
* @param newState Returns the new connection state. Can be one of
* {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_DISCONNECTED} or
* {@link BluetoothProfile#STATE_CONNECTED}
*/
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status,
int newState) {
}
/**
当远程设备的一系列服务、特性和描述被更新时,也就是新的服务被搜索到了(也就是??意思是说服务、特性和描述更新了,就是被搜索到了???有知道的大神解释下吗)
* Callback invoked when the list of remote services, characteristics and descriptors
* for the remote device have been updated, ie new services have been discovered.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#discoverServices}
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the remote device
* has been explored successfully.
*/
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
}
/**
报告进行Characteristic读操作的结果
* Callback reporting the result of a characteristic read operation.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#readCharacteristic}
* @param characteristic Characteristic that was read from the associated
* remote device.
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the read operation
* was completed successfully.
*/
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic,
int status) {
}
/**
提示Characteristic写操作的结果
* Callback indicating the result of a characteristic write operation.
*
如果一个(reliable write)可靠写操作正在进行的时候,这个回调被执行,characteristic的值代表远程设备报告的值。我们的应用应该将这个值和想要写的值进行比较。如果值不匹配,应用应该阻止这个可靠写(reliable write)操作。——由此我们可以知道可靠写操作是以牺牲效率来保证要写的值是正确的。
* If this callback is invoked while a reliable write transaction is
* in progress, the value of the characteristic represents the value
* reported by the remote device. An application should compare this
* value to the desired value to be written. If the values don't match,
* the application must abort the reliable write transaction.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#writeCharacteristic}
* @param characteristic Characteristic that was written to the associated
* remote device.
* @param status The result of the write operation
* {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the operation succeeds.
*/
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
}
/**
当一个远程设备的characteristic发送通知时触发。一般常用这个方法来接受远程设备的数据,比如温度之类的数据等等。当接收到数据后,就能做一些显示数据之类的操作了,还可以根据一些标准,来对数据进行一些处理,像是提示温度过高了之类的。
* Callback triggered as a result of a remote characteristic notification.
*
* @param gatt GATT client the characteristic is associated with
* @param characteristic Characteristic that has been updated as a result
* of a remote notification event.
*/
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
}
/**
返回descriptor读操作的结果
* Callback reporting the result of a descriptor read operation.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#readDescriptor}
* @param descriptor Descriptor that was read from the associated
* remote device.
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the read operation
* was completed successfully
*/
public void onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor,
int status) {
}
/**
返回descriptor写操作的结果
* Callback indicating the result of a descriptor write operation.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#writeDescriptor}
* @param descriptor Descriptor that was writte to the associated
* remote device.
* @param status The result of the write operation
* {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the operation succeeds.
*/
public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor,
int status) {
}
/**
当一个(reliable write)可靠写操作完成时回调
* Callback invoked when a reliable write transaction has been completed.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#executeReliableWrite}
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the reliable write
* transaction was executed successfully
*/
public void onReliableWriteCompleted(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
}
/**
远程设备连接的信号强度(RSSI Received Signal Strength Indication)
* Callback reporting the RSSI for a remote device connection.
*
这个回调在BluetoothGatt#readRemoteRssi方法被调用时触发。
* This callback is triggered in response to the
* {@link BluetoothGatt#readRemoteRssi} function.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#readRemoteRssi}
* @param rssi The RSSI value for the remote device
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the RSSI was read successfully
*/
public void onReadRemoteRssi(BluetoothGatt gatt, int rssi, int status) {
}
/**
提示设备最大传输单元(Maximum Transmission Unit,MTU),当设备的连接状态发生改变,或者MTU发生改变时触发(调用了BluetoothGatt#requestMtu,ble 4.0 的MTU最大为20,ble 4.1 为23,4.2为255 5.0也是255 参考https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42583147/article/details/80905714)。
* Callback indicating the MTU for a given device connection has changed.
* This callback is triggered in response to the
* {@link BluetoothGatt#requestMtu} function, or in response to a connection
* event.
*
* @param gatt GATT client invoked {@link BluetoothGatt#requestMtu}
* @param mtu The new MTU size
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the MTU has been changed successfully
*/
public void onMtuChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, int mtu, int status) {
}
/**
连接参数更新
* Callback indicating the connection parameters were updated.
*
* @param gatt GATT client involved
* @param interval Connection interval used on this connection, 1.25ms unit. Valid
* range is from 6 (7.5ms) to 3200 (4000ms).连接间隔,1.25ms为一个单位,范围是6到3200。也就是时间为7.5ms到4000ms。
* @param latency Slave latency for the connection in number of connection events. Valid
* range is from 0 to 499
* @param timeout Supervision timeout for this connection, in 10ms unit. Valid range is
* from 10 (0.1s) to 3200 (32s) 连接事件的等待时间,10ms为一个单位。有效范围为10到3200,即0.1s到32s。
* @param status {@link BluetoothGatt#GATT_SUCCESS} if the connection has been updated
* successfully
* @hide
*/
public void onConnectionUpdated(BluetoothGatt gatt, int interval, int latency, int timeout,
int status) {
}
}
最终调用到的代码是:
/**
这里的注释和上面一样,就不翻译了
* Connect to GATT Server hosted by this device. Caller acts as GATT client.
* The callback is used to deliver results to Caller, such as connection status as well
* as any further GATT client operations.
* The method returns a BluetoothGatt instance. You can use BluetoothGatt to conduct
* GATT client operations.
* @param callback GATT callback handler that will receive asynchronous callbacks.
* @param autoConnect Whether to directly connect to the remote device (false)
* or to automatically connect as soon as the remote
* device becomes available (true).
* @param transport preferred transport for GATT connections to remote dual-mode devices
* {@link BluetoothDevice#TRANSPORT_AUTO} or
* {@link BluetoothDevice#TRANSPORT_BREDR} or {@link BluetoothDevice#TRANSPORT_LE}
* @param phy preferred PHY for connections to remote LE device. Bitwise OR of any of
* {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_1M_MASK}, {@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_2M_MASK},
* an d{@link BluetoothDevice#PHY_LE_CODED_MASK}. This option does not take effect
* if {@code autoConnect} is set to true.
* @param handler The handler to use for the callback. If {@code null}, callbacks will happen
* on an un-specified background thread.
* @throws NullPointerException if callback is null
*/
public BluetoothGatt connectGatt(Context context, boolean autoConnect,
BluetoothGattCallback callback, int transport, int phy,
Handler handler) {
if (callback == null)
throw new NullPointerException("callback is null");
// TODO(Bluetooth) check whether platform support BLE
// Do the check here or in GattServer?
BluetoothAdapter adapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
IBluetoothManager managerService = adapter.getBluetoothManager();
try {
IBluetoothGatt iGatt = managerService.getBluetoothGatt();
if (iGatt == null) {
// BLE is not supported
return null;
}
// 传入了iGatt(IBluetoothGatt),BluetoothDevice,transport,phy,实例化一个BluetoothGatt对象
BluetoothGatt gatt = new BluetoothGatt(iGatt, this, transport, phy);
// BluetoothGatt对象调用它的connect方法
gatt.connect(autoConnect, callback, handler);
return gatt;
} catch (RemoteException e) {Log.e(TAG, "", e);}
return null;
}
}
我们看到在BluetoothDevice#connectGatt中最后是生成了一个BluetoothGatt对象gatt,然后gatt调用了connect方法,最后返回这个gatt对象。可见gatt.connect方法才是蓝牙设备连接的关键。在这里讲一下蓝牙ble多设备连接的方法,当一个设备连接成功后,得到一个gatt对象,如果是两个设备的话,就得到两个gatt对象,以此类推。多设备连接,只要找到多个BluetoothDevice对象,分别执行connectGatt方法,就各自得到了它们的gatt对象,就可以通过各自的gatt来通信了。gatt是蓝牙ble通信的核心所在,刚刚也提到了蓝牙的连接最终会调用到gatt.connect方法。那么这个connect方法究竟做了一些什么事,下一节揭晓。
BluetoothGatt
前请提要:上回说到连接设备要调用BluetoothDevice的connectGatt方法,而这个方法里面调用了gatt.connect方法。在分析gatt.connect方法之前,先来说说gatt这个类代表的含义。
官方解释如下:
蓝牙GATT协议的公共api。(Generic Attribute Profile)
该类提供蓝牙GATT功能,以启用与蓝牙智能或智能就绪设备的通信。
若要连接到远程外围设备,请创建BluetoothGattCallback和调用BluetoothDevice#connectGatt来获取到这个类的实例。
可以使用蓝牙设备发现或BLE扫描来发现具有GATT能力的设备。
蓝牙ble的数据传输基于GATT协议,BluetoothGatt就是GATT协议和相关操作的类,这个类就是蓝牙数据传输的核心。
先来看这个类的一些成员变量:
表示操作结果的
/** A GATT operation completed successfully GATT操作成功*/
public static final int GATT_SUCCESS = 0;
/** GATT read operation is not permitted GATT读操作没有权限*/
public static final int GATT_READ_NOT_PERMITTED = 0x2;
/** GATT write operation is not permitted GATT写操作没有权限*/
public static final int GATT_WRITE_NOT_PERMITTED = 0x3;
/** Insufficient authentication for a given operation 该的操作认证不足*/
public static final int GATT_INSUFFICIENT_AUTHENTICATION = 0x5;
/** The given request is not supported 不支持请求*/
public static final int GATT_REQUEST_NOT_SUPPORTED = 0x6;
/** Insufficient encryption for a given operation 该操作加密不足*/
public static final int GATT_INSUFFICIENT_ENCRYPTION = 0xf;
/** A read or write operation was requested with an invalid offset 请求一个读或写的操作时使用了不合法的偏移*/
public static final int GATT_INVALID_OFFSET = 0x7;
/** A write operation exceeds the maximum length of the attribute 一个写的操作超出了属性的最大长度*/
public static final int GATT_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE_LENGTH = 0xd;
/** A remote device connection is congested. 远程设备的连接拥挤*/
public static final int GATT_CONNECTION_CONGESTED = 0x8f;
/** A GATT operation failed, errors other than the above GATT操作失败*/
public static final int GATT_FAILURE = 0x101;
一些重要成员的变量
BluetoothGattCallback mCallback;//BluetoothDevice#connectGatt()方法中的回调接口,数据通过这个回调传递出去,在上一节有详细介绍
BluetoothDevice mDevice;//代表蓝牙设备对象
List mServices;//GATT服务,从这里看出,一个GATT可拥有多个BluetoothGattService
接下来讲连接的流程,上一节留下的问题——gatt.connect究竟做了什么事
boolean connect(Boolean autoConnect, BluetoothGattCallback callback,
Handler handler) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "connect() - device: " + mDevice.getAddress() + ", auto: " + autoConnect);
synchronized(mStateLock) {
if (mConnState != CONN_STATE_IDLE) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not idle");
}
mConnState = CONN_STATE_CONNECTING;
}
mAutoConnect = autoConnect;
// registerApp 失败就会返回false,下面贴registerApp的方法
if (!registerApp(callback, handler)) {
synchronized(mStateLock) {
mConnState = CONN_STATE_IDLE;
}
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to register callback");
return false;
}
// The connection will continue in the onClientRegistered callback
return true;
}
connect方法的关键在于registerApp方法
private boolean registerApp(BluetoothGattCallback callback, Handler handler) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "registerApp()");
if (mService == null) return false;
mCallback = callback;
mHandler = handler;
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "registerApp() - UUID=" + uuid);
try {
// mBluetoothGattCallback是IBluetoothGattCallback,用了AIDL,随后贴相关代码
mService.registerClient(new ParcelUuid(uuid), mBluetoothGattCallback);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
return false;
}
return true;
}
IBluetoothGattCallback的接口
private final IBluetoothGattCallback mBluetoothGattCallback =
new IBluetoothGattCallback.Stub() {
/**
* Application interface registered - app is ready to go.客户端注册
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onClientRegistered(int status, int clientIf) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "onClientRegistered() - status=" + status
+ " clientIf=" + clientIf);
if (VDBG) {
synchronized(mStateLock) {
if (mConnState != CONN_STATE_CONNECTING) {
Log.e(TAG, "Bad connection state: " + mConnState);
}
}
}
mClientIf = clientIf;
if (status != GATT_SUCCESS) {
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
// 回调BluetoothGattCallback#onConnectionStateChange
mCallback.onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt.this, GATT_FAILURE, BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED);
}
}
});
synchronized(mStateLock) {
mConnState = CONN_STATE_IDLE;
}
return;
}
try {
// 调用了AIDL的方法来调用底层C代码进行连接
mService.clientConnect(mClientIf, mDevice.getAddress(),
!mAutoConnect, mTransport, mPhy); // autoConnect is inverse of "isDirect"
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
/**
* Client connection state changed连接状态发生改变
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onClientConnectionState(int status, int clientIf, boolean connected, String address) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "onClientConnectionState() - status=" + status + " clientIf=" + clientIf + " device=" + address);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
int profileState = connected ? BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED :
BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED;
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
// onConnectionStateChange在这里回调
mCallback.onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt.this, status,
profileState);
}
}
});
synchronized(mStateLock) {
if (connected) {
mConnState = CONN_STATE_CONNECTED;
} else {
mConnState = CONN_STATE_IDLE;
}
}
synchronized(mDeviceBusy) {
mDeviceBusy = false;
}
}
/**
* Remote search has been completed 扫描结束
* The internal object structure should now reflect the state
* of the remote device database. Let the application know that
* we are done at this point.
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onSearchComplete(String address, List services,
int status) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "onSearchComplete() = Device=" + address + " Status=" + status);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
for (BluetoothGattService s : services) {
//services we receive don't have device set properly.
s.setDevice(mDevice);
}
mServices.addAll(services);
// Fix references to included services, as they doesn't point to right objects.
for (BluetoothGattService fixedService : mServices) {
ArrayList includedServices =
new ArrayList(fixedService.getIncludedServices());
fixedService.getIncludedServices().clear();
for(BluetoothGattService brokenRef : includedServices) {
BluetoothGattService includedService = getService(mDevice,
brokenRef.getUuid(), brokenRef.getInstanceId(), brokenRef.getType());
if (includedService != null) {
fixedService.addIncludedService(includedService);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Broken GATT database: can't find included service.");
}
}
}
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
//BluetoothGattCallback的onServicesDiscovered方法在这里触发
mCallback.onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt.this, status);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Remote characteristic has been read.特征值已被读取
* Updates the internal value.
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicRead(String address, int status, int handle, byte[] value) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "onCharacteristicRead() - Device=" + address
+ " handle=" + handle + " Status=" + status);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
synchronized(mDeviceBusy) {
mDeviceBusy = false;
}
if ((status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_AUTHENTICATION
|| status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_ENCRYPTION)
&& (mAuthRetryState != AUTH_RETRY_STATE_MITM)) {
try {
final int authReq = (mAuthRetryState == AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE) ?
AUTHENTICATION_NO_MITM : AUTHENTICATION_MITM;
// readCharacteristic方法通过AIDL调用底层函数的入口
mService.readCharacteristic(mClientIf, address, handle, authReq);
mAuthRetryState++;
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
mAuthRetryState = AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE;
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = getCharacteristicById(mDevice, handle);
if (characteristic == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "onCharacteristicRead() failed to find characteristic!");
return;
}
if (status == 0) characteristic.setValue(value);
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
// 在这里回调了onCharacteristicRead方法
mCallback.onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt.this, characteristic,
status);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Characteristic has been written to the remote device.
特征已被写到远程设备
* Let the app know how we did...
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(String address, int status, int handle) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "onCharacteristicWrite() - Device=" + address
+ " handle=" + handle + " Status=" + status);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
synchronized(mDeviceBusy) {
mDeviceBusy = false;
}
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = getCharacteristicById(mDevice, handle);
if (characteristic == null) return;
if ((status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_AUTHENTICATION
|| status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_ENCRYPTION)
&& (mAuthRetryState != AUTH_RETRY_STATE_MITM)) {
try {
final int authReq = (mAuthRetryState == AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE) ?
AUTHENTICATION_NO_MITM : AUTHENTICATION_MITM;
// 这里通过AIDL调用底层代码的入口
mService.writeCharacteristic(mClientIf, address, handle,
characteristic.getWriteType(), authReq, characteristic.getValue());
mAuthRetryState++;
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
mAuthRetryState = AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE;
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
这里就是onCharacteristicWrite被调用到的地方 mCallback.onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt.this, characteristic, status);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Remote characteristic has been updated.特征值发生改变
* Updates the internal value.
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onNotify(String address, int handle, byte[] value) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "onNotify() - Device=" + address + " handle=" + handle);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = getCharacteristicById(mDevice, handle);
if (characteristic == null) return;
// 把byte[]设置到Characteristic里面去
characteristic.setValue(value);
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
//这里就是onCharacteristicChanged被调用到的地方 mCallback.onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt.this, characteristic);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Descriptor has been read.
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onDescriptorRead(String address, int status, int handle, byte[] value) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "onDescriptorRead() - Device=" + address + " handle=" + handle);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
synchronized(mDeviceBusy) {
mDeviceBusy = false;
}
BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor = getDescriptorById(mDevice, handle);
if (descriptor == null) return;
if (status == 0) descriptor.setValue(value);
if ((status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_AUTHENTICATION
|| status == GATT_INSUFFICIENT_ENCRYPTION)
&& (mAuthRetryState != AUTH_RETRY_STATE_MITM)) {
try {
final int authReq = (mAuthRetryState == AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE) ?
AUTHENTICATION_NO_MITM : AUTHENTICATION_MITM;
mService.readDescriptor(mClientIf, address, handle, authReq);
mAuthRetryState++;
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
mAuthRetryState = AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE;
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
//这里就是onDescriptorRead被调用到的地方 mCallback.onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGatt.this, descriptor, status);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Remote device RSSI has been read 读取设备的RSSI值
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onReadRemoteRssi(String address, int rssi, int status) {
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "onReadRemoteRssi() - Device=" + address +
" rssi=" + rssi + " status=" + status);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
// onReadRemoteRssi在这里触发回调
mCallback.onReadRemoteRssi(BluetoothGatt.this, rssi, status);
}
}
});
}
/**
* Callback invoked when the MTU for a given connection changes
MTU(Maximum Transmission Unit)最大传输单元
* @hide
*/
@Override
public void onConfigureMTU(String address, int mtu, int status) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "onConfigureMTU() - Device=" + address +
" mtu=" + mtu + " status=" + status);
if (!address.equals(mDevice.getAddress())) {
return;
}
runOrQueueCallback(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mCallback != null) {
// onMtuChanged在这里触发回调
mCallback.onMtuChanged(BluetoothGatt.this, mtu, status);
}
}
});
}
};
gatt类中有几个重要的方法,比如使能通知setCharacteristicNotification:
一般的情况是,设备的数据发生了变化,然后把数据发过来,这种情况下我们应该这样做,当找到Gatt服务时,使能通知,该方法如下:
/**
使能或者禁用给定的Characteristic的notifications或indications
* Enable or disable notifications/indications for a given characteristic.
一旦某个characteristic的通知使能,在远程设备的characteristic发生改变后,BluetoothGattCallback#onCharacteristicChanged回调就会被触发(比如设备的温度数据会以byte[]的方式传入到Characteristic里面,获取到这个Characteristic之后,再取出这个bytep[]数据)
* Once notifications are enabled for a characteristic, a
* {@link BluetoothGattCallback#onCharacteristicChanged} callback will be
* triggered if the remote device indicates that the given characteristic
* has changed.
*
*
Requires {@link android.Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH} permission.
*
* @param characteristic The characteristic for which to enable notifications
* @param enable Set to true to enable notifications/indications
* @return true, if the requested notification status was set successfully
*/
public boolean setCharacteristicNotification(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic,
boolean enable) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "setCharacteristicNotification() - uuid: " + characteristic.getUuid()
+ " enable: " + enable);
if (mService == null || mClientIf == 0) return false;
BluetoothGattService service = characteristic.getService();
if (service == null) return false;
BluetoothDevice device = service.getDevice();
if (device == null) return false;
try {
// 通过mService使用AIDL来调用底层C函数
mService.registerForNotification(mClientIf, device.getAddress(),
characteristic.getInstanceId(), enable);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
return false;
}
return true;
}
写数据writeCharacteristic。我们可以把要发的数据转换为byte[],然后再把数据设置到一个Characteristic中,再调用这个writeCharacteristic方法就可以了。如果是连接多个设备的,要找到对应的那个gatt对象,来调用writeCharacteristic方法。
public boolean writeCharacteristic(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
if ((characteristic.getProperties() & BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_WRITE) == 0
&& (characteristic.getProperties() &
BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_WRITE_NO_RESPONSE) == 0) return false;
if (VDBG) Log.d(TAG, "writeCharacteristic() - uuid: " + characteristic.getUuid());
if (mService == null || mClientIf == 0 || characteristic.getValue() == null) return false;
BluetoothGattService service = characteristic.getService();
if (service == null) return false;
BluetoothDevice device = service.getDevice();
if (device == null) return false;
synchronized(mDeviceBusy) {
if (mDeviceBusy) return false;
mDeviceBusy = true;
}
try {
// 这里调用到底层的函数
mService.writeCharacteristic(mClientIf, device.getAddress(),
characteristic.getInstanceId(), characteristic.getWriteType(),
AUTHENTICATION_NONE, characteristic.getValue());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
mDeviceBusy = false;
return false;
}
return true;
}
断开gatt连接,断开连接后还可以通过调用connect连接回来
/**
断开已经建立的连接,或者取消正在进行的连接的意图
* Disconnects an established connection, or cancels a connection attempt
* currently in progress.
*
* Requires {@link android.Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH} permission.
*/
public void disconnect() {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "cancelOpen() - device: " + mDevice.getAddress());
if (mService == null || mClientIf == 0) return;
try {
//从这里进入,调用底层的代码
mService.clientDisconnect(mClientIf, mDevice.getAddress());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
调用connect连接回来
/**
* Connect back to remote device.
*
* This method is used to re-connect to a remote device after the
* connection has been dropped. If the device is not in range, the
* re-connection will be triggered once the device is back in range.
*
* @return true, if the connection attempt was initiated successfully
*/
public boolean connect() {
try {
mService.clientConnect(mClientIf, mDevice.getAddress(),
false, mTransport, mPhy); // autoConnect is inverse of "isDirect"
return true;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
return false;
}
}
关闭gatt,关闭之后就不通过上面的connect方法连回来了
/**
* Close this Bluetooth GATT client.
*
* Application should call this method as early as possible after it is done with
* this GATT client.
*/
public void close() {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "close()");
// 调用了unregisterApp()方法,更改了状态
unregisterApp();
mConnState = CONN_STATE_CLOSED;
mAuthRetryState = AUTH_RETRY_STATE_IDLE;
}
gatt.close()这个方法做的事情是调用了unregisterApp()方法,然后把表示状态的变量改了。
来看一下这个unregisterApp方法:
/**
* Unregister the current application and callbacks.
*/
private void unregisterApp() {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "unregisterApp() - mClientIf=" + mClientIf);
if (mService == null || mClientIf == 0) return;
try {
mCallback = null;
// 关键代码 mService.unregisterClient(mClientIf);
mClientIf = 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"",e);
}
}
BluetoothGattService和BluetoothGattCharacteristic
BluetoothGattService表示一个Bluetooth GATT的服务,一个BluetoothGatt包含多个BluetoothGattService,
一个BluetoothGattService包含多个BluetoothGattCharacteristic。
/**
* Primary service主服务,一个主服务包含多个服务(姑且叫它们次服务吧),
*/
public static final int SERVICE_TYPE_PRIMARY = 0;
/**
* Secondary service (included by primary services)次服务,比如,有的服务用于写数据,有的服务用于读服务,我还见过读写都用同一个服务的。
*/
public static final int SERVICE_TYPE_SECONDARY = 1;
UUID mUuid;// 服务的UUID,一个很长的字符串.比如 00001000-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB
/**
* List of included services for this service.一个主服务包含多个次服务
*/
protected List mIncludedServices;
/**
* List of characteristics included in this service.一个BluetoothGattService包含多个BluetoothGattCharacteristic。
*/
protected List mCharacteristics;
BluetoothGattCharacteristic
属性:
/**
* Characteristic properties.
* @hide
*/
protected int mProperties;
/**
* Characteristic proprty: Characteristic is broadcastable.广播的
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_BROADCAST = 0x01;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic is readable.可读的
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_READ = 0x02;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic can be written without response.写数据不需要有回应
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_WRITE_NO_RESPONSE = 0x04;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic can be written.写数据
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_WRITE = 0x08;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic supports notification支持以通知的方式传递数据
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_NOTIFY = 0x10;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic supports indication
支持indication
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_INDICATE = 0x20;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic supports write with signature支持添加签名来写数据
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_SIGNED_WRITE = 0x40;
/**
* Characteristic property: Characteristic has extended properties
*/
public static final int PROPERTY_EXTENDED_PROPS = 0x80;
权限:
/**
* Characteristic permissions.
* @hide
*/
protected int mPermissions;
/**
* Characteristic read permission读的权限
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_READ = 0x01;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow encrypted read operations允许加密读的操作
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_READ_ENCRYPTED = 0x02;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow reading with man-in-the-middle protection
允许在中间人的保护下读 */
public static final int PERMISSION_READ_ENCRYPTED_MITM = 0x04;
/**
* Characteristic write permission写的权限
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_WRITE = 0x10;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow encrypted writes允许加密写数据
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_WRITE_ENCRYPTED = 0x20;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow encrypted writes with man-in-the-middle
* protection
允许在中间人保护加密写数据
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_WRITE_ENCRYPTED_MITM = 0x40;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow signed write operations允许写数据加签名
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_WRITE_SIGNED = 0x80;
/**
* Characteristic permission: Allow signed write operations with
* man-in-the-middle protection
允许在中间人保护下写数据加签名
*/
public static final int PERMISSION_WRITE_SIGNED_MITM = 0x100;
重要的属性还有:
/**
* Back-reference to the service this characteristic belongs to.
本BluetoothGattCharacteristic属于的BluetoothGattService
* @hide
*/
protected BluetoothGattService mService;
/**
* The cached value of this characteristic.
包含的数据
* @hide
*/
protected byte[] mValue;
/**
* List of descriptors included in this characteristic.
包含的
*/
protected List mDescriptors;
蓝牙ble的介绍就到这里了,可能介绍的比较笼统,下面贴一张思维导图,让读者朋友们看的清楚一些。本文也是根据这份思维导图写出来的。
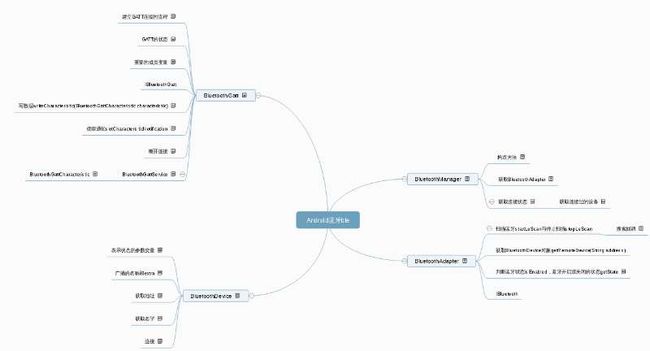
看不清脑图可以用以下链接:http://naotu.baidu.com/file/432d752a17683be9e8bc970ef3eab026?token=05d18dc358a067b4
如果读者觉得有帮助可以扫扫支付宝的领红包二维码。
